- Clone
- IM7 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Hermes, Pgp-1, H-CAM, HUTCH-1, ECMR III, gp85, Ly-24
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
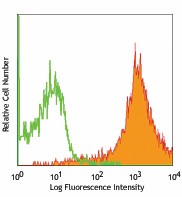
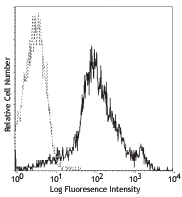
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 PE -
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with IM7 PE
CD44 is a 80-95 kD glycoprotein also known as Hermes, Pgp1, H-CAM, or HUTCH. It is expressed on all leukocytes, endothelial cells, hepatocytes, and mesenchymal cells. As B and T cells become activated or progress to the memory stage, CD44 expression increases from low or mid levels to high levels. Thus, CD44 has been reported to be a valuable marker for memory cell subsets. High CD44 expression on Treg cells has been associated with potent suppressive function via high production of IL-10. CD44 is an adhesion molecule involved in leukocyte attachment to and rolling on endothelial cells, homing to peripheral lymphoid organs and to the sites of inflammation, and leukocyte aggregation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Human
- Reported Reactivity
- Chimpanzee, Baboon, Cynomolgus, Rhesus, Squirrel Monkey, Horse, Cow, Pig, Dog, Cat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Dexamethasone-induced myeloid leukemia M1 cells
- Formulation
-
test sizes: Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
µg sizes: Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide. - Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- µg sizes: 0.2 mg/mLtest sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining using the test sizes, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. For µg sizes, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Clone IM7 has been reported to recognize an epitope common to alloantigens and all isoforms of CD4417,18 that is located between amino acids 145 and 18620. This clone has been verified for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and frozen immunohistochemistry (IHC-F). Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemistry of acetone-fixed frozen sections and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections6,7, complement-mediated cytotoxicity1, immunoprecipitation1,3, in vivo inhibition of DTH4,5, and spatial biology (IBEX)23,24. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 103046, 103065 - 103069).
Cross-reactivity to ferret has been reported by a collaborator, but not verified in house. -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Trowbridge IS, et al. 1982. Immunogenetics 15:299. (ICFC, IP, CMCD)
- Katoh S, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 153:3440. (ELISA)
- Budd RC, et al. 1987. J. Immunol. 138:3120. (IP)
- Camp RL, et al. 1993. J. Exp. Med. 178:497. (Block)
- Weiss JM, et al. 1997. J. Cell Biol. 137:1137. (Block)
- Frank NY, et al. 2005. Cancer Res. 65:4320. (IHC) PubMed
- Cuff CA, et al. 2001. J. Clin. Invest. 108:1031. (IHC)
- Lee JW, et al. 2006. Nature Immunol. 8:181.
- Zhang N, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 174:6967. PubMed
- Huabiao C, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:591. PubMed
- Gui J, et al. 2007. Int. Immunol. 19:1201. PubMed
- Wang XY, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2436. PubMed
- Kenna TJ, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2091. PubMed
- Yamazaki J, et al. 2009. Blood PubMed
- Kmieciak M, et al. 2009. J. Transl. Med. 7:89. (FC) PubMed
- Chen YW, et al. 2010. Mol. Cancer Ther. 9:2879. PubMed
- Zheng Z, et al. 1995. J. Cell. Biol. 130:485.
- Wiranowska M, et al. 2010. Int. J. Cancer 127:532.
- Hirokawa Y, et al. 2014. Am J Physiol Gastrointerest Liver Physiol. 306:547. PubMed
- Sandmaier BM, et al. 1998. Blood 91:3494.
