- Clone
- W20092C (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2), bone morphogenetic protein 2A (BMP-2A), BDA2
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
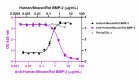
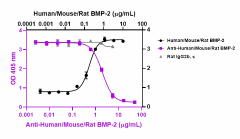
Recombinant human/mouse/rat BMP-2 (Cat. No. 767306) (black circles) induces the differentiation of ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cells. Ultra-LEAF™ purified anti-human/mouse/rat BMP-2 (clone W20092C) (purple squares) inhibits the effect of recombinant human/mouse/rat BMP-2 at 0.6 µg /mL and 2 µg/mL heparin in ATDC5 cells in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the GoInVivo™ purified rat IgG2b, κ isotype control (Cat. No. 400666) (gray triangles) does not have the effect. ND50 range: 1 - 5 μg/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 605853 | 100 µg | £247 | ||||
| 605854 | 1 mg | £613 | ||||
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) belongs to the TGF-β superfamily. Like other members of BMP family, BMP-2 is synthesized as an inactive propeptide precursor which dimerizes and then it is further processed into mature form by proprotein convertases (PCs). Some evidence indicates that PC5/6A and Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) are involved in maturation of BMP-2. Mature BMP-2 is a 26 kD protein composed of 114 amino acids, forming three intramolecular and one intermolecular disulfide bond. BMP-2 forms homodimer or heterodimer with other BMP proteins, including BMP-4, BMP-6, and BMP-7. BMP-2 signal through heterodimeric serine/threonine kinase receptors composed of a type I (BMPR1a/ALK3, BMPR1b/ALK6, ActRIa/ALK2) and a type II (BMPR2, ACVR2a/ActRIIA, ACVR2b/ActRIIB). BMP-2 binds to the type I receptor with high affinity, which in turn recruits the type II receptor. BMP-2 stimulation initiates receptor shutting, leading to receptor clustering and activation of the downstream signaling. BMP-2 signals via canonical Smad or other downstream kinase, such as p38 and JNK in a context-dependent manner. BMP-2 is involved in several processes, including cartilage and bone formation, differentiation, and embryogenesis. BMP-2 induces osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells and myogenic cells. BMP-2 induces cartilage repair and remodeling by stimulating chondrocyte proliferation and expression of matrix proteins. BMP-2/BMP-7 heterodimer is more potent in the induction of bone formation in vivo than BMP-2 homodimer. BMP-2-deficiency leads to embryonic lethality with abnormal cardiac development, malformation of the amnion/chorion, severe chondrodysplasia, and defects in myocardial patterning, suggesting that BMP-2 mediates organ morphogenesis. Noggin is an antagonist to reverse BMP-2-mediated effect and its expression is induced by BMP-2 in osteoblasts as a negative feedback loop. In addition, BMP-2 stimulates epithelial to mesenchymal cell transformation through TGF-β type III receptor.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat BMP-2
- Formulation
- 0.2 µm filtered in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing no preservative.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 EU/µg of the protein (< 0.001 ng/µg of the protein) as determined by the LAL test.
- Preparation
- The Ultra-LEAF™ (Low Endotoxin, Azide-Free) antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- The antibody is bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial, typically between 2 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. This Ultra-LEAF™ solution contains no preservative; handle under aseptic conditions.
- Application
-
Neut - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by neutralizing the differentiation induced by recombinant human/mouse/rat BMP-2 (Cat. No. 767306) at 0.6 µg/mL on ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cells. ND50 range: 1 - 5 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- RRID
-
AB_2936680 (BioLegend Cat. No. 605853)
AB_2936680 (BioLegend Cat. No. 605854)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulfide-linked homodimer
- Distribution
-
Abundant in lung, spleen and colon in human, low expression but detectable in heart, kidney, brain, liver, skeletal muscle, pancreases, placenta, prostate, ovary, and small intestine
- Function
- BMP-2 is involved in osteogenesis, cartilage repair, and organogenesis.
- Interaction
- Chondroblast, osteoblast, proprotein convertases, BMP family members
- Ligand/Receptor
- BMP receptor type IA (BMPR1a/ALK3), type IB (BMPR1b/ALK6), Activin receptor type IA (ACVR1a/ActRIa/ALK2) and BMP receptor type II (BMPR2), Activin receptors type IIA (ACVR2a/ActRIIA), type IIB (ACVR2b/ActRIIB)
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Bragdon B, et al. 2011. Cell Signal. 23:609-20.
- Israel DI, et al. 1992. Growth Factors. 7:139-50.
- Lee SN, et al. 2015. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 52:749-61.
- Roedel EK, et al. 2013. J Biol Chem. 288:7193-203.
- Nohe A, et al. 2002. J Biol Chem. 277:5330-8.
- Zhou AJ, et al. 2012. Growth Factors. 30:267-75.
- Miyazono K, et al. 2010. J Biochem. 147:35-51.
- Nohe A et al. 2004. J Cell Sci. 118:643-50.
- Hay E, et al. 2001. J Biol Chem. 276:29028-36.
- Wozney JM, et al. 1988. Science. 242:1528-34.
- Ryoo HM, et al. 2006. Gene. 366:51-7.
- Lavery K, et al. 2008. J Biol Chem. 283:20948-58.
- Israel DI, et al. 1996. Growth Factors. 13:291-300.
- Mundy G, et al. 1999. Science. 286:1946-9.
- De Luca F et al. 2001. Endocrinology. 142:430-6.
- Blaney Davidson EN, et al. 2007. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R102.
- Zhang H, Bradley A. 1996. Development. 122:2977-86.
- Pera MF, et al. 2004. J Cell Sci. 117:1269-80.
- Wang RN, et al. 2014. Genes Dis. 1:87-105.
- Kirkbride KC, et al. 2008. J Biol Chem. 283:7628-37.
- Gene ID
- 650 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about BMP-2 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Do you guarantee that your antibodies are totally pathogen free?
-
BioLegend does not test for pathogens in-house aside from the GoInVivo™ product line. However, upon request, this can be tested on a custom basis with an outside, independent laboratory.
- Does BioLegend test each Ultra-LEAF™ antibody by functional assay?
-
No, BioLegend does not test Ultra-LEAF™ antibodies by functional assays unless otherwise indicated. Due to the possible complexities and variations of uses of biofunctional antibodies in different assays and because of the large product portfolio, BioLegend does not currently perform functional assays as a routine QC for the antibodies. However, we do provide references in which the antibodies were used for functional assays and we do perform QC to verify the specificity and quality of the antibody based on our strict specification criteria.
- Does BioLegend test each Ultra-LEAF™ antibody for potential pathogens?
-
No, BioLegend does not test for pathogens in-house unless otherwise indicated. However, we can recommend an outside vendor to perform this testing as needed.
- Have you tested this Ultra-LEAF™ antibody for in vivo or in vitro applications?
-
We don't test our antibodies for in vivo or in vitro applications unless otherwise indicated. Depending on the product, the TDS may describe literature supporting usage of a particular product for bioassay. It may be best to further consult the literature to find clone specific information.
Other Formats
View All BMP-2 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human/mouse/rat BMP-2 | W20092C | Neut |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human/mouse/rat BMP-2
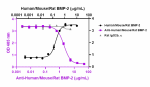
Recombinant human/mouse/rat BMP-2 (Cat. No. 767306) (black c...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us