- Clone
- MP6-XT22 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Tumor necrosis factor-α, Cachectin, Necrosin, Macrophage cytotoxic factor (MCF), Differentiation inducing factor (DIF), TNFSF-2, TNF-a, TNF-alpha
- Isotype
- Rat IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
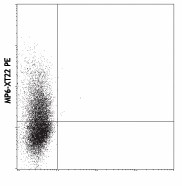
-

PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated BALB/c T cells were stained with MP6-XT22 PE -
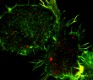
Immortalized murine bone marrow-derived macrophages stimulated overnight with LPS were stained with Atto-488 phalloidin (green) and purified TNF-α (clone MP6-XT22), secondarily stained with Goat anti-Rat IgG Dylight 594 (red). Data provided by James Harris, Trinity College.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 506301 | 50 µg | 67€ | ||||
| 506302 | 500 µg | 188€ | ||||
TNF-α is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, and NK-cells. Many transformed cell lines also secrete TNF-α. Monomeric mouse TNF-α is a 156 amino acid protein (N-glycosylated) with a reported molecular weight of 17.5 kD. TNF-α forms multimeric complexes; stable trimers are most common in solution. A 26 kD membrane form of TNF-α has also been described. TNF-α binding to surface receptors elicits a wide array of biologic activities including: cytolysis and cytostasis of many tumor cell lines in vitro, hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors in vivo, increased fibroblast proliferation, and enhanced chemotaxis and phagocytosis in neutrophils.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- E. coli-expressed, recombinant mouse TNF-α
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
ELISA, ICFC - Quality tested
CyTOF®, ICC - Verified
IHC-F, WB - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
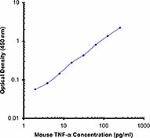
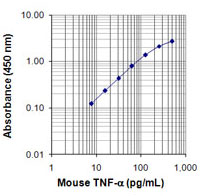
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by ELISA assay. For ELISA capture applications, a concentration range of 2.0 - 6.0 µg/mL is recommended. To obtain a linear standard curve, serial dilutions of mouse TNF-α recombinant protein ranging from 500 to 4 pg/mL are recommended for each ELISA plate. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
ELISA or ELISPOT Detection: The biotinylated MP6-XT22 antibody is useful as a detection antibody for a sandwich ELISA or ELISPOT assay, when used in conjunction with purified 6B8 antibody (Cat. Nos. 510802 & 510804) as the capture antibody.
ELISA Capture: The purified MP6-XT22 antibody is useful as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA when used in conjunction with the biotinylated Poly5160 antibody (Cat. No. 516003) as the detection antibody and recombinant mouse TNF-α (Cat. No. 575209) as the standard.
Flow Cytometry6,11,12:The fluorochrome-labeled MP6-XT22 antibody is useful for intracellular immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometric analysis to identify TNF-a-producing cells within mixed cell populations.
Neutralization1,5,10,16,17:The MP6-XT22 antibody can neutralize the bioactivity of natural or recombinant TNF-α. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for neutralization of mouse TNF-α bioactivity in vivo and in vitro(Cat. No. 506310). For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 506332) with a lower endotoxin limit than standard LEAF™ purified antibodies (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg).
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: Western blotting, immunohistochemical staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed, saponin-treated frozen tissue sections7-9 in vivo detection5, immunofluorescence, and immunocytochemistry.
Note: For testing mouse TNF-α in serum, plasma or supernatant, BioLegend's ELISA Max™ Sets (Cat. No. 430901) are specially developed and recommended. - Application References
-
- Abrams J, et al. 1992. Immunol. Rev. 127:5. (Neut)
- Abrams J, et al. 1995. Curr. Prot. Immunol. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Unit 6.20
- Mo X, et al. 1995. J. Virol. 69:1288.
- Sarawar S, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 153:1246.
