- Clone
- P88C5B8 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV, CaM kinase-GR, CAMK4
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

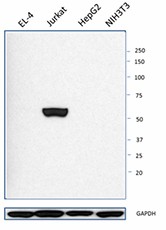
Total cell or tissue lysates (15 µg protein) from EL-4, Jurkat, HepG2, and NIH3T3 were resolved by 4-20% Tris-glycine gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with purified anti-CAMK IV antibody (clone P88C5B8) antibody (upper) or loading control GAPDH (clone poly6314) antibody (lower). Proteins were visualized using a goat anti-mouse-IgG secondary antibody conjugated to HRP and chemiluminescence detection.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 691102 | 100 µg | £174 | ||||
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMK IV) is a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase regulating different cellular processes. CaMK IV resides in both the nucleus and cytosol, but the active phosphorylated form of CaMK IV is predominantly nuclear. Once activated, CAMK IV enhances BCL2 gene expression. CaMK IV also actively regulates gene transcription by phosphorylating HDAC4. Phosphorylation of HDAC4 by CaMK IV promotes HDAC4 nuclear exports in neurons, resulting in major cell death mechanism in cerebral ischemia. CaMK IV–mTOR-dependent autophagy was fundamentally important for IL-6 production in vitro and in vivo.
CaMK IV is abnormally increased in T cells from patients with SLE and lupus-prone mice. Genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of CaMK IV resulted in a significant decrease of autoantibody production, mesangial cell proliferation, improved Treg function, improvement of lupus-related pathology, and the survival rates. CaMK IV inhibition has potential as a therapeutic strategy for Th17-driven autoimmune diseases.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Purified recombinant fragment of human CAMK4 (AA:35-292) expressed in E. coli.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.5 - 2.5 µg per ml. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- RRID
-
AB_2629828 (BioLegend Cat. No. 691102)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 473 amino acids with an expected molecular weight of 52 kD.
- Distribution
- Cytoplasm and the nucleus. Expressed in the brain, thymus, CD4 T-cells, testis, and epithelial ovarian cancer tissue.
- Function
- In the thymus, regulates the CD4+/CD8+ double positive thymocytes selection threshold during T-cell ontogeny. In CD4 memory T-cells, is required to link T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling to the production of IL2, IFNG, and IL4 (through the regulation of CREB and MEF2). Regulates the differentiation and survival phases of osteoclasts and dendritic cells (DCs). Mediates DCs survival by linking TLR4 and the regulation of temporal expression of BCL2.
- Interaction
- Phosphatase 2A (PPP2CA/PPP2CB)
- Antigen References
-
1. Racioppi L, et al. 2008. Trends Immunol 29:600.
2. Zhang, et al. 2014. J. Immunol. 193:2405.
3. McCullough LD, et al. 2013. Stroke. 44:2559.
4. Bolger TA, et al. 2005. J. Neurosci. 25:9544.
5. Juang YT, et al. 2005. J. Clin. Invest. 115:996.
6. Koga T, et al. 2014. J. Clin. Invest. 124:2234. - Gene ID
- 814 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CAMK IV on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All CAMK IV Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-CAMK IV | P88C5B8 | WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-CAMK IV

Total cell or tissue lysates (15 µg protein) from EL-4...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us