Monocytes are a population of circulating white blood cells with the potential to differentiate into tissue macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs). Monocytes are derived from precursors in the bone marrow and can be subdivided into subsets that differ in size, trafficking and innate immune receptor expression. Monocytes mediate host antimicrobial defense and are also implicated in many inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis.
In addition, monocyte-like cells can be recruited to tumor sites and inhibit tumor-specific immune defense mechanisms. In both mice and humans, monocytes display some typical morphological features, such as irregular cell shape, oval- or kidney-shaped nuclei and cytoplasmic vesicles. However, they are still very heterogeneous and difficult to distinguish from other cells just by morphology or light scatter analysis.
Monocytes
| Development and Differentiation |



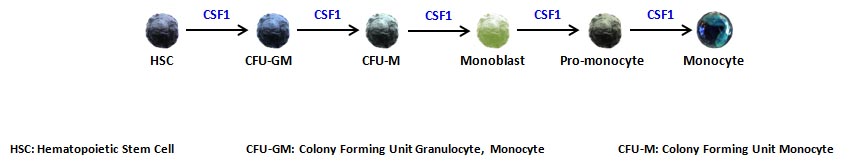
Once in the blood stream, monocytes can enter peripheral tissues and further differentiate into macrophages or dendritic cells, depending on the environmental stimuli. Researchers have been also successful in differentiating macrophages and DCs in vitro from monocytes. Although these cells may differ from their naturally, in vivo monocyte-derived counterpart, they have been instrumental in the study of the immune system and their functions.



