- Clone
- 11A2SC (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- RAD23 homolog B (S. cerevisiae), RAD23, yeast homolog of B, UV excision repair protein RAD23 homolog B, HHR23B
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, λ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

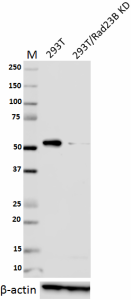
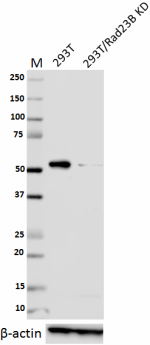
Total lysates (15 µg protein) from 293T and 293T/Rad23B CRISPR/Cas9 knockdown (KD) cells were resolved by electrophoresis (4-20% Tris-Glycine gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1:1000 diluted (0.5 µg/mL) purified anti-Rad23B antibody, clone 11A2SC (upper). Proteins were visualized using chemiluminescence detection by incubating with 1:3000 dilution of HRP goat anti-mouse-IgG secondary antibody (Cat. No. 405306). 1:2000 dilution of Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-β-actin Antibody (Cat. No. 643807) was used as a loading control (lower). Lane M: MW ladder. -
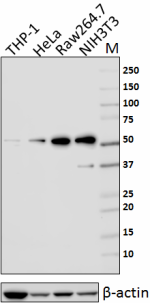
Total lysates (15 µg protein) from THP-1, HeLa, Raw264.7 and NIH3T3 cells were resolved by electrophoresis (4-20% Tris-glycine gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1:2500 (0.2 µg/ml) purified anti- Rad23B antibody , clone 11A2SC (upper). Proteins were visualized using chemiluminescence detection by incubating with HRP goat anti-mouse-IgG secondary antibody (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-β-actin Antibody (Cat. No. 643807) was used as a loading control (lower). Lane M is the MW ladder.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 654201 | 25 µg | £101 | ||||
Yeast Rad23, originally identified as a DNA repair protein, has been proposed to participate in other cellular functions, i.e., the proteasome-degradation pathway, the process of spindle pole body duplication, and as a component of the anaphase checkpoint. Two human homologs of yeast Rad23 (Rad23A and Rad23B) exhibit high sequence homology with yeast Rad23 and also have been shown to be involved in DNA repair and proteasome-dependent degradation.
Rad23B is involved in global genome nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER) by acting as a component of the XPC complex. The XPC complex recognizes a wide spectrum of damaged DNA, characterized by distortions of the DNA helix such as single-stranded loops, mismatched bubbles, and single-stranded overhangs.
The Rad23 family provides an essential connection between the 26S proteasome and ubiquitinated proteins. It can bind simultaneously to the 26S proteasome and to polyubiquitinated substrates to deliver ubiquitinated proteins to the proteasome. It may play a role in endoplasmatic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded glycoproteins by association with PNGase and by delivering deglycosylated proteins to the proteasome. The interactions of Rad23B, Atx3, and valosin-containing protein (VCP) are dynamic and modulated by proteotoxic stresses. Recent studies also show that Rad23B is a candidate cancer biomarker identified in a genome-wide loss-of-function screen, which influences sensitivity to HDAC inhibitors.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Full length recombinant human Rad23B protein.
- Formulation
- This antibody is provided in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- Protein G affinity purified.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- Upon receipt, store undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
KO/KD-WB - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.2 - 1.0 µg per ml. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Rad23B has two isoforms, and the predicted Mws are 43kD and 35kD respectively. For 43kD isoform, the observed Mw is 53kD.
- RRID
-
AB_2561795 (BioLegend Cat. No. 654201)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 409 amino acids, predicted molecular weight of 43 kD
- Distribution
-
Nucleus, cytoplasm (the intracellular distribution is cell cycle dependent)
- Function
- Modulation of proteasomal degradation; involved in global genome nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER) by acting as component of the XPC complex
- Interaction
- Component of the XPC complex composed of XPC, RAD23B and CETN2; interacts with NGLY1, PSMC1, ATXN3, PSMD4, PSMC5, and AMFR
- Cell Type
- B cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Ubiquitin/Protein Degradation
- Antigen References
-
1. Sugasawa K, et al. 1997. Mol. Cell Biol. 17:6924.
2. Thoma BS and Vasquez KM. 2003. Mol. Carcinog. 38:1.
3. Reina CP, et al. 2010. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19:235.
4. Farmer LM, et al. 2010. Plant Cell 22:124.
5. Khan O, et al. 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:6532.
6. Kamiya Y, et al. 2012. FEBS Lett. 586:1141. - Gene ID
- 5887 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Rad23B on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Rad23B Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Rad23B | 11A2SC | WB,KO/KD-WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us