- Clone
- O91D3 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CTRCT30, HEL 113, Epididymis Luminal Protein 113
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
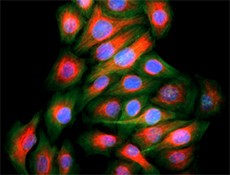
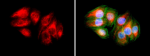
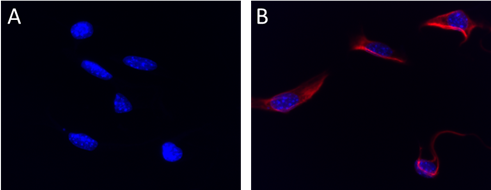
HeLa cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for ten minutes and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for five minutes followed by blocking with 5% FBS for 30 minutes. The cells were then intracellularly stained with 2.5 µg/ml Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Vimentin (clone O91D3) antibody (red) in 5% FBS for two hours at room temperature, followed by Alexa Fluor® 488 Phalloidin (green) staining for 20 minutes at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). -
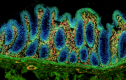
Human paraffin-embedded colon tissue slices were prepared with a standard protocol of deparaffinization and rehydration. Antigen retrieval was done with Tris Buffered 1X (1.0M, pH6.0) at 95°C for 40 minutes. Tissue was washed with PBS/0.05% Tween 20 twice for five minutes and blocked with 5% FBS and 0.2% gelatin for 30 minutes. Then, the tissue was stained with 10 µg/mL of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Vimentin Antibody (Clone O91D3, red) and Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-Galectin-9 Antibody (Clone 9M1-3, royal blue) antibody overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (green). The image was scanned with a 10X objective and stitched with MetaMorph® software. -
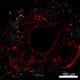
Confocal image of human liver sample acquired using the IBEX method of highly multiplexed antibody-based imaging: HLA-DR (cyan) in Cycle 2 and Vimentin (red) in Cycle 4. Tissues were prepared using ~1% (vol/vol) formaldehyde and a detergent. Following fixation, samples are immersed in 30% (wt/vol) sucrose for cryoprotection. Images are courtesy of Drs. Andrea J. Radtke and Ronald N. Germain of the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH). -
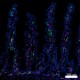
Confocal image of human jejunum sample acquired using the IBEX method of highly multiplexed antibody-based imaging: Hoechst (blue) in Cycle 1, CD54 (green) in Cycle 1, and Vimentin (magenta) in Cycle 6. Tissues were prepared using ~1% (vol/vol) formaldehyde and a detergent. Following fixation, samples are immersed in 30% (wt/vol) sucrose for cryoprotection. Images are courtesy of Drs. Andrea J. Radtke and Ronald N. Germain of the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH). -
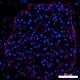
Confocal image of human kidney sample acquired using the IBEX method of highly multiplexed antibody-based imaging: Hoechst (blue) and Vimentin (magenta) in Cycle 5. Images are prepared from formalin fixed paraffin embedded human kidney sections. Images are courtesy of Drs. Andrea J. Radtke and Ronald N. Germain of the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 677807 | 25 µg | 109€ | ||||
Vimentin are class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is a widely expressed and highly conserved 54 kD protein that is constitutively expressed in mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells lining blood vessels, renal tubular cells, macrophages, neutrophils, fibroblasts, and leukocytes1,2. Vimentin is used as a marker of mesenchymal cells to distinguish them from epithelial cells3. Increased vimentin expression is frequently used as an EMT marker in cancer4. Autoantibodies to vimentin are commonly found in patients with autoimmune diseases such as Lupus5 and rheumatoid arthritis6, and also found after transplantation7.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Full length human vimentin produced in E. coli.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICC - Quality tested
IHC-P - Verified
SB - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunocytochemistry. For immunocytochemistry, a concentration range of 1.0 - 5.0 μg/mL is recommended. For immunohistochemical staining on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections, the suggested use of this reagent is 5.0 - 10 µg per mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
While this clone recognizes mouse Vimentin, we do not recommend its usage for western blot due to poor affinity of the antibody for the protein. Additional reported applications for the relevant formats include: spatial biology (IBEX)1,2.
- Additional Product Notes
-
Iterative Bleaching Extended multi-pleXity (IBEX) is a fluorescent imaging technique capable of highly-multiplexed spatial analysis. The method relies on cyclical bleaching of panels of fluorescent antibodies in order to image and analyze many markers over multiple cycles of staining, imaging, and, bleaching. It is a community-developed open-access method developed by the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2616801 (BioLegend Cat. No. 677807)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 466 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 54 kD.
- Distribution
-
Cytoplasm.
- Function
- Vimentins are class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is attached to the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, either laterally or terminally.
- Interaction
- HCV core protein, LGSN, SYNM, PLEC, SLC6A4, STK33, LARP6, RAB8B, TOR1A, TOR1AIP1, and BCAS3.
- Cell Type
- B cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells, Neutrophils
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Cell Motility/Cytoskeleton/Structure, Immunology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Intermediate Filaments
- Antigen References
-
1. Kidd ME, et al. 2014. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 50:1.
2. Fuchs E, et al. 1994. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 63:345.
3. Zeisberg M, et al. 2009. J. Clin. Invest. 119:1429.
4. Scanlon CS, et al. 2013. J. Dent. Res. 92:114.
5. Thebault S, et al. 2002. J. Immunol. 169:4046.
6. Vossenaar ER, et al. 2004. Arthritis Res. Ther. 6:R142.
7. Rose ML. 2013. Hum. Immunol. 74:1459. - Gene ID
- 7431 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Vimentin on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- If an antibody clone has been previously successfully used in IBEX in one fluorescent format, will other antibody formats work as well?