- Via C, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 167:6821. (Neut)
- Infante-Duarte C, et al. 2000 J. Immunol. 165:6107. (FC)
- Jacobs M, et al. 2000. Immunology 100:494. (IHC)
- Marinova-Mutachieva L, et al. 1997. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 107:507. (IHC)
- Williams RO, et al. 2000. J. Immunol. 165:7240. (IHC)
- Scanga CA, et al. 1999. Infect. Immun. 67:4531. (Neut)
- Akilov OE, et al. 2007. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007;10.1189/jlb.0706439. (FC)
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366. (FC)
- Patole PS, et al. 2005. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16:3273. PubMed
- Wu S, et al. 2005. Neurosci Lett. 394:158. PubMed
- Carlson MJ, et al. 2009. Blood 113:1365. PubMed
- Shivakumar P, et al. 2017. JCI Insight. 2:e88747 1. PubMed
- Kearney CJ, et al. 2017. Cell Death Differ. 10.1038/cdd.2017.94. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_315423 (BioLegend Cat. No. 506301)
AB_315423 (BioLegend Cat. No. 506302)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- TNF superfamily; dimer/trimer; 17.5-150 kD (Mammalian)
- Bioactivity
- Paracrine/endocrine mediator of inflammatory and immune functions; selectively cytotoxic for transformed cells; endothelial cell alterations; chemoattractant
- Cell Sources
- Activated monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, T cells, B cells, NK cells, LAK cells
- Cell Targets
- Monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, T cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, osteoclasts, adipocytes, astroglia, microglia
- Receptors
- TNFRSF1A (TNF-R1, CD120a, TNFR-p60 Type β, p55); TNFRSF1B (TNF-R2, CD120b, TNFR-p80 Type A, p75)
- Cell Type
- Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Fitzgerald K, et al. Eds. 2001. The Cytokine FactsBook. Academic Press, San Diego.
2. Beutler B, et al. 1988. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 57:505.
3. Beutler B, et al. 1989. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 7:625.
4. Tracey K, et al. 1993. Crit. Care Med. 21:S415. - Regulation
- Processed by TACE for secretion; upregulated by interferons, IL-2, GM-CSF, substance P, bradykinin, PAF, immune complexes, and cyclooxygenase; downregulated by IL-6, TGF-β, vitamin D3, prostaglandin E2, and PAF antagonists
- Gene ID
- 21926 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about TNF-alpha on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All TNF-α Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
FITC anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 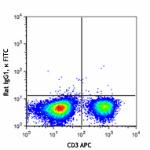
-
PE anti-mouse TNF-α
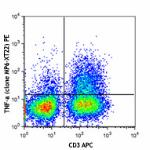
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
Purified anti-mouse TNF-α
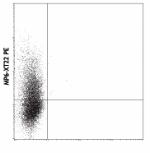
PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated BALB/c T cells were stained with MP... 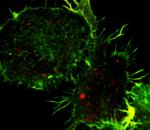
Immortalized murine bone marrow-derived macrophages stimulat... -
Biotin anti-mouse TNF-α
-
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse TNF-α
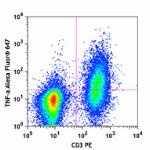
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse TNF-α
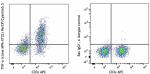
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse TNF-α
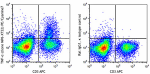
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse TNF-α
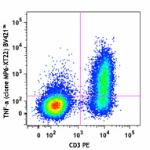
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 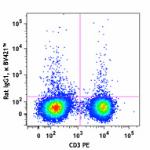
-
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA+Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA/Ionomycin-stimulated BALB/c T cells were stained with MP... 
Immortalized murine bone marrow-derived macrophages stimulat... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA+ Ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyte... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... 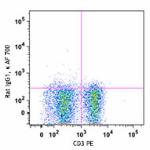
-
Purified anti-mouse TNF-α (Maxpar® Ready)
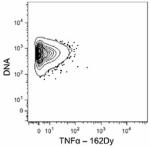
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were incubated for 6 hours in medi... 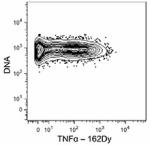
-
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse TNF-α
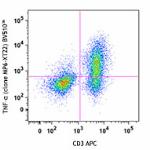
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... 
-
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse TNF-α
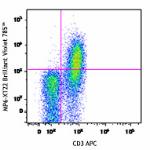
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (six-ho... 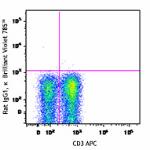
-
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse TNF-α
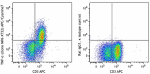
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (six-ho... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse TNF-α
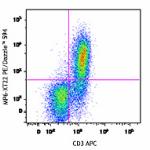
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6-hour... 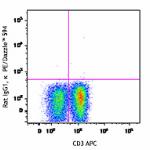
-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse TNF-α

PMA+ Ionomycin-stimulated (six hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocy... 
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse TNF-α
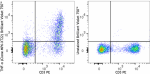
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (in the... -
GoInVivo™ Purified anti-mouse TNF-α
-
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse TNF-α
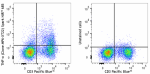
Cell Activation Cocktail (with Brefeldin A) stimulated C57BL...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us