Akt Signaling
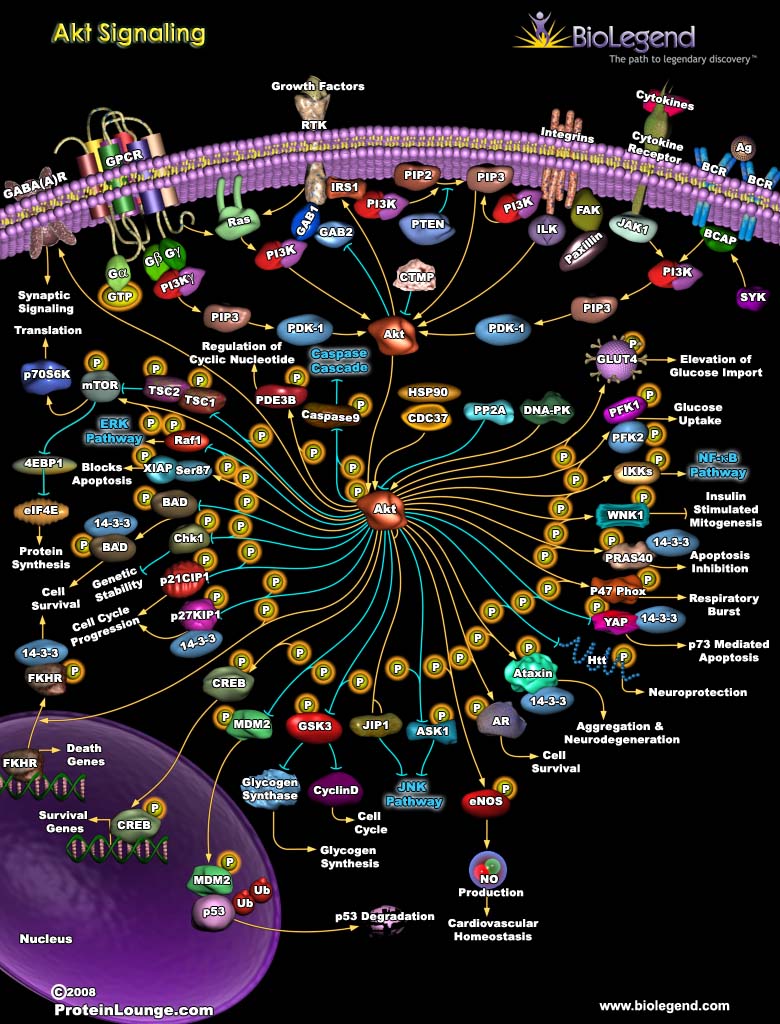
Signaling through the Akt pathway regulates cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis in response to extracellular growth factors and cytokines. Akt, also known as protein kinase B, is a serine/threonine kinase that is ubiquitously expressed. Binding of growth factors or cytokines to a receptor tyrosine kinase results in recruitment and formation of active P13K. Active P13K produces phosphatidylinositol which can bind to AKT and result in a conformational change, exposing the Akt kinase domain. Akt can also be activated through phosphorylation by other kinases such as PDK-1 and ILK. Once activated, Akt phosphorylates a number of targets involved in other signaling pathways including ERK, JNK, and NF-κB pathways. In addition, Akt phosphorylates proteins involved in cell cycle regulation (e.g. p21, p27, and MDM2) and protein synthesis (e.g. mTOR).
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us