- Clone
- SMI 312 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- SMI-312, SMI312
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1/Mouse IgM
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

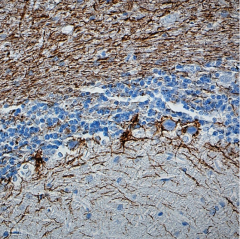
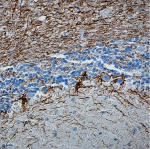
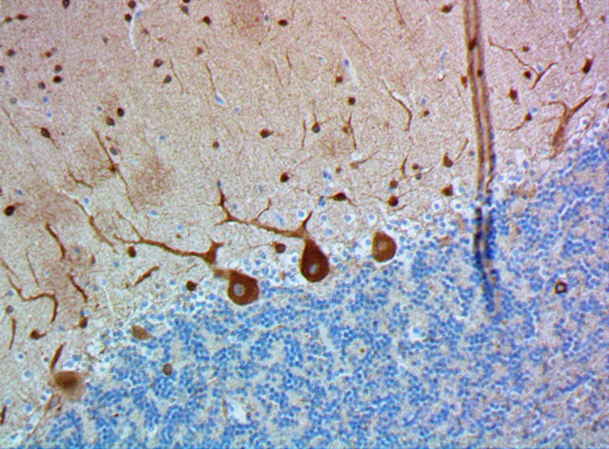
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail) antibody (clone SMI 312) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieval-ALL Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927601), the tissue was incubated with 1 µg/ml of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend’s Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. -
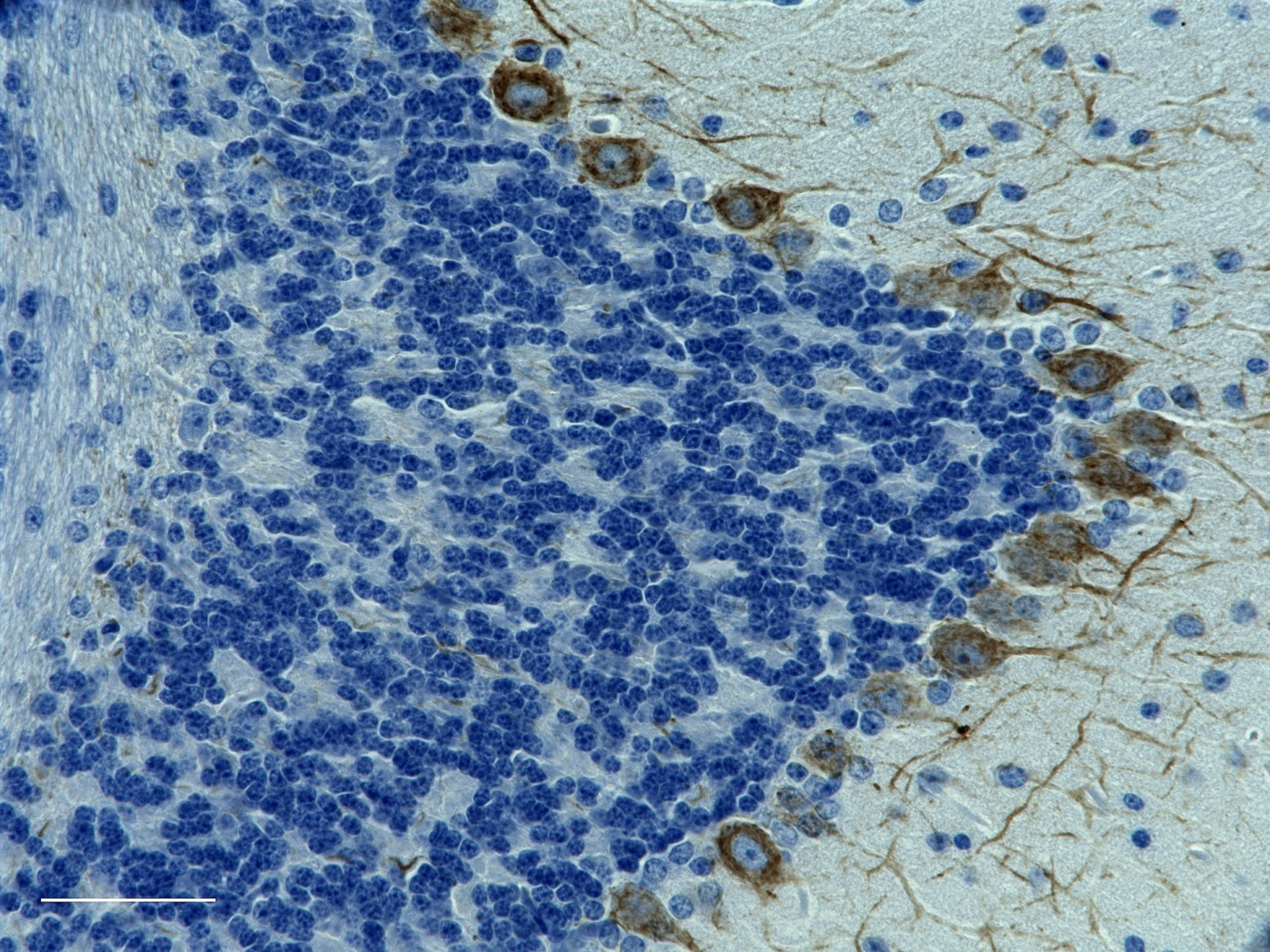
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail) antibody (clone SMI 312) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieval-ALL Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927601), the tissue was incubated with 5 µg/ml of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend’s Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. -
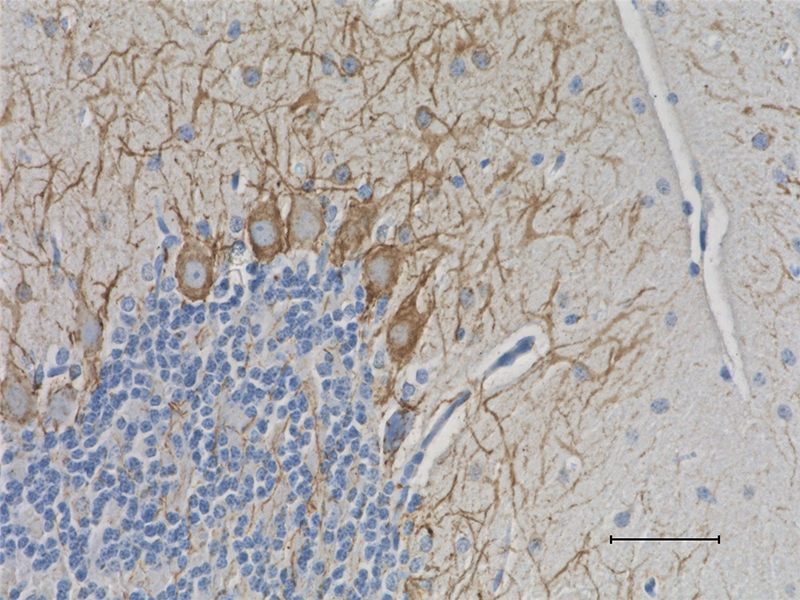
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail) antibody (clone SMI 312) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieval-ALL Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927601), the tissue was incubated with 1 µg/ml of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend’s Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. -
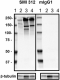
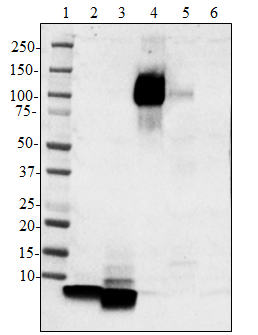
