- Clone
- 150D (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Forkhead box protein P3, Scurfin, JM2, IPEX, Zinc finger protein JM2
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- 43 publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320007 | 25 tests | 162€ | ||||
| 320008 | 100 tests | 317€ | ||||
FOXP3 is a 50-55 kD transcription factor, also known as Forkhead box protein P3, Scurfin, JM2, or IPEX. It is proposed to be a master regulatory gene and more specific marker of T regulatory cells than most cell surface markers (such as CD4 and CD25). Transduced expression of FOXP3 in CD4+/CD25- cells has been shown to induce GITR, CD103, and CTLA4 and impart a T regulatory cell phenotype. FOXP3 is mutated in X-linked autoimmunity-allergic dysregulation syndrome (XLAAD or IPEX) in humans and in "scurfy" mice. Overexpression of FOXP3 has been shown to lead to a hypoactive immune state suggesting that this transcriptional factor is a central regulator of T cell activity. In human, unlike in mouse, two isoforms of FOXP3 have been reported: one (FOXP3) corresponding to the canonical full-length sequence; the other (FOXP3 δ2) lacking exon 2. The 150D monoclonal antibody reacts with human, mouse and rat FOXP3. The 150D antibody recognizes FOXP3 epitope encoded by exon 2.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Reported Reactivity
- Cynomolgus, Rhesus, Baboon
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Full-length FOXP3 protein
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The FOXP3 antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICFC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by intracellular flow cytometry using our True-Nuclear™ Transcription Factor Staining Protocol. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
NOTE: For flow cytometric staining with this clone, True-Nuclear™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 424401) offers improved staining and is highly recommended.
- Additional Product Notes
-
View more applications data for this product in our Scientific Poster Library.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Roncador G, et al. 2005 Eur. J. Immunol. 35:1681.
- Mayack. S,et al. 2006. J. Immunol.176:2059. J. Immunol
- Yang ZZ, et al. 2006. Blood 107:3639.
- Gavin MA, et al. 2006. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:6659.
- Groh V, et al. 2006. Nature Immunology 7:755.
- Lewkowicz P, et al. 2006 J. Immunol. 177:7155.
- Luke PPW, et al. 2006. Amer. J. Transplant. 6(9):2023.
- Bamias G, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:1809.
- Valencia X, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:2579.PubMed
- Davidson TS, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4022.
- MacDonald K PA, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-01-067249.
- Jaffar Z, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:6193.
- Müller M, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:2774.
- Jordan JM,et al. 2008.Infect Human. 76:3717. PubMed
- Golovina TN,et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:2855. PubMed
- Fallarino F, et al. 2009. J. Exp Med. 206:2511. PubMed
- Banham Alison, et al. 2009. Vet Immunol and Immunop 127.3-4:376-381
- Klunker S, et al. 2009. J. Exp Med. PubMed
- Haque A, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:2583. PubMed
- Liu Y, et al. 2012. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1920. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_492981 (BioLegend Cat. No. 320007)
AB_492980 (BioLegend Cat. No. 320008)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Forkhead/winged-helix transcription factor family, approximately 50 kD, contains zinc finger and forkhead domains
- Distribution
-
Nuclear; expressed in T regulatory cells
- Function
- Transcription factor proposed to be a master regulatory gene in T regulatory cell development and a critical factor for immune homeostasis
- Interaction
- Interacts with DNA
- Cell Type
- Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Transcription Factors
- Molecular Family
- Nuclear Markers
- Antigen References
-
1. Hori S, et al. 2003. Science 299:1057.
- Regulation
- FOXP3 is present at high levels in T regulatory cell can also be induced by T cell activation
- Gene ID
- 20371 View all products for this Gene ID 317382 View all products for this Gene ID 50943 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FOXP3 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
- Can I stain whole blood with anti-FOXP3 using your Foxp3 staining kit?
-
It is not recommended. It is best to use PBMCs for this testing.
- Can FOXP3 be costained with cytokines?
-
The larger holes created by the nuclear permeabilization required for FOXP3 may allow cytokines to leak out of the cell, making it harder to detect lowly-expressed cytokines. You may have to use a control where the cells are only permeabilized through the cell membrane.
Other Formats
View All FOXP3 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3 | 150D | WB,ICFC |
| PE anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3 | 150D | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3 | 150D | ICFC |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3 | 150D | ICFC |
| True-Nuclear™ Human Treg Flow Kit | 150D | ICFC |
| True-Nuclear™ Mouse Treg Flow Kit | 150D | ICFC |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3
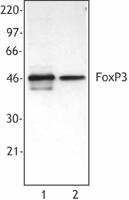
Cell extract from HEK293T cells transfected with either huma... -
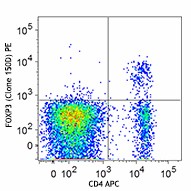
PE anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3

C57BL/6 splenocytes were surface stained with CD4 APC and th... 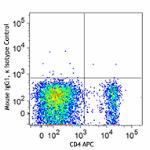
-
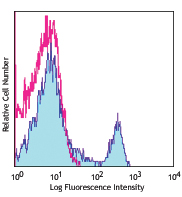
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3
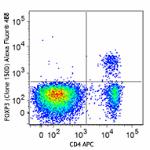
C57BL/6 splenocytes were surface stained with CD4 APC and th... 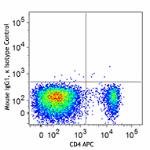
-
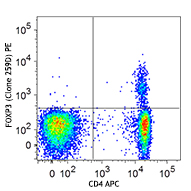
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse/rat/human FOXP3
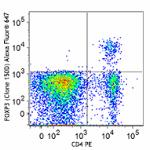
C57BL/6 splenocytes were surface stained with CD4 PE and the... 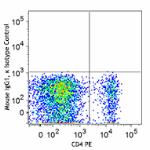
-
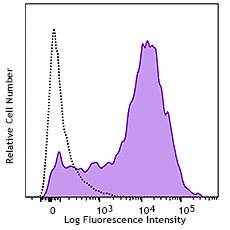
True-Nuclear™ Human Treg Flow Kit

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with True-Nu... 
-
True-Nuclear™ Mouse Treg Flow Kit

BALB/c mouse splenocytes were stained with True-Nuclear™ Mou... 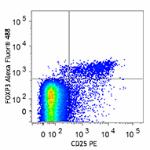

 Login / Register
Login / Register 

















Follow Us