- Yang Y, et al. 2015. Hypertension. 65:1047. PubMed
- Peterson VM, et al. 2017. Nat. Biotechnol. 35:936. (PG)
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312958 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103023)
AB_312958 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103007)
AB_312958 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103024)
AB_312958 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103008)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Variable splicing of CD44 gene generates many CD44 isoforms, 80-95 kD
- Distribution
-
All leukocytes, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, hepatocytes, mesenchymal cells
- Function
- Leukocyte attachment and rolling on endothelial cells, stromal cells and ECM
- Ligand/Receptor
- Hyaluronan, MIP-1β, fibronectin, collagen
- Cell Type
- B cells, Endothelial cells, Epithelial cells, Leukocytes, Mesenchymal cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Haynes BF, et al. 1991. Cancer Cells 3:347.
3. Goldstein LA, et al. 1989. Cell 56:1063.
4. Mikecz K, et al. 1995. Nat. Med. 1:558.
5. Hegde V, et al. 2008. J. Leukocyte Biol. 84:134.
6. Liu T, et al. 2009. Biol. Direct 4:40. - Gene ID
- 12505 View all products for this Gene ID 960 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD44
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD44
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- FC
- UniProt
- View information about CD44 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All CD44 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
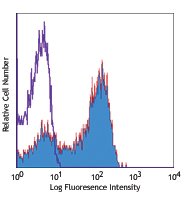
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse/human CD44
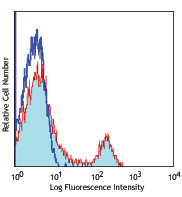
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 APC -
Biotin anti-mouse/human CD44
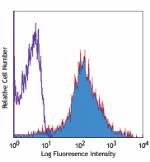
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with biotinylated CD4... 
Mouse embryonic fibroblast NIH/3T3 cell line was fixed with ... -
FITC anti-mouse/human CD44
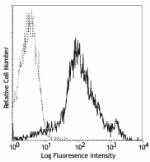
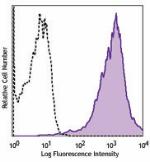
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with IM7 FITC 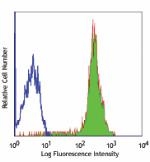
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with IM7 FITC -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse/human CD44
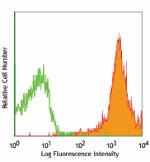
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 PE/Cyanine5 -
Purified anti-mouse/human CD44
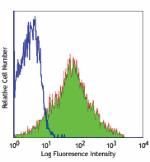
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with purified IM7, followe... 
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD44 cl... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse/human CD44
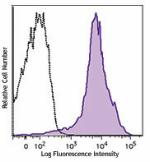
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
PE anti-mouse/human CD44
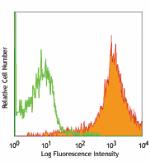
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 PE 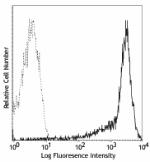
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with IM7 PE -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse/human CD44
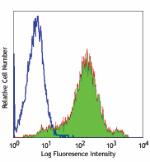
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 Alexa Fluor® 488 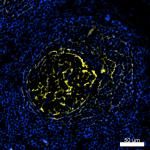
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... 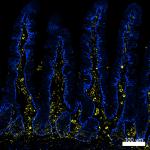
Confocal image of human jejunum sample acquired using the IB... 
Confocal image of human skin sample acquired using the IBEX ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse/human CD44
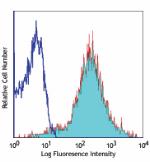
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 Alexa Fluor® 647 
MDA-MB231 breast cancer cell line was stained with 5 µg/mL a... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse lung sample acquired using t... 
