Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) can be used as a tool to study protein:DNA complexes and identify protein-binding sites in the DNA. We offer a wide-array of purified antibodies ideal for clean and consistent experimental results.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Purified antibodies listed as being validated for use in ChIP experiments are compared to a competitor ChIP-validated antibody to ensure equal or better performance. Additionally, many of our clones are validated for use in other applications including Western Blot, Immunofluorescence, and Immunohistochemistry. All our products are supported by our 100% satisfaction guarantee and our highly capable technical team can assist if you have any questions.
Our purified antibodies are provided at concentrations between 0.5 mg/mL - 1.0 mg/mL, and our ascites antibodies are estimated to be between 1-3 mg/ml.
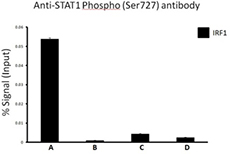
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed using commercial Protein-G coated 96 well high-throughput ChIP assay kit by loading 3µg of cross-linked chromatin samples from HeLa cells treated with Nocodazole with either A) 1:50 dilution of Go-ChIP-Grade™ Purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) Antibody (Clone A15158B), or B) equal amount of Purified Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control Antibody, or C) competitor’s ChIP-grade Purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) Antibody and D) equal amount of matched Isotype Control Antibody as recommended by the manufacturer. The enriched DNA was purified and quantified by real-time qPCR using primers targeting human IRF1 gene region. The amount of immunoprecipitated DNA in each sample is represented as signal relative to the 5% of total amount of input chromatin.
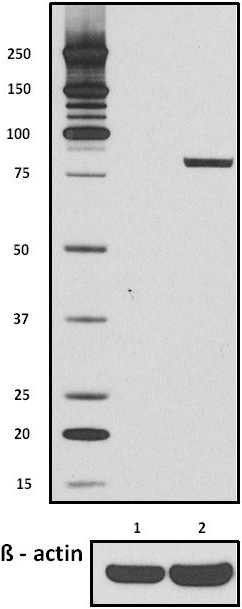
Total lysates (15µg protein) from untreated HeLa cells (lane 1) and HeLa cells treated with nocodazole (lane 2) were resolved by electrophoresis (4-12% Bis-Tris gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1:500 diluted (1µg/mL) Purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) Antibody, clone A15158B (upper) or 1:3000 diluted Purified anti-β-actin Antibody, clone Poly6221 (lower). Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using a 1:3000 diluted goat anti-mouse-IgG secondary antibody conjugated to HRP for the anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) Antibody, and a donkey anti-rabbit IgG Antibody conjugated to HRP for anti-β-actin Antibody.
|
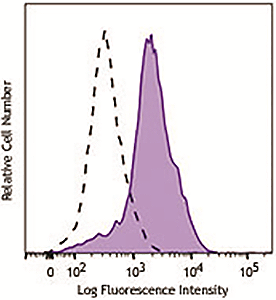
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with (filled histogram) or without (open histogram) Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefeldin A) for 15 minutes, fixed with Fixation Buffer, permeabilized with True-Phos™ Perm Buffer, then intracellularly stained with purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) antibody (clone A15158B), followed by anti- mouse IgG PE. |
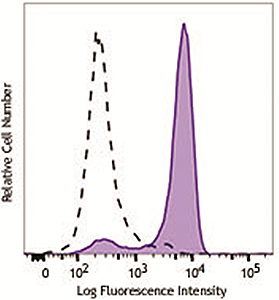
HeLa cells were stimulated with (filled histogram) or without (open histogram) nocodozole for 24 hours, fixed with Fixation Buffer, permeabilized with True-Phos™ Perm Buffer, then intracellularly stained with purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) antibody (clone A15158B), followed by anti- mouse IgG PE. |
