- Clone
- M0312E3 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Erythropoietin, MVCD2, EP, Epoetin
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
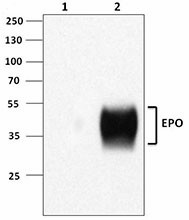
-

Immunoprecipitation/Western blot analysis using EPO antibody (M0312E3). 100 ng of recombinant human EPO (Cat No. 587106) was tested in 1 ml of immunoprecipitation lysis buffer. Lane 1 was immunoprecipitated with mouse IgG control antibody and lane 2 was immunoprecipitated with EPO antibody (M0312E3). Western blot analysis was performed using goat polyclonal anti-EPO antibody generated in house.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 662202 | 100 µg | £182 | ||||
EPO is the major regulator of differentiation, proliferation, and survival of erythroid progenitors. Hypoxia induces erythropoiesis which causes cells to produce hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) that is directly involved in EPO expression. HIF-Prolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PH) is a sensor of levels of iron, oxygen, and metabolic activity. High levels of HIF protein induce EPO production in the kidneys and liver, and mobilize iron to support erythropoiesis. EPO has been used in the treatment of anemia associated with a number of conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, cancer patients on chemotherapy, and antiviral HIV therapy.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant human EPO
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
IP - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunoprecipitation. This antibody can be used at 1 - 5 µg/mL for immunoprecipitation. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- RRID
-
AB_2564245 (BioLegend Cat. No. 662202)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 165 amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 18 kD. It migrates at approximately 37-57 kD as a result of its glycosylation.
- Distribution
- EPO is primarily expressed in kidney (70-90% of the total EPO) and liver cells. EPO is expressed by hepatocytes, cortical interstitial fibroblasts in ischemic kidneys, astrocytes, and neurons under hypoxic conditions.
- Function
- EPO is the major regulator of differentiation, proliferation, and survival of erythroid progenitors. EPO expression is induced by hypoxia, HIF, and other transcription factors. EPO also plays a role in neuroprotection.
- Interaction
- Erythroid progenitor cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- EpoR (homodimer)
- Cell Type
- Fibroblasts, Neurons
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Signal Transduction
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Shoemaker CB, et al. 1986. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:849.
2. McDonald JD, et al. 1986. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:842.
3. Chin K, et al. 2000. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 81:29.
4. Snow JW, et al. 2009. J. Biol. Chem. 284:29310.
5. Kassouf MT, et al. 2010. Genome Res. 2010:20:1064.
6. Paliege A, et al. 2010. Kidney Int. 77:312.
7. Sinclair AM, et al. 2010. Blood 115:4264.
8. Alnaeeli M, et al. 2012. Anat. Res. Int. 2012:953264. - Gene ID
- 2056 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about EPO on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All EPO Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-EPO | M0312E3 | IP |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-EPO
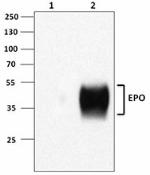
Immunoprecipitation/Western blot analysis using EPO antibody...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us