The Experimental Applications of Functional Antibodies
Functional antibodies are indispensable tools for research through their capacity to affect cell processes in vitro and in vivo, and they typically fall into one of these categories: activation, neutralization, blocking, and depletion. Functional antibodies can be leveraged to ask specific questions on cell signalling pathways, making it possible to elucidate effector functions of such signalling pathways. In this blog, we discuss how functional antibodies can be experimentally applied, with focus on activation, blocking, and neutralizing examples.
Activating antibodies can be used to induce a cell from a resting to an active state. For example, the expression of surface marker CD44 increases as B cells become activated or progress to the memory phenotype, making CD44 a valuable marker for memory cell subsets. Our Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD44 Antibody activates CD44 on murine B cells and induces B cell spreading on anti-mouse CD44 coated surfaces.

Murine B-cells were isolated using the MojoSort™ Mouse Pan B Cell Isolation Kit (Cat. No. 480051) and activated overnight with 20 ng/mL recombinant mouse IL-4 (carrier-free) (Cat. No. 574302) and 10 µg/mL Purified anti-mouse IgM (Cat. No. 406501). Activated B cells were seeded onto tissue culture plates pre-coated with 20 µg/mL Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD44 (clone W19210A) or isotype control. After 4 hours, the number of elongated cells (circularity < 0.5) was quantified using brightfield imaging and morphometric analysis with ImageJ. The assay was performed in triplicate, and four images per well at 20x magnification were analyzed. Data shown are normalized to rat IgG2a, κ isotype control treated wells.
Neutralizing antibodies bind a soluble factor and neutralize or negate its downstream cell effect, such as cell differentiation or cell proliferation. For example, granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), is a growth and development factor that promotes the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells, leading to the generation of macrophages. Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human GM-CSF Antibody is designed to neutralize the proliferation of cells induced by GM-CSF, enabling investigation of effector functions of macrophages.
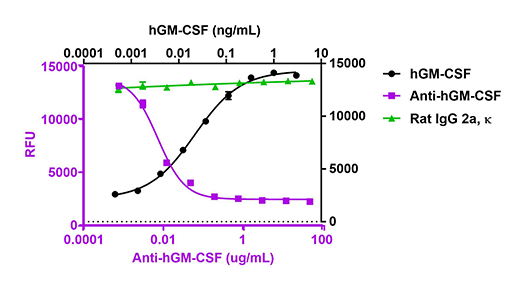
Recombinant human GM-CSF (Cat. No. 572904, black circles) induces the proliferation of human erythroleukemia TF-1 cells. Anti-human GM-CSF antibody (Clone BVD2-21C11, purple squares) neutralizes the proliferation function of recombinant human GM-CSF at 0.3 ng/mL in TF-1 cells in a dose dependent manner while the isotype control (Cat. No. 400562, green triangles) does not have the effect.
Blocking antibodies bind a cell surface target to block or interfere with a biological response. For example, TIGIT is an immunosuppressive receptor expressed by NK and T cells and an emerging immune checkpoint due to its property of mediating exhaustion of NK cells in tumors. Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse TIGIT (Vstm3) Antibody blocks binding between TIGIT and ligand CD155, giving researchers insight into downstream NK cell functions and NK cell-associated TIGIT signaling pathways used by tumors to evade immune responses.
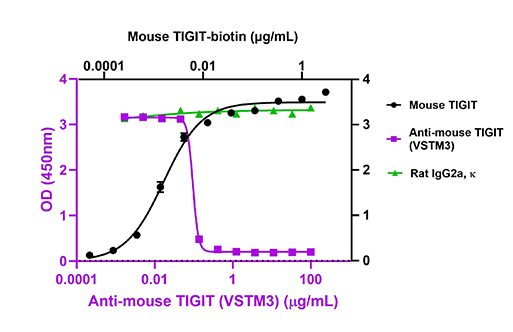
Recombinant biotinylated mouse TIGIT (black circles) binds to immobilized recombinant mouse CD155/PVR. Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse TIGIT (Vstm3) Antibody (Clone A17200C, purple squares) inhibits the binding in a dose-dependent manner whereas the isotype control (Cat. No. 400562, green triangles) does not have the effect. This antibody blocks the binding of 0.04 µg/mL biotinylated recombinant mouse TIGIT to 1 µg/mL of immobilized recombinant mouse CD155 with an ND50 = 0.01 - 0.06 µg/mL.
In summary, scientists rely on functional antibodies for an array of research purposes: to bind to and inhibit the function of a protein so as to mitigate its effector functions on cells at the molecular level, or to bind to cell surface receptors so as to investigate the functionality of receptors and specific cell signal pathways.Through their capacity to mimic or disrupt cell functions in vitro or in vivo, functional antibodies are powerful tools aiding manipulation of biological functions enabling scientists to query specific questions.

 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us