-
It’s likely that other fluorophore conjugates to the same antibody clone will also be compatible with IBEX using the same sample fixation procedure. Ultimately a directly conjugated antibody’s utility in fluorescent imaging and IBEX may be specific to the sample and microscope being used in the experiment. Some antibody clone conjugates may perform better than others due to performance differences in non-specific binding, fluorophore brightness, and other biochemical properties unique to that conjugate.
- Will antibodies my lab is already using for fluorescent or chromogenic IHC work in IBEX?
-
Fundamentally, IBEX as a technique that works much in the same way as single antibody panels or single marker IF/IHC. If you’re already successfully using an antibody clone on a sample of interest, it is likely that clone will have utility in IBEX. It is expected some optimization and testing of different antibody fluorophore conjugates will be required to find a suitable format; however, legacy microscopy techniques like chromogenic IHC on fixed or frozen tissue is an excellent place to start looking for useful antibodies.
- Are other fluorophores compatible with IBEX?
-
Over 18 fluorescent formats have been screened for use in IBEX, however, it is likely that other fluorophores are able to be rapidly bleached in IBEX. If a fluorophore format is already suitable for your imaging platform it can be tested for compatibility in IBEX.
- The same antibody works in one tissue type but not another. What is happening?
-
Differences in tissue properties may impact both the ability of an antibody to bind its target specifically and impact the ability of a specific fluorophore conjugate to overcome the background fluorescent signal in a given tissue. Secondary stains, as well as testing multiple fluorescent conjugates of the same clone, may help to troubleshoot challenging targets or tissues. Using a reference control tissue may also give confidence in the specificity of your staining.
- How can I be sure the staining I’m seeing in my tissue is real?
-
In general, best practices for validating an antibody in traditional chromogenic or fluorescent IHC are applicable to IBEX. Please reference the Nature Methods review on antibody based multiplexed imaging for resources on validating antibodies for IBEX.
Other Formats
View All Vimentin Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | ICC,IHC-P,SB |
| Purified anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | WB,ICC,ICFC,IHC-P,IHC-F,SB |
| Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | WB |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | ICC,IHC-P,SB |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | ICC,ICFC,IHC-P,SB |
| TotalSeq™-Bn1302 anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | SB |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-Vimentin | O91D3 | ICFC,SB |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-Vimentin
HeLa cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for ten... 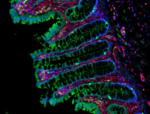
Human paraffin-embedded colon tissue slices were prepared wi... 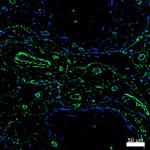
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... 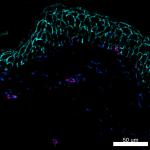
Confocal image of human skin sample acquired using the IBEX ... -
Purified anti-Vimentin
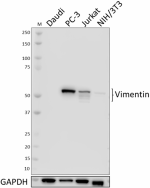
Total cell lysates (15 µg total protein) from Daudi (negativ... 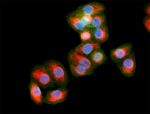
HeLa cells were stained with purified anti-Vimentin (clone O... 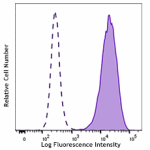
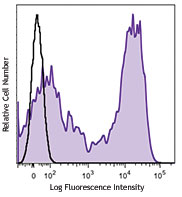
Jurkat cells (filled histogram, positive control) and Daudi ... 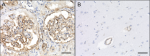
IHC staining of anti-Vimentin antibody (clone O91D3) on form... 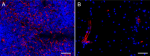
IHC staining of anti-Vimentin antibody (clone O91D3) on froz... 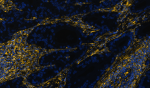
SeqIF™ (sequential immunofluorescence) staining on COMET™ of... -
Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-Vimentin
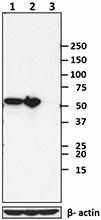
Total cell lysate from HeLa cells (lane 1, 15 µg), Jurkat ce... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Vimentin
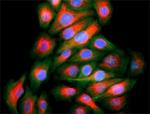
HeLa cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for ten... 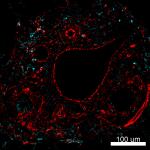
Confocal image of human liver sample acquired using the IBEX... 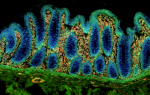
Human paraffin-embedded colon tissue slices were prepared wi... 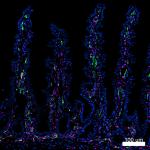
Confocal image of human jejunum sample acquired using the IB... 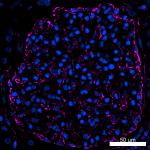
Confocal image of human kidney sample acquired using the IBE... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Vimentin
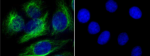
HeLa cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 15 ... 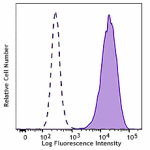
Jurkat cells (filled histogram, positive control) and Daudi ... 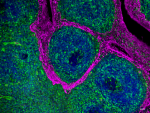
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Vimentin (clone O91D3)... 
Multiplexed IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Viment... -
TotalSeq™-Bn1302 anti-Vimentin
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-Vimentin

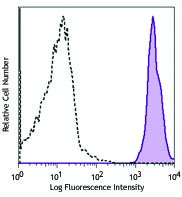
Daudi cells (negative control, open histogram) or Jurkat cel... 
Multiplexed IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Vimentin (...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us