ILK Signaling
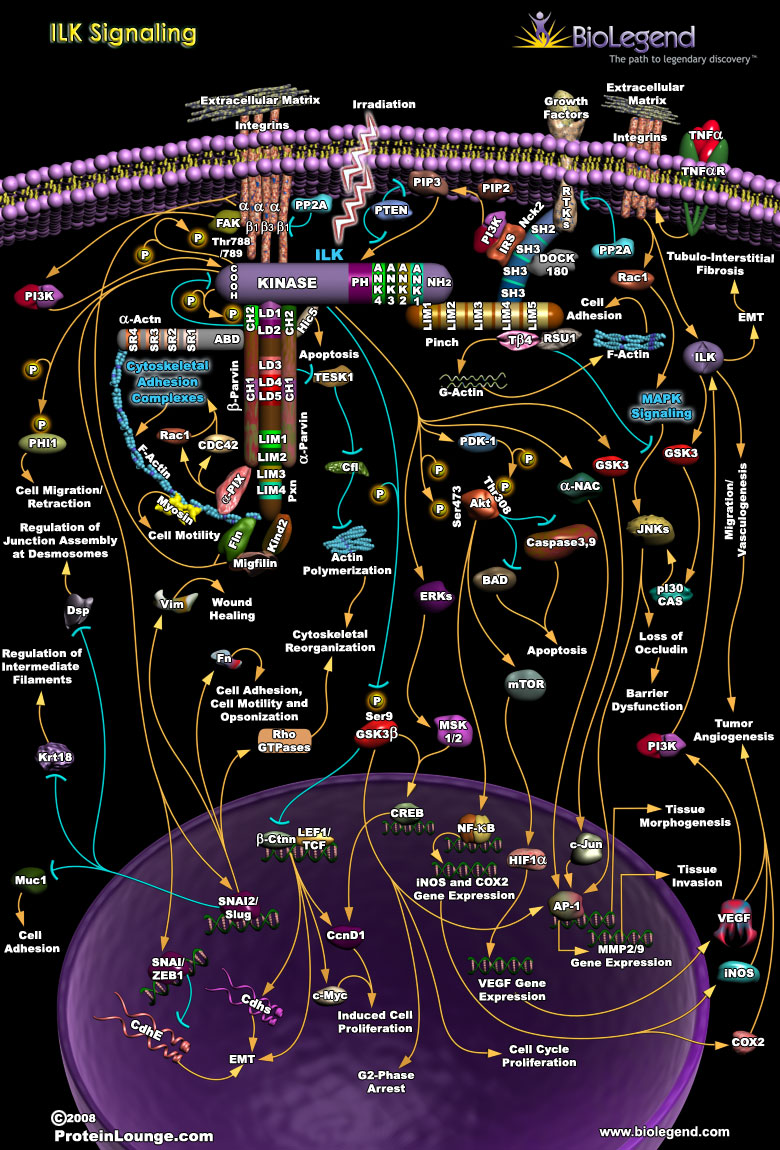
As a critical connection between intracellular structural components and the extracellular matrix, integrin-linked kinase (ILK) signaling allows for control of cytoskeletal organization and cell motility. Structurally, ILK is comprised of four ANK repeats at the N-terminus and a kinase domain at the C-terminus. ILK stays anchored to the plasma membrane through interactions with the intracellular regions of integrins. A protein complex that includes α-Parvin, β-Parvin, and Paxilin, binds to ILK at its kinase domain and directly links the cytoskeleton to ILK signaling. The ANK repeats on ILK bind with LIM domains on a protein called PINCH, which signals for PI3K activity through the adaptor protein Nck-2, leading to activation of ILK’s kinase domain. ILK activation results in phosphorylation of AKT, GSK-3, and other signaling proteins that drive gene expression for cell proliferation. This process involves nuclear translocation of β-catenin and activation of transcription factors AP-1 and CREB.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us