Antibodies are immunoglobulins, abbreviated as Ig, made by the body's adaptive immune system. Through complex maturation processes, specific antibodies are created to target antigens. This webpage discusses how antibodies are naturally made in the body and how they can be generated for research use.
Loading...

Antibody Structure
An antibody is roughly shaped as a ”Y“, consisting of 2 heavy chains and 2 light chains.
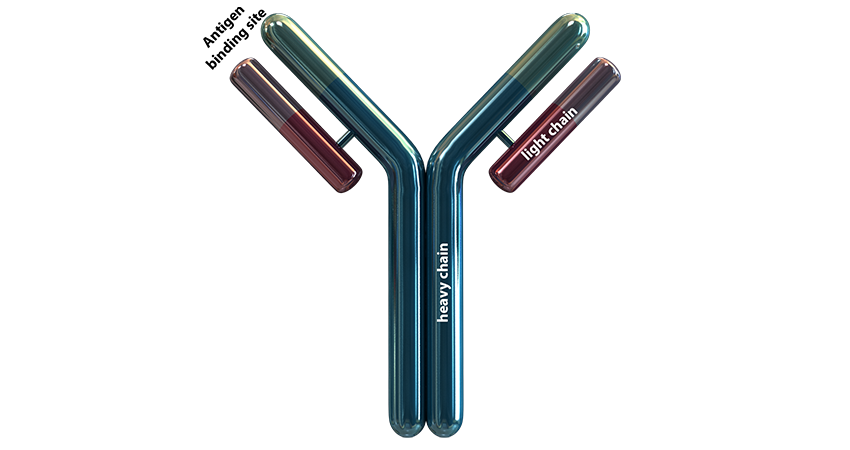
Functions of Antibodies:
For more information, view this helpful Youtube video: What are Antibodies?- Neutralizes toxins by binding to them
- Directs phagocytosis and killing of foreign microbes
- Mediates complement killing of foreign cells, bacteria, or viruses
Two types of light chains: kappa (κ) and lambda (λ)
Five types of heavy chains:
- IgG – most abundant Ig and activates classical complement pathways
- IgM - large agglutinating pentamer that is the first response to antigens
- IgD - expressed by mature B cells and bound to B cell membranes
- IgA - found in external secretions such as tears, mucus, and saliva
- IgE - involved in allergic reactions
The antigen binding site is formed by both the light and heavy chains and is complementary to the epitope of an antigen.
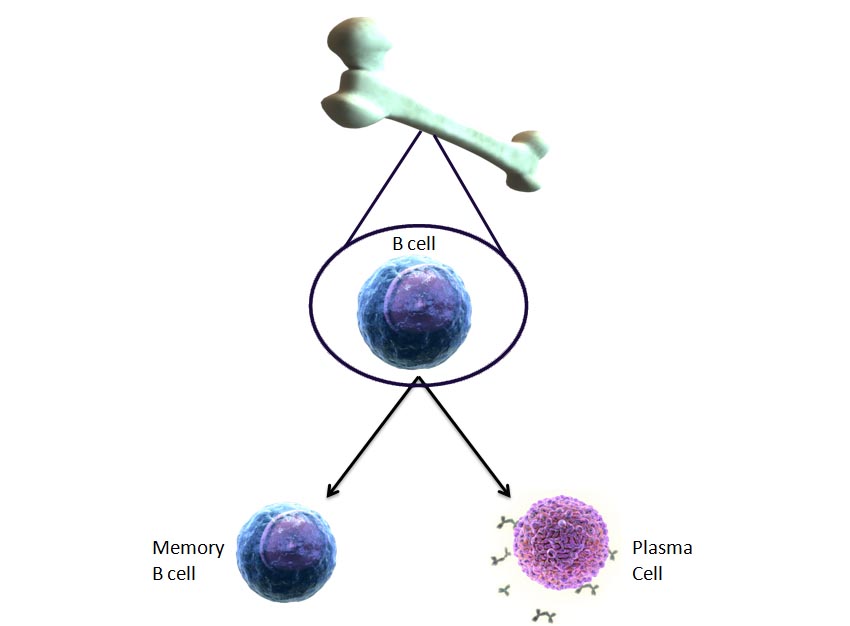 B cells mature in the bone marrow and create antigen-specific antibodies.
B cell maturation involves class switching and creation of antigen specificity. Antigen specificity is created by the random rearrangement of genes that code the antibody.
When the B cells first encounter the matching antigen, the B cells become highly specific from antibody affinity mutations.
B cells differentiate into either memory B cells or plasma cells.
Memory B cells live longer and express the same antibody as the parent.
Plasma cells produce mass amounts of altered antibodies that recognize the same antigen.
For more information, see our Maturation Markers page.
|
ProductsHere
 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us