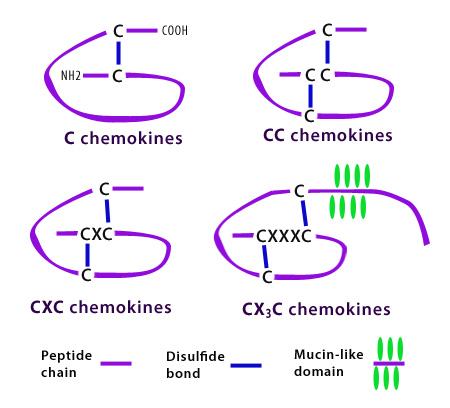
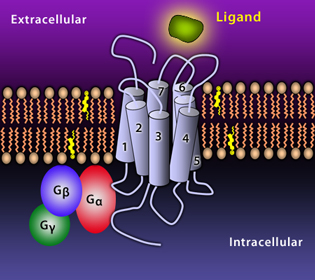
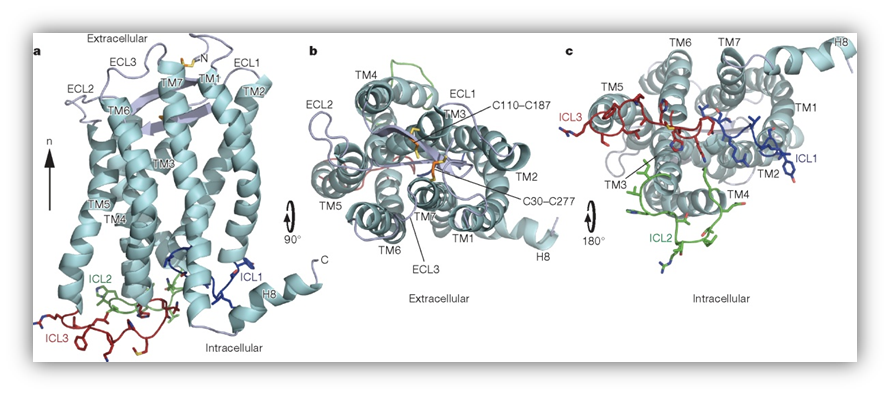
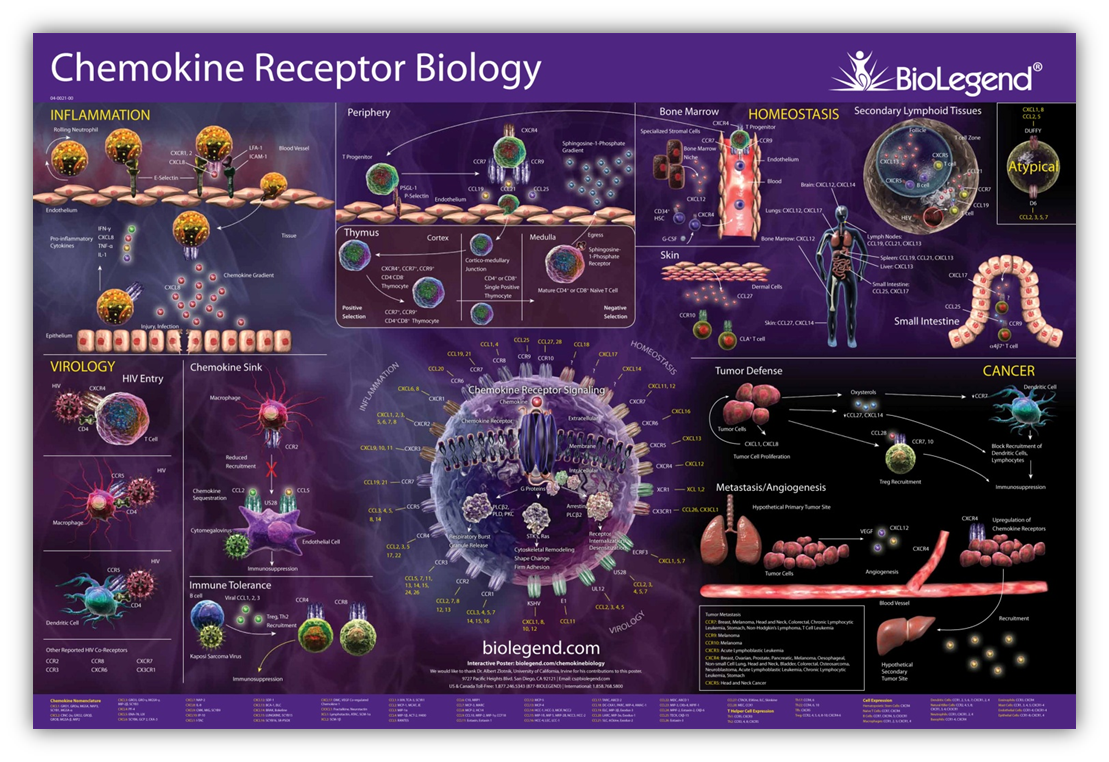
| Chemokines are a class of cytokines that induce chemotaxis (migration) of target cells. Chemokines work through concentration gradients. Attracted cells move toward areas of higher concentrations of the chemokine. While some chemotaxis is induced by inflammation or damaged cells, other chemokines function in homeostasis. | Chemokines receptors are seven transmembrane spanning G protein-coupled receptors that allow cells to migrate towards increasing chemokine gradients. The receptor N-terminus is external and contributes to ligand binding while the carboxy terminus (COOH) allows for interaction with signaling molecules and downstream signaling. |

 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us