- Clone
- HIB19 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Workshop
- V CD19.11
- Other Names
- B4
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- 92 publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 302207 | 25 tests | 23€ | ||||
| 302208 | 100 tests | 53€ | ||||
| 302254 | 100 µg | 59€ | ||||
CD19 is a 95 kD type I transmembrane glycoprotein also known as B4. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily expressed on B-cells (from pro-B to blastoid B cells, absent on plasma cells) and follicular dendritic cells. CD19 is involved in B cell development, activation, and differentiation. CD19 forms a complex with CD21 (CR2) and CD81 (TAPA-1), and functions as a BCR co-receptor.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Reported Reactivity
- Chimpanzee
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
-
µg size: Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
test size: Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA). - Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
-
µg sizes: 0.2 mg/mL
test sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.) - Storage & Handling
- The CD19 antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining using the µg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application. For flow cytometric staining using the test sizes, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen tissue sections8 and blocking of B cell proliferation. Clone HIB19 is not recommended for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 302267 & 302268).
Clone HIB19 partially blocks anti-human CD19 clones 4G7 and SJ25C1 staining based on in-house testing
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Schlossman S, et al. 1995. Leucocyte Typing V. Oxford University Press. New York.
- Knapp W, et al. 1989. Leucocyte Typing IV. Oxford University Press. New York.
- Bradbury L, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2915.
- Joseph A, et al. 2010. J. Virol. 84:6645. PubMed
- Wang X, et al. 2010. Haematologica. 95:884. (FC) PubMed
- Walker JD, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 182:1548. (Block) PubMed
- Yoshino N, et al. 2000. Exp. Anim. (Tokyo) 49:97. (FC)
- Hansen A, et al. 2002. Arthritis Rheum. 46:2160. (IHC)
- Stoeckius M, et al. 2017. Nat. Methods. 14:865. (PG)
- Peterson VM, et al. 2017. Nat. Biotechnol. 35:936. (PG)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_314237 (BioLegend Cat. No. 302207)
AB_314238 (BioLegend Cat. No. 302208)
AB_2564142 (BioLegend Cat. No. 302254)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, type I transmembrane glycoprotein, 95 kD
- Distribution
-
B lineage (except plasma cells), follicular dendritic cells
- Function
- B cell activation and differentiation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Forms complex with CD21 (CR2) and CD81 (TAPA-1), BCR coreceptor
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells
- Biology Area
- Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Tedder T, et al. 1994. Immunol. Today 15:437.
2. Bradbury L, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2915. - Gene ID
- 930 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD19
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD19
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- FC
- UniProt
- View information about CD19 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All CD19 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
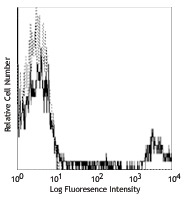
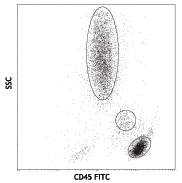
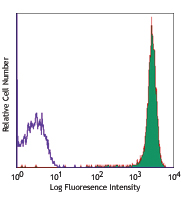
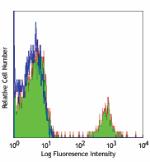
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-human CD19
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 APC -
Biotin anti-human CD19
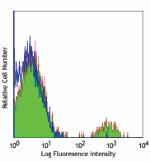
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with biotinylated... -
FITC anti-human CD19
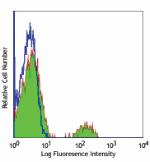
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 FITC -
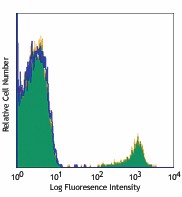
PE anti-human CD19
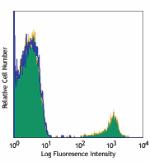
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 PE -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD19
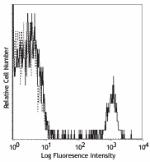
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 PE/Cya... -
Purified anti-human CD19
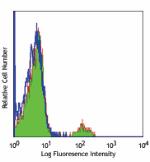
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified HIB... 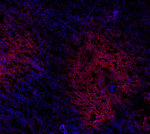
Human frozen spleen tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD19
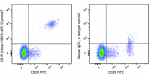
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD20 FI... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD19
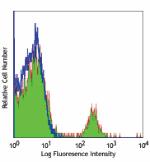
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 PE/Cya... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human CD19
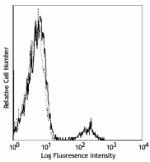
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 Alexa ... 
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD19
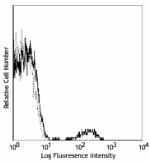
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 Alexa ... 
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD19
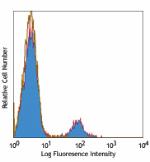
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 Pacifi... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-human CD19
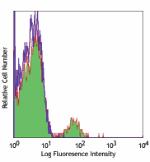
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 Alexa ... -
PerCP anti-human CD19
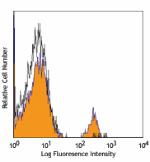
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with HIB19 PerCP -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD19
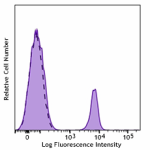
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 (c... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... 
Human peripheral mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% parafo... 
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... 
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD19
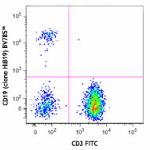
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 APC... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... 
-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... 
-
Purified anti-human CD19 (Maxpar® Ready)