macrophages
derived cells

Mouse and Human Subsets
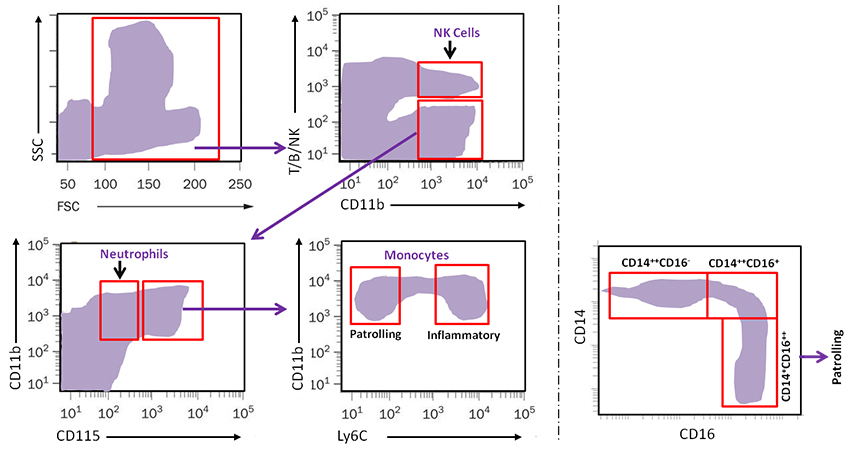
In general, monocytes can be divided depending on their surface expression level of two important chemokine receptors. These are CCR2 and CX3CR1. The pattern of chemokine expression also correlates with the expression of another surface molecule, Ly6C. In mice, Ly6Chi monocytes are considered proinflammatory with anti-microbial function, whereas Ly6Clo patrol in the blood stream and participate in tissue repair. Their recognized human equivalents are the CD14hi CD16neg and CD14lo CD16hi, respectively.
| Subset | Markers | Chemokine receptors | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | |||
| Ly6Chi | CD11b+CD115+Ly6Chi | CCR2hiCX3CR1low | Pro-inflammatory and antimicrobial roles |
| Ly6Clow | CD11b+CD115+Ly6Clow | CCR2lowCX3CR1hi | Patrolling; early responses; tissue repair |
| Human | |||
| Classical | CD14++CD16- | CCR2hiCX3CR1low | Resemble Ly6Chi monocytes based on gene-expression arrays |
| Intermediate | CD14++CD16+ | CCR2lowCX3CR1hi | Pro-inflammatory |
| Non-classical | CD14+CD16++ | CCR2lowCX3CR1hi | Patrolling; antiviral roles |
A major feature of is to patrol the body and populate several tissues as needed, where they can further differentiate into other cell types. It happens during both steady state and inflammatory conditions. This is a very important physiological function and multiple factors are involved, most notably chemokines and their receptors, as well as adhesion molecules.
Click on a chemokine or adhesion molecules to see their function:
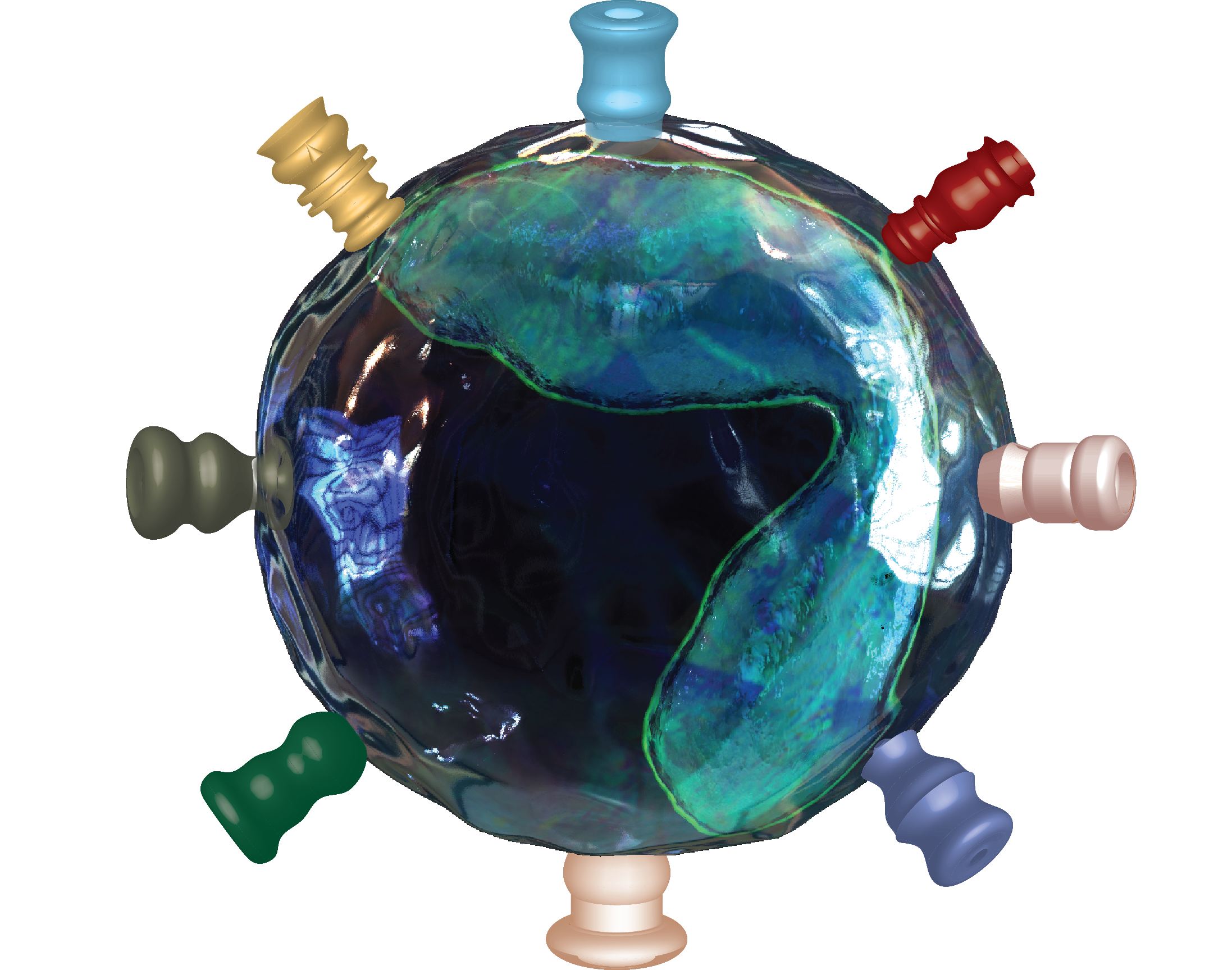                                               Emigration of Ly6Chi Monocytes from bone marrow
       Patrolling
|
TruStain FcX™ Fc receptor blockers
 Unintended staining can occur due to antibodies binding to Fc receptors expressed primarily on monocytes and B cells. Our TruStain FcX™ Fc receptor blocking solution will help mitigate this effect and ensure the observed staining is antigen-specific. Our new TruStain FcX™ PLUS (anti-mouse CD16/32) antibody offers superior Fc blocking compared to the original TruStain FcX™ based on in-house testing.
Unintended staining can occur due to antibodies binding to Fc receptors expressed primarily on monocytes and B cells. Our TruStain FcX™ Fc receptor blocking solution will help mitigate this effect and ensure the observed staining is antigen-specific. Our new TruStain FcX™ PLUS (anti-mouse CD16/32) antibody offers superior Fc blocking compared to the original TruStain FcX™ based on in-house testing.
MojoSort™ Cell Separation Products
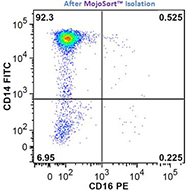 We offer several pre-optimized MojoSort™ kits for easy monocyte/macrophage isolation, including our MojoSort™ Human Pan Monocyte Isolation Kit, MojoSort™ Human CD14+ Monocytes Isolation Kit, and the MojoSort™ Mouse CX3CR1 Selection Kit.
We offer several pre-optimized MojoSort™ kits for easy monocyte/macrophage isolation, including our MojoSort™ Human Pan Monocyte Isolation Kit, MojoSort™ Human CD14+ Monocytes Isolation Kit, and the MojoSort™ Mouse CX3CR1 Selection Kit.
True-Stain Monocyte Blocker™
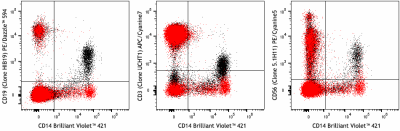
True-Stain Monocyte Blocker™ has been formulated to block non-specific binding of PE/Dazzle™ 594, PE/Cyanine5, PE/Cyanine7, APC/Cyanine7, APC/Fire™ 750, and PE/Fire™ 744 commonly seen on monocytes and macrophages. The blocker is most effective when doing surface staining on live cells prior to the fixation step in a staining protocol. Learn more.
Cell Markers and Other Resources
Just like the related macrophages and dendritic cells, monocyte subtype characterization is complex. In the pages below, you can find guidelines for working with surface molecules to study monocytes. We also recommend the following literature to learn more about monocyte development, differentiation, subsets, and function:
- Gordon S, Taylor PR. 2005. Nat Rev Immunol. 5(12):953-64 (PubMed)
- Chow A, Brown BD, Merad M. 2011. Nat Rev Immunol. 11(11):788-98 (PubMed)
- Shi C, Pamer EG. 2011. Nat Rev Immunol. 11(11):762-74 (PubMed)
- Geissmann F et al. 2010. Science. 327(5966): 656-61 (PubMed)
- Woollard KJ and Geissmann F. 2010. Nat Rev Cardiol. 7(2):77-86 (PubMed)
- Heine GH et al. 2012. Nat Rev Nephrol. 8(6): 362-69 (PubMed)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 









Follow Us