- Clone
- MEL-14 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- L-selectin, LECAM-1, Ly-22, LAM-1, MEL-14
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
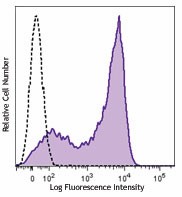
-

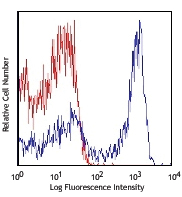
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes cells were stained with CD62L (clone MEL-14) Brilliant Violet 605™.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104437 | 125 µL | £170 | ||||
| 104438 | 50 µg | £187 | ||||
CD62L is a 74-95 kD glycoprotein also known as L-selectin, LECAM-1, Ly-22, LAM-1, and MEL-14. It is a member of the selectin family and is expressed on the majority of B and naïve T cells, a subset of memory T cells, monocytes, granulocytes, most thymocytes, and a subset of NK cells. CD62L is important in lymphocyte homing to high endothelial venules (HEV) in peripheral lymph nodes and leukocyte "rolling" on activated endothelium. CD62L also contributes to neutrophil emigration at inflammatory sites. CD62L is rapidly shed from lymphocytes and neutrophils upon cellular activation and the expression levels of CD62L (in conjunction with other markers) have been used to distinguish naïve, effector, and memory T cells. CD62L has been reported to interact with CD34, GlyCAM-1, and MAdCAM-1.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- C3H/eb mouse B lymphoma 38C-13
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Brilliant Violet 605™ under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- µg sizes: 0.2 mg/mLµL sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For immunofluorescent staining using the µg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. For immunofluorescent staining using the µl size, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 605™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 603 nm. The bandpass filter 610/20 nm is recommended for detection, although filter optimization may be required depending on other fluorophores used. Be sure to verify that your cytometer configuration and software setup are appropriate for detecting this channel. Refer to your instrument manual or manufacturer for support. Brilliant Violet 605™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet™.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents. - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1-3, complement-dependent cytotoxicity4, in vivo and in vitro blocking of adhesion1-3,5, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections and zinc-fixed paraffin-embedded sections6. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. Nos. 104457-104462).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Gallatin WM, et al. 1983. Nature 304:30. (IP, Block)
- Siegelman MH, et al. 1990. Cell 61:611. (IP, Block)
- Lewinsohn DM, et al. 1987. J. Immunol. 138:4313. (IP, Block)
- Iwabuchi K, et al. 1991. Immunobiology 182:161. (CMCD)
- Pizcueta P, et al. 1994. Am. J. Pathol. 145:461.
- Reichert RA, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 136:3535. (IHC, FC)
- Olver S, et al. 2006. Cancer Res. 66:571.
- Fukushima A, et al. 2006. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47:657. PubMed
- Benson MJ, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. doi:10.1084/jem.20070719. (FC) PubMed
- Chappaz S, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-074245. (FC) PubMed
- Lee JW, et al. 2006. Nature Immunol. 8:181.
- Shigeta A, et al. 2008. Blood 112:4915 (FC) PubMed
- de Vries VC, et al. 2009. Am. J. Transplant. 9:2270 PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_11125577 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104437)
AB_2563058 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104438)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Selectin, 95 kD (neutrophils) or 74 kD (lymphocytes)
- Distribution
-
Subsets of B and T cells, monocytes, granulocytes, subset of NK cells
- Function
- Lymphocyte homing to HEV, rolling on activated endothelium
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD34, GlyCAM-1, MAdCAM-1
- Cell Type
- B cells, Granulocytes, Monocytes, Neutrophils, NK cells, T cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Kishimoto TK, et al. 1990. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:2244.
3. Tedder TF, et al. 1995. J. Exp. Med. 181:2259. - Gene ID
- 20343 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD62L on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD62L Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD62L
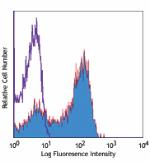
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD62L (clone MEL... -
Biotin anti-mouse CD62L
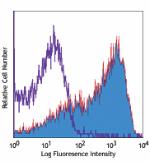
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with biotinylated CD6... -
FITC anti-mouse CD62L
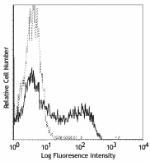
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with MEL-14 FITC -
PE anti-mouse CD62L
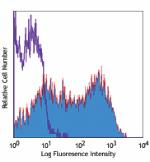
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with MEL-14 PE -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD62L
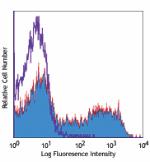
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
Purified anti-mouse CD62L
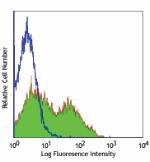
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with purified MEL-14, foll... 
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD62L c... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD62L
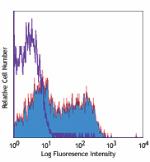
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD62L (clone MEL... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor®... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor®... 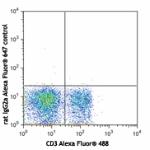
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor&... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD62L
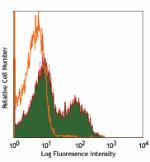
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD62L
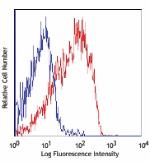
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD62L (clone MEL... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD62L
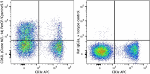
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e APC and CD6... -
PerCP anti-mouse CD62L
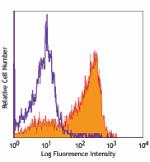
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD62L
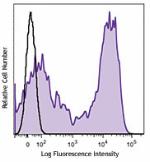
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse CD62L
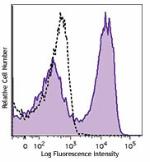
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD62L
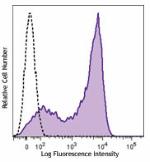
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and CD62... -
Purified anti-mouse CD62L (Maxpar® Ready)
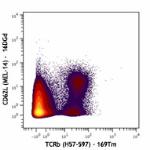
Mouse splenocytes stained with 169Tm-anti-TCRβ (H57-597) and... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD62L
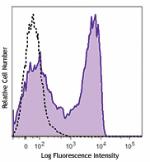
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD62L (clo... -
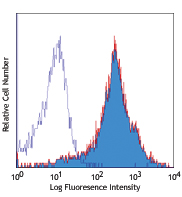
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD62L
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD6... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD62L
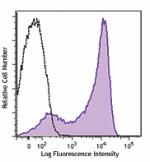
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD62L (clone MEL... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD... 
-
TotalSeq™-A0112 anti-mouse CD62L
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD62L
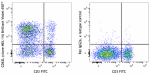
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD6... -
TotalSeq™-C0112 anti-mouse CD62L
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD62L
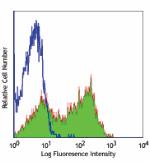
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ultra-LEAF™ puri... -
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-mouse CD62L
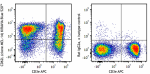
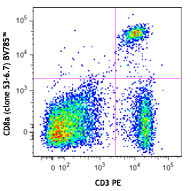
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e APC and CD6... -
TotalSeq™-B0112 anti-mouse CD62L
-
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD62L (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark PLUS B550™ anti-mouse CD62L

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 
















Follow Us