- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Liver-type arginase, Type I arginase, Arg-I
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 552502 | 10 µg | 179€ | ||||
| 552504 | 25 µg | 352€ | ||||
| 552506 | 100 µg | 934€ | ||||
| 552508 | 500 µg | 2808€ | ||||
Arginase is a divalent cation-dependent enzyme that converts L-arginine into nonprotein amino acid L-ornithine and urea; it is the final enzyme of the urea cycle. Arginase is a trimeric metalloenzyme and Mn2+ is the physiologic activator. Mammals have two arginase isozymes, arginase I and arginase II, which are encoded by different genes. Arginase I, also called liver arginase, is highly expressed in the cytosol of hepatocytes and is involved in ammonia detoxification in the liver. Arginase II is localized in the mitochondria in extrahepatic tissues, such as kidney, brain, prostate, small intestine, lactating mammary gland, and skeletal muscle, and provides L-ornithine for proline and polyamine biosynthesis. Since L-arginine is also the substrate for nitric oxide (NO) synthase (NOS), it has been shown that both arginase isozymes can reciprocally regulate NOS activity by modulating L-arginine availability. Therefore, arginase I and II modulate many biological functions through regulating NO production. The role of arginase I in the immune response, including anti-parasite and anti-viral responses, has been studied. The induction of mouse (but not human) arginase I in macrophages by exogenous stimuli, including Th2 cytokines IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13, is well known. A study has shown that alternative activated monocytes/macrophages from humans affected by filariasis can express arginase I. Arginase I is constitutively expressed in human granulocytes and is localized to the azurophil granules, and is involved in antimicrobial activity. The role of arginase I in tumor biology has also been studied; in this sense, arginase I may promote growth of some types of tumors via polyamine synthesis or downregulation of NO-mediated tumor cytotoxicity. In contrast, arginase I can also promote death of some types of tumors by L-arginine depletion. The involvement of arginase I in axonal regeneration in the central nervous system after injury has also been reported.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Source
- Human arginase I, amino acids Met1-Lys322 (Accession# P05089) with an N-terminal Met and 6-His tag, was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 329 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 36 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 40 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met.
- Purity
- >92%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 20 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 10% glycerol.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored at -70°C for six months. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
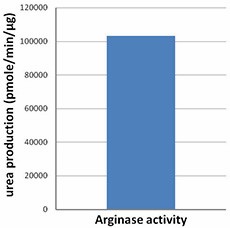
- Activity
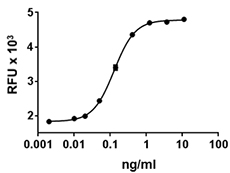
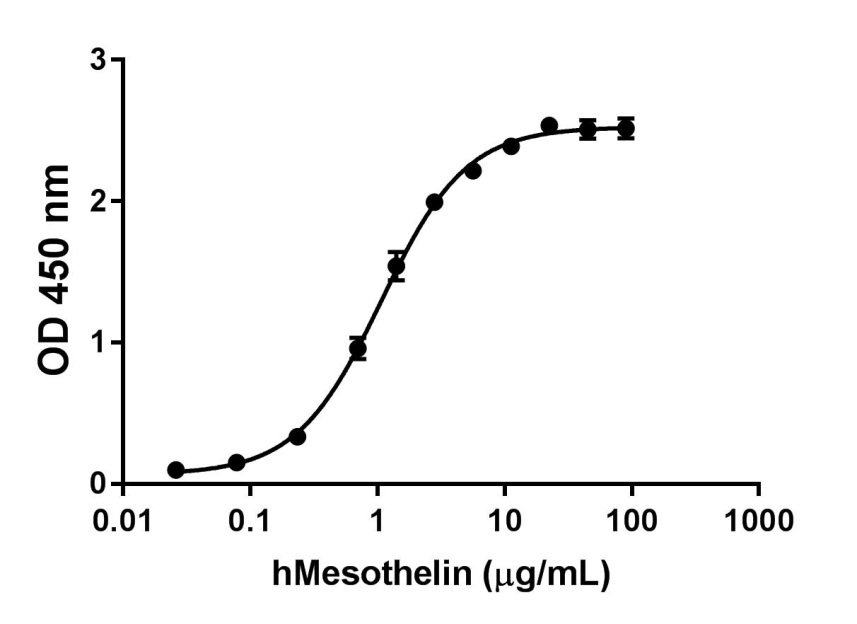
- The activity of arginase I is determined by the production of urea from the hydrolysis of L-arginine. The specific activity is >100,000 pmol/min/µg.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homotrimer
- Distribution
-
Hepatocytes, monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, alveolar endotheleial cells, airway and capillary epithelial cells.