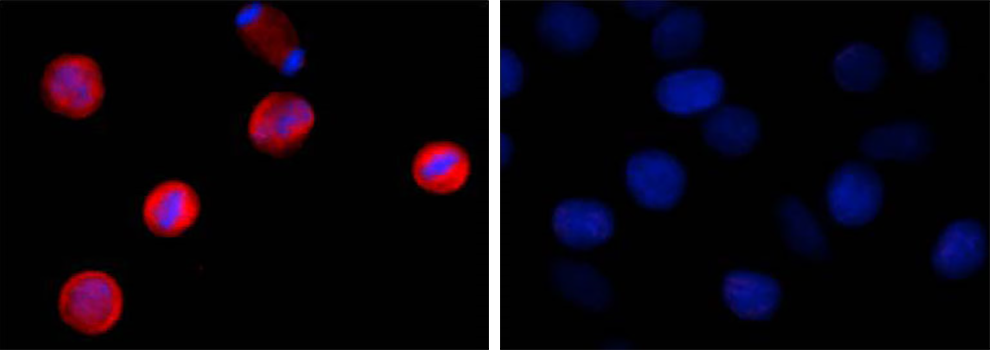
Two aliquots of HeLa cells in suspension, treated with (left) 200 ng/mL nocodazole for 24 hours or left un-treated (right) were adhered on poly-lysine pre-coated slides. Then they were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for three minutes, and blocked with 5% FBS for 60 minutes. The cells were intracellularly stained with 2 µg/ml of purified anti-STAT1 Phospho (Ser727) antibody (clone A15158B) overnight at 4°C followed by Alexa Fluor®594 (red) conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG for one hour at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The image was captured with a 60X objective. |
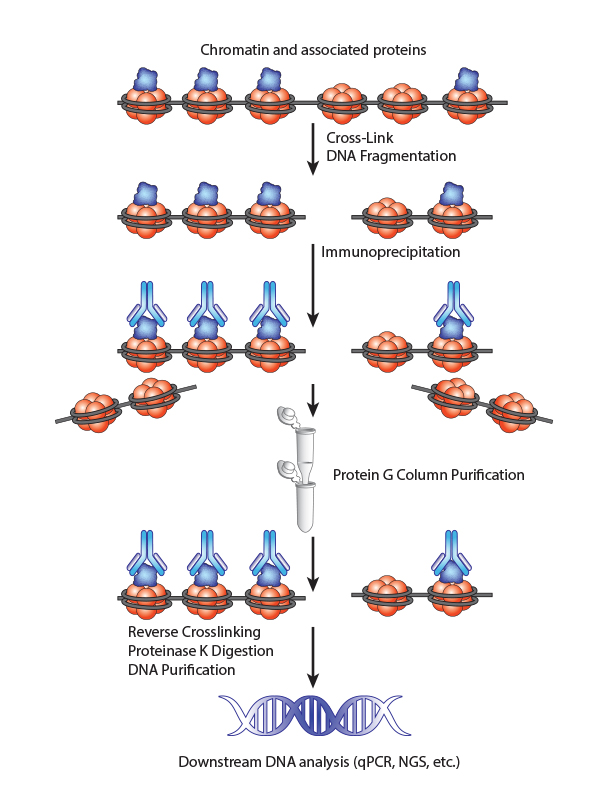
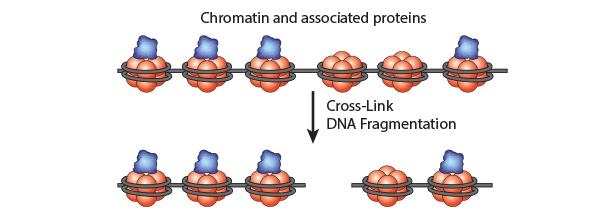
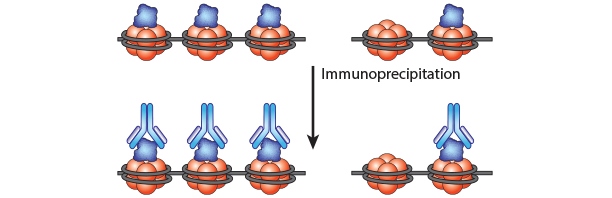
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation is a powerful tool to study protein:DNA complexes and can be used to map transcription factor binding sites or to study epigenetic modifications. In this assay, chromatin bound proteins are crosslinked and the DNA is fragmented. Next, the sheared DNA:protein complexes are incubated with an antibody against the protein-of-interest and immunoprecipitated to enrich for bound DNA. Finally, the crosslinks are reversed and the DNA is eluted for analysis. Purified DNA can analyzed using qPCR, Next-Generation Sequencing, ChIP-on-chip analysis, etc.
Click on the steps below to learn more about how to optimize your ChIP assays.
Chromatin Preparation
Step 1: Crosslinking
(Stabilization of Protein-DNA complexes) with 1% formaldehyde, and glycine solution for quenching
Step 2: Cell Lysis
with Hypotonic Buffer
Step 3: DNA Fragmentation by Enzymatic Digestion
with Digestion buffer, lysis buffer, PIC, shearing cocktail, enzymatic stop solution, DNA sample quality and quantity checking
Immunopreciptation
Step 4: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
with purified antibody, isotype control antibody
Step 5: Column Conditioning, Washing and Elution
with wash buffers and elution buffer
Step 6: Reverse Crosslinking
with 1M NaHCO3, 5M NaCl
Downstream DNA Analysis
Step 7: Digestion with Proteinase K and DNA Purification
with Proteinase K, Proteinase K stop solution, DNA purification cols and buffers
Step 8: qPCR to quantify DNA
with primers to the target gene of interest
Step 9: Data Acquisition and Analysis
(The amount of IP'ed DNA in each sample is represented as signal relative to the 5% of total amount of input chromatin)
Tips for a successful ChIP assay:
- Always keep your chromatin on ice unless otherwise indicated as it can degrade very quickly and avoid freeze/thaw cycles
- Make fresh fixation solution and optimize fixation times to ensure that your cells have not been over-fixed
- Optimize lysis conditions. The number of cells used will dictate the amount of lysis buffer necessary. For hard to lyse cells, you may want to use a homogenizer to efficiently lyse the cells
- Choose an appropriate shearing method and ensure that the chromatin has been sheared to a size of 150-900 bp. Shearing conditions will need to be optimized for your cell type and amount of chromatin input.
