- Clone
- QA20A44 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- VE-Cadherin, cadherin-5, CDH5
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
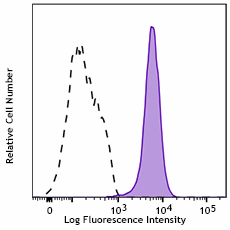
HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recombinant (clone QA20A44) purified (filled histogram) or mouse IgG1, κ isotype control (open histogram) followed by PE goat-anti-mouse IgG.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 376502 | 100 µg | £161 | ||||
CD144, also known as VE-cadherin and cadherin-5, is a 140 kD glycoprotein which is composed of five extracellular cadherin repeats and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail region. It is a calcium-dependent transmembrane cell-cell adhesion molecule localized at the intercellular boundaries of endothelial cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and perineurial cells. It functions as a classic cadherin by mediating homophilic adhesion and functions as a plasma membrane attachment site for the cytoskeleton. CD144 is thought to play a role in vascular development, permeability, and remodeling.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Recombinant
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µL volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
It is also recommended using EDTA-based solutions for dissociating attachment-dependent cell lines. - RRID
-
AB_2904407 (BioLegend Cat. No. 376502)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Member of the cadherin family; calcium-dependent transmembrane cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein composed of five extracellular cadherin repeats and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail region.
- Distribution
-
Endothelial cells, hematopoietic stem cells, perineurial cells
- Function
- Mediates calcium-dependent homophilic cell adhesion, plays fundamental roles in microvascular permeability and in the morphogenic and proliferative events associated with angiogenesis
- Cell Type
- Endothelial cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Taddei A, et al. 2008. Nat. Cell Biol. 10:923.
2. Gavard J, et al. 2006. Nat. Cell Biol. 8:1223.
3. Kim I, et al. 2005. Blood 106:903.
4. Suzuki S, et al. 1991. Cell Regul. 2:261. - Gene ID
- 1003 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD144 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD144 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody | QA20A44 | FC |
| PE anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody | QA20A44 | FC |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody | QA20A44 | FC |
| APC anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody | QA20A44 | FC |
| FITC anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody | QA20A44 | FC |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody
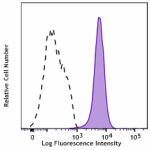
HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recom... -
PE anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody

HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recom... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody

HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recom... -
APC anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody

HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recom... -
FITC anti-human CD144 Recombinant Antibody

HUVEC cells were surface stained with anti-human CD144 recom...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us