Human PBMCs stained with 154Sm-anti-CD45 (HI30) and 142Nd-an... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-human CD19
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% ... 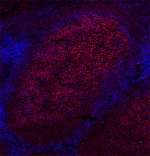
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD19
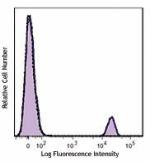
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 (c... -
PE anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD19
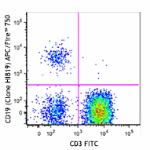
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 FIT... 
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD19
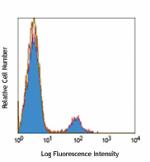
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
APC anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
TotalSeq™-A0050 anti-human CD19
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-human CD19
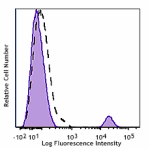
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with CD19 (clone ... -
TotalSeq™-B0050 anti-human CD19
-
TotalSeq™-C0050 anti-human CD19
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-human CD19
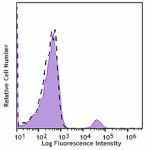
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 (c... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD19
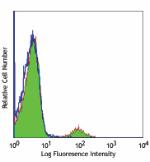
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with Ultra-LEAF™ ... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-human CD19
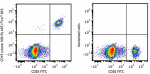
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD20 FI... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-human CD19
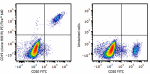
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD20 FI... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-human CD19
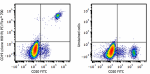
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
TotalSeq™-D0050 anti-human CD19
-
Spark YG™ 593 anti-human CD19
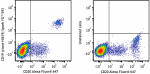
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD20 Al... -
GMP Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD19
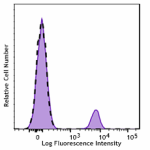
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-human CD19
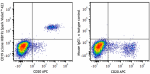
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
GMP PE anti-human CD19
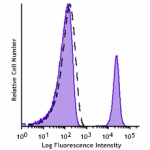
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP APC anti-human CD19
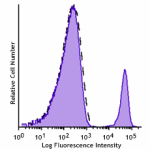
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-human CD19
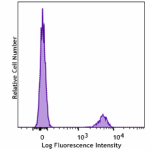
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with anti-human C... -
GMP PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD19
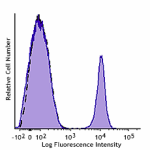
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD19
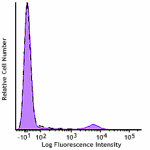
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark Violet™ 500 anti-human CD19
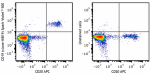
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-human CD19
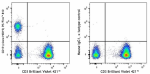
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-human CD19
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-human CD19
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD19
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD19
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Alexa Fluor® 660 anti-human CD19
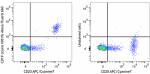
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
PerCP/Fire™ 806 anti-human CD19
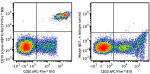
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
PerCP/Fire™ 780 anti-human CD19
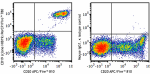
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human CD19
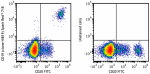
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
PE/Fire™ 744 anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
FITC anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD19

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
StarBright UltraViolet 575 anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
StarBright UltraViolet 795 anti-human CD19

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 


















Follow Us