Western blot of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail) antibody (clone SMI 312). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 20 µg of human brain lysate; Lane 3: 20 µg of Mouse brain lysate; Lane 4: 20 µg of rat brain lysate. The blots were incubated with 5 ug/mL of clone SMI 312 or mouse IgG1 overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-Tubulin Beta 3 (TUBB3) antibody (clone AA10, Cat. No. 657409) was used as a loading control. Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 837904 | 100 µg | 221€ | ||||
Neurofilaments (NF) are approximately 10 nanometer intermediate filaments found in neurons. They are a major component of the neuronal cytoskeleton and their function is primarily to provide structural support for the axon and to regulate axon diameter. There are three major NF subunits, and the names given to these subunits are based upon the apparent molecular mass of the mammalian subunits on SDS-PAGE. The light or lowest (NF-L) runs at 68-70 kD, the medium or middle (NF-M) runs at about 145-160 kD, and the heavy or highest (NF-H) runs at 200-220 kD. However, the actual molecular weight of these proteins is considerably lower due to the highly charged C-terminal regions of the molecules. The level of NF gene expression correlates with the axonal diameter, which controls how fast electrical signals travel down the axon. Mutant mice with NF abnormalities have phenotypes resembling amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NF immunostaining is common in diagnostic neuropathology. It is useful for differentiating neurons (positive for NF) from glia (negative for NF).
