- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CD152, CELIAC3, GSE, IDDM12, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, ALPS5, and GRD4
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
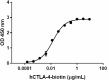
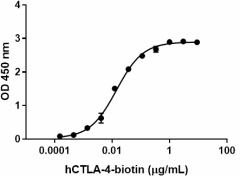
When human CD86-Fc Chimera (Cat. No. 775602) is immobilized at 1.0 µg/mL, Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4-Fc Chimera binds with an EC50 of 12 - 48 ng/mL. HRP Avidin (Cat. No. 405103) was used to detect the binding. -
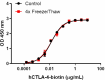
Stability testing for Biotinylated Recombinant Human CTLA-4-Fc Chimera. Recombinant human CTLA-4-Fc Chimera Biotin was aliquoted in PBS, pH 7.2, 5% glycerol at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw), and compared to a control kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested in a binding assay with Recombinant Human B7-2/CD86-Fc Chimera (Cat. No. 775602).
Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) is a member of the IgG superfamily. It encodes a 223 amino acid protein and possesses a single extracellular V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. CTLA-4 is ~30% homologous with CD28, and both bind to the same ligands (B7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86) although CTLA-4 binds with higher affinity than CD28. Parallel recognition of a specific MHC-peptide complex by the T-cell receptor and of CD80 or CD86 by the costimulatory receptor CD28 results in T cell activation, cytokine production, proliferation, and differentiation. After the T cells' activation process and upregulation of CTLA-4, co-ligation of the TCR to the MHC-peptide complex and CTLA-4 to its ligands results in cell cycle arrest and ends T cell activation. It has been suggested that the negative regulatory mechanism of CTLA-4 is mediated through trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86 (capture of ligands from opposing cells). The ligands are removed from the original cell and degraded inside of CTLA-4-expressing cells. As a result, the action of CD28 is impaired. Alternative splice variants of CTLA-4 have been described in mice and humans that have transcripts that skip exon 2 (ligand-binding domain) or exon 3 (transmembrane domain). The ligand independent CTLA-4 is expressed in mice, but not in humans, and soluble CTLA-4 (sCTLA-4) is expressed in mice and humans. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed by Tregs, and they are an important source of sCTLA-4. It has been suggested that sCTLA-4 potentiates regulatory T cell function. High levels of sCTLA-4 in Tregs have been associated with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and other autoimmune diseases, such as Grave's disease and myasthenia gravis. Also, CTLA-4 has been linked with proliferation and survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. CTLA-4 is a target for therapeutic intervention; in fact, a monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4 (Ipilimumab) has been approved for the treatment of melanoma.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Source
- Human CTLA-4, amino acids Ala31-Phe162 (Accession # BC070162) with a C-terminal human IgG1 Fc tag was expressed in CHO cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The unlabeled 360 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 39.9 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced glycosylated protein migrate at approximately 56 kD and 105 kD respectively by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Ala.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2, 5% glycerol.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng/µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for one month, at -20°C for six months, or at -70°C for one year. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Stock solutions should be prepared at no less than 50 - 100 µg/mL in sterile buffer (PBS, HPBS, DPBS, and EBSS) containing carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA and stored in working aliquots at -20°C to -70°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- When Recombinant Human B7-2/CD86-Fc Chimera (Cat. No. 775602) is immobilized at 1.0 µg/mL, biotinylated human CTLA-4-Fc Chimera binds with an EC50 of 12 - 48 ng/mL. HRP Avidin (Cat. No. 405103) was used to detect the binding.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulfide-linked homodimer, biotinylated via amines
- Distribution
-
Activated T cells, CD4, CD8, and Tregs
- Function
- Inhibits T cell activation by reducing IL-2 production and IL-2R expression, also arresting T cells in G1 phase of the cell cycle; protects against the development of autoimmunity
- Interaction
- Antigen presenting cells, B cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD86, CD80
- Bioactivity
- Measured by its ability to bind mouse CD200R1
- Cell Type
- Antigen-presenting cells, B cells, Dendritic cells, Monocytes, T cells
- Biology Area
- Adaptive Immunity, Immuno-Oncology, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- Immune Checkpoint Receptors, Soluble Receptors
- Antigen References
-
- Linsley PS, et al. 1991. J. Exp. Med. 174:561-9.
- Pentcheva-Hoang T, et al. 2004. Immunity 21:401-13.
- Qureshi OS, et al. 2011. Science 10.1126/science.1202947.
- Gerold KD, et al. 2011. Diabetes. 10.2337/db11-0130.
- Rydén A, et al. 2012. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 10.1002/dmrr.1286.
- Mittal AK, et al. 2013. PloS One 8:e70352.
- Ward FJ, et al. 2013. Eur. J. Immunol. 10.1002/eji.201242529.
- Gene ID
- 1493 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CTLA-4 on UniProt.org

 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us