- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP), plasma retinol-binding protein (PRBP)
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

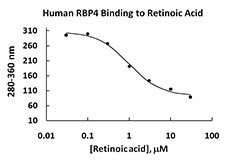
The activity of human RBP4 (49 µg/ml) is measured by its ability to bind all-trans retinoic acid at the concentration depicted here. The binding of retinoic acid results in the quenching of tryptophan fluorescence in RBP4. >0.5 µM all-trans retinoic acid is bound under the described conditions. The final assay condition per well is 4.41 µg of human RBP4.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 594906 | 100 µg | 400€ | ||||
RBP4 belongs to the lipocalin family, and it is the retinol (vitamin A alcohol) specific transport protein present in plasma. It has a β barrel structure with a well defined cavity, which accommodates retinol. The stability of the retinol-RBP (holo-RBP) complex is further enhanced when the complex is bound to transthyretin (TTR). RBP4 delivers retinol from the liver stores to the peripheral tissues. The interaction of RBP-retinol complex with TTR prevents its loss by filtration through the kidney glomeruli. Apo-RBP4 (without retinol) is reabsorbed in the proximal tubular cells. A deficiency of vitamin A blocks secretion of the binding protein post-translationally and results in defective delivery and supply to the epidermal cells.
Defects in RBP4 cause retinol-binding protein deficiency and can cause night vision problems. RBP4 has been described as an adipokine and is found to be expressed in adipose tissue and correlated with obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. It has been postulated that RBP4 acts as the mechanistic link by which decreased adipocyte GLUT4 expression contributes to insulin resistance. Circulating RBP4 concentrations are increased in insulin-resistant mice. Moreover, transgenic overexpression of human RBP4 and injection of recombinant RBP4 decreased insulin sensitivity in normal mice, whereas genetic deletion of the RBP4 gene or normalization of RBP4 concentrations in obese mice improved insulin sensitivity. RBP4 concentrations are also increased in obese humans, and higher concentrations have been correlated with lower insulin sensitivity and other components of the metabolic syndrome.
Product Details
- Source
- Human RBP4, amino acids (Glu19-Leu201) (Accession# NP_006735.2), was expressed with a C-terminal IHHHHHH tag in CHO cell line.
- Molecular Mass
- The 190 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 22 kD. The protein migrates as above 25 kD in SDS-PAGE in DTT-reducing condition and above 22 kD in non-reducing condition. The N-terminal amino acid is Gln.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg of protein as determine by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Measured by its ability to bind all-trans retinoic acid. The binding of retinoic acid results in the quenching of tryptophan fluorescence in RBP4. The ED50 of RBP4 to all-trans rentinoic acid is >0.5 µM.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Monomer
- Distribution
-
Hepatocytes, adipocytes, and present in plasma.
- Function
- RBP4 delivers retinol from the liver stores to the peripheral tissues. Deficiency of vitamin A inhibits its secretion, and IL-1 downregulates adipocyte RBP4 secretion.
- Interaction
- Endothelial cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- Retinol
- Bioactivity
- Binds all-trans retinoic acid.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Family
- Steroid Receptors/Nuclear Receptors
- Antigen References
-
1. Newcomer ME and Ong DE. 2000. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1482:57.
2. Zanotti G and Berni R. 2004. Vitamins and Hormones 69:271.
3. Yang Q, et al. 2005. Nature 436:356.
4. Frey KS, et al. 2008 Lipids in Health and Disease 7:29.
5. Tepper BJ, et al. 2010. Clin. Biochem. 43:320.
6. Kotnik P, et al. 2013. PLoS One 8:57796. - Gene ID
- 5950 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about RBP4 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- Why choose BioLegend recombinant proteins?
-
• Each lot of product is quality-tested for bioactivity as indicated on the data sheet.
• Greater than 95% Purity or higher, tested on every lot of product.
• 100% Satisfaction Guarantee for quality performance, stability, and consistency.
• Ready-to-use liquid format saves time and reduces challenges associated with reconstitution.
• Bulk and customization available. Contact us.
• Learn more about our Recombinant Proteins. - How does the activity of your recombinant proteins compare to competitors?
-
We quality control each and every lot of recombinant protein. Not only do we check its bioactivity, but we also compare it against other commercially available recombinant proteins. We make sure each recombinant protein’s activity is at least as good as or better than the competition’s. In order to provide you with the best possible product, we ensure that our testing process is rigorous and thorough. If you’re curious and eager to make the switch to BioLegend recombinants, contact your sales representative today!
- What is the specific activity or ED50 of my recombinant protein?
-
The specific activity range of the protein is indicated on the product datasheets. Because the exact activity values on a per unit basis can largely fluctuate depending on a number of factors, including the nature of the assay, cell density, age of cells/passage number, culture media used, and end user technique, the specific activity is best defined as a range and we guarantee the specific activity of all our lots will be within the range indicated on the datasheet. Please note this only applies to recombinants labeled for use in bioassays. ELISA standard recombinant proteins are not recommended for bioassay usage as they are not tested for these applications.
- Have your recombinants been tested for stability?
-
Our testing shows that the recombinant proteins are able to withstand room temperature for a week without losing activity. In addition the recombinant proteins were also found to withstand four cycles of freeze and thaw without losing activity.
- Does specific activity of a recombinant protein vary between lots?
-
Specific activity will vary for each lot and for the type of experiment that is done to validate it, but all passed lots will have activity within the established ED50 range for the product and we guarantee that our products will have lot-to-lot consistency. Please conduct an experiment-specific validation to find the optimal ED50 for your system.
- How do you convert activity as an ED50 in ng/ml to a specific activity in Units/mg?
-
Use formula Specific activity (Units/mg) = 10^6/ ED50 (ng/mL)

 Login / Register
Login / Register 









Follow Us