- Clone
- PC10 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen, DNA Polymerase δ Auxiliary Protein
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
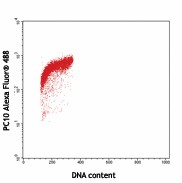
-

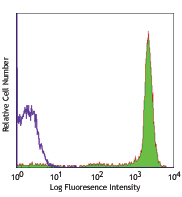
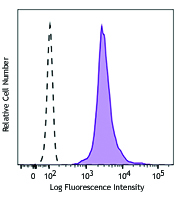
MOLT-4 cells fixed in 70% ethanol then stained with PC10 Alexa Fluor® 488 or MOPC-173 Alexa Fluor® 488 -

| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 307909 | 25 tests | 100€ | ||||
The PC10 monoclonal antibody reacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen also known as PCNA or the DNA polymerase δ auxiliary protein. PCNA is a 36 kD trimeric ring that acts as a DNA-polymerase sliding clamp expressed in the nucleus of all proliferating cells. A prime function of PCNA appears to be increasing DNA polymerase δ processibility during elongation of the leading strand. PCNA is a useful marker for DNA synthesis and is highly conserved among most species, thus highlighting the very broad reactivity of this antibody.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant rat PCNA
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 488 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration, please enter the lot number in our Concentration and Expiration Lookup or Certificate of Analysis online tools.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICFC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by intracellular immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. Please follow the Cell Fixation and Permeabilization Protocol Using 70% Ethanol. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells in 100 µL staining volume or 5 µL per 100 µL of whole blood.
* Alexa Fluor® 488 has a maximum emission of 519 nm when it is excited at 488 nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining2,5,6 of acetone-fixed frozen sections and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections, immunoprecipitation, intracellular flow cytometry3, immunofluorescence microscopy9, and Western blotting10.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Ogata K, et al. 1985. J. Immunol. 135:2623.
- Garcia R, et al. 1989. Am. J. Pathol. 134:733.
- Landberg G, et al. 1990. Exp. Cell. Res. 187:111.
- Waseem N, et al. 1990. J. Cell Sci. 96:121.
- Yu C, et al. 1991. Histopathology 19:29.
- Wilkins B, et al. 1992. J. Pathol. 166:45.
- Yang W, et al. 1996. Human Pathol. 27:70.
- Galkowska H, et al. 1996. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 53:329.
- Chou HYE, et al. 2006. J. Biol. Chem. 10:1074.
- Fulvio MD, et al. 2006. Oncogene 25:3932.
- Eswarakumar VP and Schlessinger J. 2007. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:3937.
- Henkels KM, et al. 2009. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 389:224. PubMed
- Brobeli A, et al. 2010. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 45:159. PubMed
- Wallace HA, et al. 2014. Development. 141:1332. PubMed
- Mizokami A, et al. 2014. Bone. 69:68. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2160546 (BioLegend Cat. No. 307909)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- DNA-polymerase sliding clamp, trimeric ring; 36 kD
- Distribution
-
Nuclear, all proliferating cells
- Function
- RAD6-dependent DNA repair pathway; increases DNA polymerase δ processibility during elongation of the leading strand
- Interaction
- PCNA, DNA polymerase δ, Rad6, Rad18, UBC9, MMS2, UBC13, RAD5
- Ligand/Receptor
- Ubiquitination, Sumoylation
- Cell Type
- Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Cycle/DNA Replication, DNA Repair/Replication, Immunology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Nuclear Markers
- Antigen References
-
1. Travali S, et al. 1989. J. Biol. Chem. 264:7466.
2. Waseem N, et al. 1990. J. Cell Sci. 96:121.
3. Hall P, et al. 1990. J. Pathol. 162:285.
4. Landberg G, et al. 1991. Cancer Res. 51:4570.
5. Woods A, et al. 1991. Histopathol. 19:21.
6. Hoege C, et al. 2002. Nature 419:135.
7. Yue H, et al. 2003. World J. Gastroenterol. 9:377.
8. Shan B, et al. 2003. J. Biol. Chem. 278:44009. - Gene ID
- 5111 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about PCNA on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All PCNA Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | ICFC |
| PE anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | ICFC |
| Purified anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | ICFC,ICC,IHC,IP,WB |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | ICFC |
| TotalSeq™-Bn0037 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA | PC10 | SB |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA
-
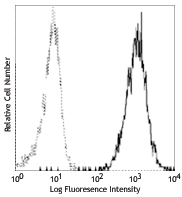
PE anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA
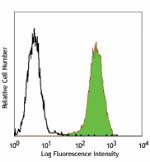
MOLT-4 cells fixed in 70% ethanol then stained with PC10 PE -
Purified anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA
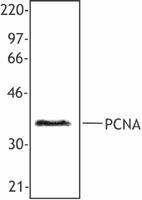
Hela cell nuclear extract was resolved by electrophoresis, t... 
HeLa cells were fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 ... 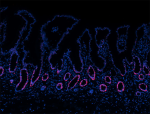
Human paraffin-embedded intestine tissue slices were prepare... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA

MOLT-4 cells fixed in 70% ethanol then stained with PC10 Ale... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA
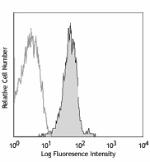
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes fixed with 70% ethanol, t... -
TotalSeq™-Bn0037 anti-human/mouse/rat PCNA

 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us