- Use a ChIP validated antibody with a positive and negative control antibody to ensure that your methodology and experimental conditions were sufficient
- Use an excess antibody to chromatin ratio, the amount of antibody should be determined empirically
FAQs
How do I know if my chromatin has been sheared?
Purify the DNA from your sheared chromatin samples and run the DNA on a 1-2% agarose gel. DNA should be sheared to a range of 100-900 bp. Below is an example of chromatin from a number of different cells lines that has been sheared optimally using enzymatic digestion compared to chromatin which was over-digested.
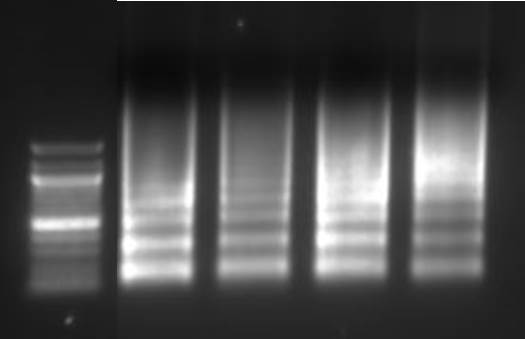
Lane 1: Ladder, Lane 2: HeLa, Lane 3: Jurkat, Lane 4: NCCIT, Lane 5: HeLa IL-6
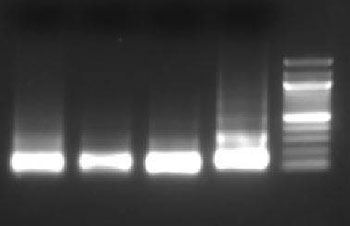
Lane 1: HT1080+ IFNγ, Lane 2: NIH353, Lane 3: HT29, Lane 4: HCT116, Lane 5: Ladder
Which points in the protocol can I stop and save my experiment?
Sheared chromatin may be saved at -80°C prior to performing the immunoprecipitation. If you are saving the chromatin, we would recommend aliquoting the chromatin as it can be sensitive to freeze thaw cycles. Alternatively, purified DNA can be saved prior to downstream analysis.
Should I use sonciation or enzymatic shearing?
Sonication may be ideal for difficult to lyse cell types and provides random fragmentation but may damage epitopes. It is not suitable for Native ChIP experiments (in which the chromatin has not been cross-linked). Enzymatic digestion is milder and can be used in Native ChIP experiments but will exhibit sequence bias and may not be suitable for hard to lyse cells.
What cell types have been validated with this ChIP protocol?
Human and mouse cell lines such as HeLa, Jurkat, Daudi, THP-1, NIH3T3, and 293T have been validated using this protocol. Other cell types (plant, yeast, tissue, FFPE samples, etc.) may require optimization.
How do I determine optimal number of cells for ChIP assay?
An important consideration when performing ChIP is the amount of chromatin that will need to be loaded to the column in order to elute sufficient IP’ed DNA for downstream analysis. Sufficient cell numbers should be used so that at least 3µg of chromatin can be used per IP. Start with 1-15 million cells. However, the cell number can be scaled up and the reagents need to be adjusted accordingly.
How much antibody for target protein should be used per ChIP?
This should be determined empirically by the end-user. Refer to the datasheet for ChIP-validated antibodies. The suggested dilution of the Purified anti-RNA Polymerase II Antibody; Clone 8WG16 (positive control) is 1:300 – 1:500 by volume. Or, contact technical support for more guidance.
What is causing high background?
The quality of the ChIP antibody has a major impact on the success of the assay. Use only ChIP-validated antibodies. Make sure to have good quality chromatin samples with fragments between 150-900bp. Insufficient DNA shearing leads to longer DNA fragment length that can cause high background in downstream experiments. Insufficient wash steps can also leave traces of non-specific chromatin alongside enriched DNA. If background remains high, include an additional wash step during the IP protocol.
Why do I not have any enrichment?
Make sure to only use ChIP-validated antibodies and follow the instructions for the amount of antibody to be used or titrate the antibody for your experiment. It is also recommended to include ChIP validated positive and negative controls (included in the kit) to validate the efficiency of your ChIP assay. Good quality chromatin samples and chromatin fragment sizes between 150 – 900 bp are also critical. Other factors can include whether cells were effectively lysed, over-fixation and reduced antibody binding due to decreased epitope availability, and insufficient starting material (chromatin sample per IP).
 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us