Mice were injected subcutaneously with sheep red blood cells... 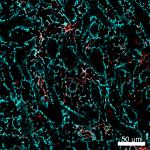
Confocal image of human spleen sample acquired using the IBE... 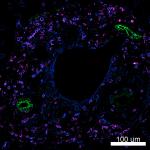
Confocal image of human liver sample acquired using the IBEX... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse/human CD44
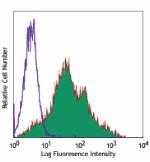
C57BL/6 Mouse Splenocytes stained with IM7 Pacific Blue&trad... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse/human CD44
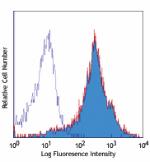
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 Alexa Fluor® 700 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse liver sample acquired using ... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human CD44
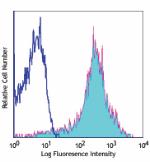
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with IM7 PE/Cyanine7 -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human CD44
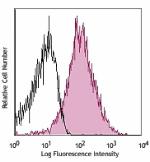
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with IM7 APC/Cyanine7 -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse/human CD44
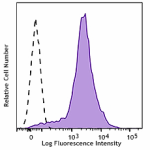
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
PerCP anti-mouse/human CD44
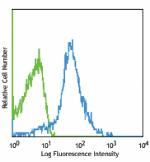
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with IM7 PerCP -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse/human CD44
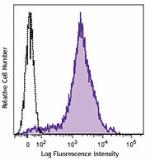
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse/human CD44
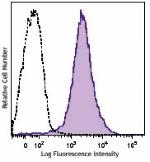
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse/human CD44
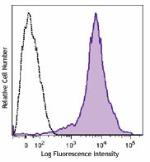
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse/human CD44
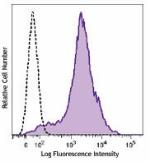
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse/human CD44
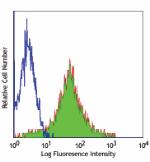
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Ultra-LEAF™ purified ... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse/human CD44
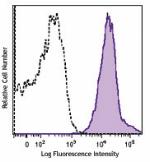
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Purified anti-mouse/human CD44 (Maxpar® Ready)
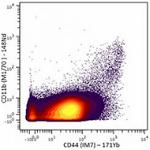
Mouse splenocytes stained with 148Nd-anti-CD11b (M1/70) and ... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse/human CD44
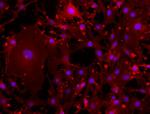
bEND3 cells were fixed and blocked according to standard imm... 
Human paraffin-embedded intestine tissue was prepared with s... 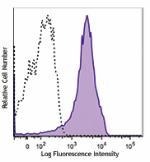
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse/human CD44
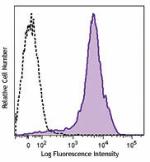
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse/human CD44
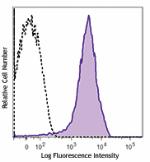
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse/human CD44
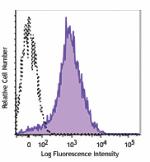
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... -
TotalSeq™-A0073 anti-mouse/human CD44
-
TotalSeq™-C0073 anti-mouse/human CD44
-
TotalSeq™-B0073 anti-mouse/human CD44
-
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse/human CD44
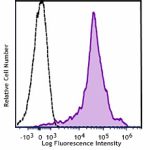
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD44 (clone IM7)... 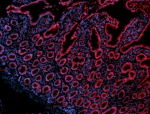
Human paraffin-embedded intestine tissue slices were prepare... -
Spark YG™ 593 anti-mouse/human CD44
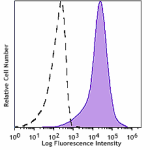
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse/human CD44 ... -
TotalSeq™-D0073 anti-mouse/human CD44
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse/human CD44
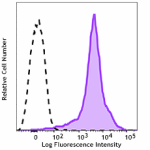
Mouse (C57BL/6) splenocytes stained with anti-mouse/human CD... -
PerCP/Fire™ 806 anti-mouse/human CD44
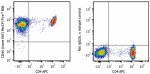
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse/human CD44
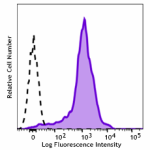
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti -mouse/huma... -
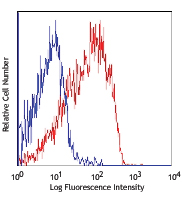
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse/human CD44

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 (... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse/human CD44 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse/human CD44 (Flexi-Fluor™)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us