- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interleukin-6, Interferon-β2, B cell stimulating factor-2 (BSF-2), Cytotoxic T cell differentiation factor (CDF), Hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), Hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF)
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications

-

Recombinant Mouse IL-6 induces the proliferation of mouse 7TD1 cells in a dose dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is < 10 pg/mL. -

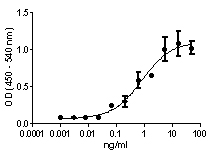
Stability Testing for Recombinant Mouse IL-6. Recombinant mouse IL-6 was aliquoted in 0.1% TFA (trifluoroacetic acid), 10% ACN (Acetonitrile) at 0.2 mg/mL and one aliquot was kept at 4°C (Control), and another was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw). The samples were tested by their property to induce the proliferation of mouse 7TD1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is < 10 pg/mL.
IL-6 is a multifunctional cytokine that can regulate various immune and inflammatory responses. Several studies have suggested a crucial role for IL-6 in angiogenesis. The use of mice deficient in IL-6 (-/-) demonstrated a critical role for this protein in a mouse model of lung angiogenesis. IL-6 has been shown to cause proliferation and migration of systemic endothelial cells in culture (1). The classical responsiveness to IL-6 is governed by a receptor complex consisting of two membrane-bound subunits, an 80-kD cognate chain (IL-6R), and a ubiquitously expressed 130-kD β-chain receptor (gp130) which acts as the universal signal-transducing element for all IL-6 family cytokines (2). Alternatively, IL-6 regulation of leukocyte trafficking relies upon signaling via its soluble IL-6R (termed IL-6 trans-signaling) (3). IL-6 plays a major role in regulating neutrophil clearance during acute peritoneal inflammation; as a result of specific down-regulation of neutrophil-attracting chemokine (CXCL1/KC) production (4). IL-6 is a key factor that reciprocally regulates Th17 and Foxp3(+) Treg differentiation by inhibition of TGF-beta induced Foxp3 and induction of RORgammat, a Th17 lineage-specific transcription factor (5).
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Source
- Mouse IL-6, amino acids Phe25-Thr211 (Accession# NM_031168), was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 188 amino acid N-terminal methionylated recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of 21,866 Da. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 22 kD and the non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 21.5 kD by SDS-PAGE.
- Purity
- Purity is >98%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 0.1% TFA, 10% Acetonitrile
- Endotoxin Level
- Endotoxin level is <0.1 EU/µg (<0.01ng/µg) protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Recombinant Mouse IL-6 induces the proliferation of mouse 7TD1 cells in a dose dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is < 10 pg/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Additional Product Notes
-
Get a 50% discount on this product when purchased in our Activation Bundles. Restrictions apply. Learn more…
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
IL-6 is released by activated T cells, B cells, monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells.
- Function
- Upregulated by IL-1, PDGF, IFN-β, TNF-α, NGF, IL-17; downregulated by glucocorticoids IL-4, TGF-β
- Interaction
- T cells, B cells, hepatocytes, cholinergic neurons
- Bioactivity
- Hematopoiesis, antigen-specific immune responses, inflammatory reactions, acute phase reactions
- Receptors
- Heterodimer IL-6Rα (CD126)/IL-6Rβ (CD130; gp130) and soluble IL-6R
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. McClintock JE and Wagner EM. 2005. 99:861-866
2. Murakami M. 1993. Science 260:1808-1810.
3. Jones SA,et al. 2001.J. FASEB. 15:43-58.
4. Fielding CA,et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:2189-2195.
5. Sonderegger I,et al. 2008. Eur. J. Immunol. 38:1833-1838. - Gene ID
- 16193 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- IL-6
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- IL-6
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- BA
- UniProt
- View information about IL-6 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Why choose BioLegend recombinant proteins?
-
• Each lot of product is quality-tested for bioactivity as indicated on the data sheet.
• Greater than 95% Purity or higher, tested on every lot of product.
• 100% Satisfaction Guarantee for quality performance, stability, and consistency.
• Ready-to-use liquid format saves time and reduces challenges associated with reconstitution.
• Bulk and customization available. Contact us.
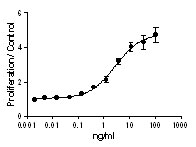
• Learn more about our Recombinant Proteins. - How does the activity of your recombinant proteins compare to competitors?
-
We quality control each and every lot of recombinant protein. Not only do we check its bioactivity, but we also compare it against other commercially available recombinant proteins. We make sure each recombinant protein’s activity is at least as good as or better than the competition’s. In order to provide you with the best possible product, we ensure that our testing process is rigorous and thorough. If you’re curious and eager to make the switch to BioLegend recombinants, contact your sales representative today!
- What is the specific activity or ED50 of my recombinant protein?
-
The specific activity range of the protein is indicated on the product datasheets. Because the exact activity values on a per unit basis can largely fluctuate depending on a number of factors, including the nature of the assay, cell density, age of cells/passage number, culture media used, and end user technique, the specific activity is best defined as a range and we guarantee the specific activity of all our lots will be within the range indicated on the datasheet. Please note this only applies to recombinants labeled for use in bioassays. ELISA standard recombinant proteins are not recommended for bioassay usage as they are not tested for these applications.
- Have your recombinants been tested for stability?
-
Our testing shows that the recombinant proteins are able to withstand room temperature for a week without losing activity. In addition the recombinant proteins were also found to withstand four cycles of freeze and thaw without losing activity.
- Does specific activity of a recombinant protein vary between lots?
-
Specific activity will vary for each lot and for the type of experiment that is done to validate it, but all passed lots will have activity within the established ED50 range for the product and we guarantee that our products will have lot-to-lot consistency. Please conduct an experiment-specific validation to find the optimal ED50 for your system.
- How do you convert activity as an ED50 in ng/ml to a specific activity in Units/mg?
-
Use formula Specific activity (Units/mg) = 10^6/ ED50 (ng/mL)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 






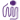



Follow Us