- Function
- Arginase I converts L-arginine to L-ornithine and urea. The activities of arginase and other urea cycle enzymes are regulated by dietary protein; RON receptor tyrosin kinase induces arginase I expression in macrophages and oxidative species increase arginase activity in endothelial cells. LPS induces arginase I and II in macrophages.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Enzymes and Regulators
- Antigen References
-
1. Durante W, et al. 2007. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 34:906.
2. Yang Z and Ming XF. 2013. Front Immunol. 4:149.
3. Munder M. 2009. Br. J. Pharmacol. 158:638.
4. Babu S, et al. 2009. J. Infect. Dis. 199:1827.
5. Ochoa JB, et al. 2001. Ann. Surg. 233:393.
6. Steppan J, et al. 2013. Front. Immunol. 4:278.
7. Sharda DR, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 187:2181.
8. Chandra S, et al. 2012. Br. J. Pharmacol. 165:506. - Gene ID
- 383 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Arginase I on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- Why choose BioLegend recombinant proteins?
-
• Each lot of product is quality-tested for bioactivity as indicated on the data sheet.
• Greater than 95% Purity or higher, tested on every lot of product.
• 100% Satisfaction Guarantee for quality performance, stability, and consistency.
• Ready-to-use liquid format saves time and reduces challenges associated with reconstitution.
• Bulk and customization available. Contact us.
• Learn more about our Recombinant Proteins. - How does the activity of your recombinant proteins compare to competitors?
-
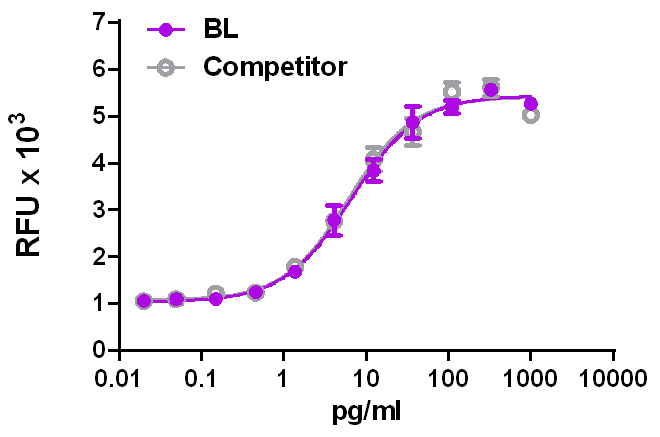
We quality control each and every lot of recombinant protein. Not only do we check its bioactivity, but we also compare it against other commercially available recombinant proteins. We make sure each recombinant protein’s activity is at least as good as or better than the competition’s. In order to provide you with the best possible product, we ensure that our testing process is rigorous and thorough. If you’re curious and eager to make the switch to BioLegend recombinants, contact your sales representative today!
- What is the specific activity or ED50 of my recombinant protein?
-
The specific activity range of the protein is indicated on the product datasheets. Because the exact activity values on a per unit basis can largely fluctuate depending on a number of factors, including the nature of the assay, cell density, age of cells/passage number, culture media used, and end user technique, the specific activity is best defined as a range and we guarantee the specific activity of all our lots will be within the range indicated on the datasheet. Please note this only applies to recombinants labeled for use in bioassays. ELISA standard recombinant proteins are not recommended for bioassay usage as they are not tested for these applications.
- Have your recombinants been tested for stability?
-
Our testing shows that the recombinant proteins are able to withstand room temperature for a week without losing activity. In addition the recombinant proteins were also found to withstand four cycles of freeze and thaw without losing activity.
- Does specific activity of a recombinant protein vary between lots?
-
Specific activity will vary for each lot and for the type of experiment that is done to validate it, but all passed lots will have activity within the established ED50 range for the product and we guarantee that our products will have lot-to-lot consistency. Please conduct an experiment-specific validation to find the optimal ED50 for your system.
- How do you convert activity as an ED50 in ng/ml to a specific activity in Units/mg?
-
Use formula Specific activity (Units/mg) = 10^6/ ED50 (ng/mL)

 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us