MojoSort™ anti-Biotin Nanobeads Column Protocol – Positive or Negative Selection
Introduction
BioLegend MojoSort™ Nanobeads work in commonly used separation columns, based on our internal research as well as validation by external testing by academic labs. This simple protocol consists of following the MojoSort™ protocol to label the cells with pre-diluted MojoSort™ reagents and using the columns as indicated by the manufacturer.
Note: Due to the properties of our beads, it may be possible to use far fewer beads and less antibody cocktail that with other commercial suppliers. We recommend a titration to find the best dilution factor. However, as a general rule, dilutions ranging from 1:2 to 1:10 for the antibody cocktail can be used. Dilutions ranging from 1:5 to 1:20 for the anti-Biotin Nanobeads can be used. Please contact BioLegend Technical Service (tech@biolegend.com) if further assistance is needed.
Important Note
MojoSort™ magnetic particles can be used with other commercially available magnetic separators, both free standing magnets and column-based systems. Because MojoSort™ protocols are optimized for the MojoSort™ separator, the protocols may need to be adjusted for other systems. Please contact BioLegend Technical Service (tech@biolegend.com) for more information and guidance. We do not recommend using MojoSort™ particles for BD’s IMag™ or Life Technologies’ DynaMag™.
Positive vs. Negative Selection on columns: If your target cells are the labeled cells (the positive fraction), the desired cells are eluted from the column in step 5 of the “Example of magnetic separation with medium capacity columns” protocol below. If your target cells are the unlabeled cells (negative fraction), your desired cells are collected in step 3 and 4 of the “Example of magnetic separation with medium capacity columns” protocol below.
Protocol Steps
- Prepare cells from your tissue of interest or blood without lysing erythrocytes.
- In the final wash of your sample preparation, resuspend the cells in MojoSort™ Buffer by adding up to 4 mL in a 5 mL (12 x 75 mm) polypropylene tube.
Note: Keep MojoSort™ Buffer on ice throughout the procedure. - Filter the cells with a 70 µm cell strainer, centrifuge at 300xg for 5 minutes, and resuspend in an appropriate volume of MojoSort™ Buffer. Count and adjust the cell concentration to 1 x 108 cells/mL in MojoSort™ Buffer.
- Aliquot 100 µL of cell suspension (107 cells) into a new tube. Check the recommended usage for flow cytometric staining of the Biotin-conjugated antibody indicated in the antibody technical datasheet. Calculate the volume to stain 107 cells (or desired amount of cells). Add the appropriate volume of pre-diluted Biotin-conjugated antibody to the cell suspension, mix well and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.
Note: For the Biotin-conjugated antibodies, we recommend to do a titration to determine the optimal concentration. - Wash the cells by adding MojoSort™ Buffer up to 4 mL. Centrifuge the cells at 300xg for 5 minutes.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend cells in 100 µL of MojoSort™ Buffer.
- Resuspend the beads by vortexing, maximum speed, 5 touches. Add the appropriate volume of pre-diluted anti-Biotin Nanobeads. Mix well and incubate on ice for 15 minutes. Scale up the volume accordingly if separating more cells. For example, if the volume of pre-diluted Nanobeads for 1x107 cells is 10 µL, add 100 µL for 1 x 108 cells. When working with less than 107 cells, use indicated volumes for 107 cells.
Note: The amount of Nanobeads to use always depends on the frequency of the target, among a few other factors. We recommend to do a titration to determine the optimal concentration. - Wash the cells by adding MojoSort™ Buffer up to 4 mL. Centrifuge the cells at 300xg for 5 minutes.
- Discard the supernatant.