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Homogenized hypothalami recovered from Fischer 344 rats.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
IHC-P - Quality tested
WB - Verified
EM, ICC, IHC-F - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 1.0 - 5.0 µg/mL is suggested. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1.0 - 5.0 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunocytochemistry1, 6, 12, 16, 19, immunofluorescent staining3, 8, 9, 18.
SMI 312 is a mixture of monoclonal antibodies that react against complex networks of axons. It is directed against extensively phosphorylated axonal epitopes on neurofilaments M and H. SMI 312 has been selected to provide a specific marker for axons in tissue sections and cultures. In contrast to individual anti-phosphoneurofilament antibodies that identify different subsets of neurofilament phosphoepitopes, which are suitable for defining functional and regional differences in normal and pathologic axons, SMI 312 is a convenient marker for axons in general. SMI 312 visualizes axons in an area-specific maturation pattern in human fetal brain. The antibody cocktail defines nuclear borderlines and is useful in establishing early connectivity with SMI 311, anti-neurofilament (not phosphorylated) identified dendrites. SMI 312 visualizes aberrantly sprouting axons in neuritic plaques derived from cortico-cortical fibers in Alzheimer's disease and identifies loss of synaptic circuitry proposed to be the basis of memory. - Application References
-
- Sternberger LA, et al. 1982. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 79:1326. (IHC, ICC)
- Choi Y, et al. 2008. Genes & Dev. 22:2485. (IHC) PubMed
- BussiFre T, et al. 2004. Am. J. Pathol. 165:987. (IHC-F)
- Chung RS, et al. 2003. J. Neurosci. 23:3336. (IHC)
- De Repentigny Y, et al. 2011. PLoS One. 6:e21093. (IHC)
- Wilkins A, et al. 2003. J. Neurosci. 23:4967. (ICC)
- Rudinskiy N, et al. 2012. Nat. Neurosci. 15:1422. (IHC)
- Wang JY, et al. 2014. Dev. Cell. 28:670. (EM)
- Canetta SE, et al. 2011. PLoS One. 6:e25108. (ICC) PubMed
- Nicaise C, et al. 2012. J. Neurotrauma. 29:2748. (IHC)
- Ma M, et al. 2013. Neurobiol. Dis. 56:34. (IHC)
- Zurashvili T, et al. 2013. Mol. Cell Biol. 33:1027. (ICC)
- Powers BE, et al. 2013. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110:4075. (IHC)
- Riddle A, et al. 2012. Stroke. 43:178. (IHC)
- Sahni V, et al. 2010. Neurosci. 30:1839. (IHC)
- Liu HY, et al. 2013. J. Neurosci. 33:11479. (ICC)
- Nicaise C, et al. 2013. J. Neurotrauma. 30:1092. (IHC)
- Klusch A, et al. 2013. J. Invest. Dermatol. 133:1387. (ICC) PubMed
- Huang TN, et al. 2014. Nat. Neurosci. 17:240. (ICC)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2566782 (BioLegend Cat. No. 837904)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Three major neurofilament subunits. Its names given to these subunits are based upon the apparent molecular mass of the mammalian subunits on SDS-PAGE: The medium or middle (NF-M) runs at about 145-160 kD and the heavy or highest (NF-H) runs at 200-220 kD.
- Distribution
-
Tissue distribution: CNS, peripheral nerves, and glandular cells of the prostate.
Cellular distribution: Cytoskeleton, nucleus, cytosol, and mitochondrion. - Function
- Neurofilaments are the major components of the neuronal cytoskeleton. They provide axonal support and regulate axon diameter.
- Cell Type
- Mature Neurons
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Motility/Cytoskeleton/Structure, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Intermediate Filaments
- Antigen References
-
1. Petzold A. 2005. J. Neurol. Sci. 233:183. PubMed
- Gene ID
- 4747 View all products for this Gene ID 4744 View all products for this Gene ID 4741 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Neurofilament Marker on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All Neurofilament Marker Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail) | SMI 312 | IHC-P,WB,EM,ICC,IHC-F |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axonal, cocktail)
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axon... 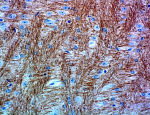
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axon... 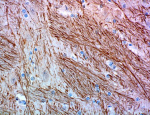
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axon... 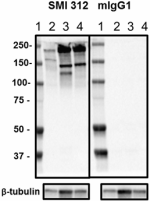
Western blot of purified anti-Neurofilament Marker (pan axon...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us