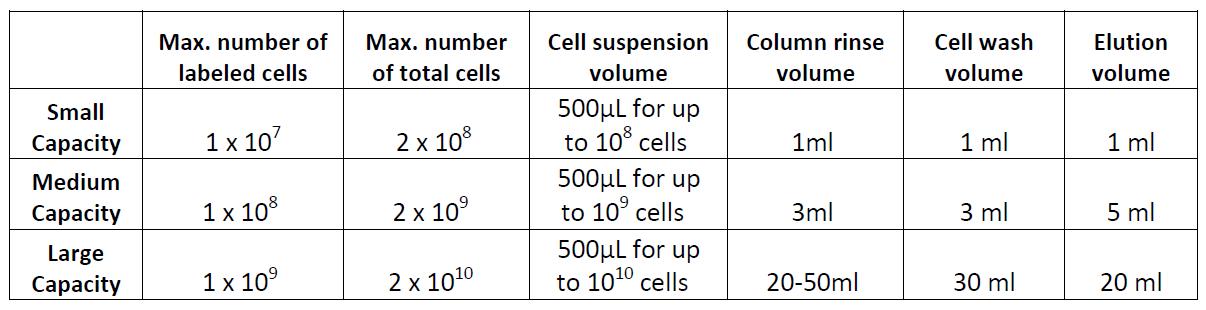
- Resuspend the cells in appropriate amount of MojoSort™ Buffer and proceed to separation. At least 500 µL is needed for column separation. Note: There are several types of commercially available columns, depending on your application. Choose the one that fits best your experiment:
Columns:
Example of magnetic separation with medium capacity columns:
- Place the column in a magnetic separator that fits the column.
- Rinse the column with 3 mL of cell separation buffer.
- Add the labeled cell suspension in at least 500 µL of buffer to the column through a 30 µm filter and collect the fraction containing the unlabeled cells. For negative selection, these are the unlabeled cells of interest; do not discard.
- Wash the cells in the column 2 times with 3 mL of buffer and collect the fraction containing the untouched cells. Combine with the collected fraction from step 3. For negative selection, these are the unlabeled cells of interest; do not discard.
- Do not discard the column if you are performing positive selection. The labeled cells must be eluted from the column. Remove the column from the magnetic separator and it over a collection tube. Then add 5 mL of buffer and flush out the magnetically labeled fraction with a plunger or supplied device. For positive selection, these are the labeled cells of interest; do not discard. To increase the purity of the magnetically labeled fraction repeat the isolation process with a new, freshly prepared column.
Data
Flow cytometry. High purity and yield. “After Isolation” plot shows purified population of interest using pre-diluted MojoSort™ reagents in separation columns.
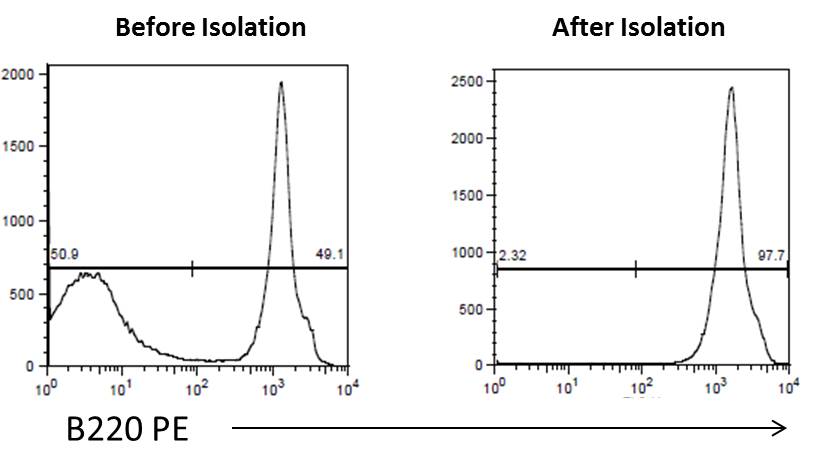
| Kit | Purity | Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse CD19 Nanobeads | 97.7% | 94% |
Electron Microscopy. MojoSort™ Nanobead-isolated CD19+ cells using columns do not display more bound beads on the cell surface (A) as compared to cells isolated with a compatible commercial product using the same columns (B). Red arrows indicate where the particles are located. Numbers indicate either 2 or 3 magnetic particles adjacent to each other. Pictures were taken at the same magnification, scale shown in B. Images are representative of 41 different cells each.
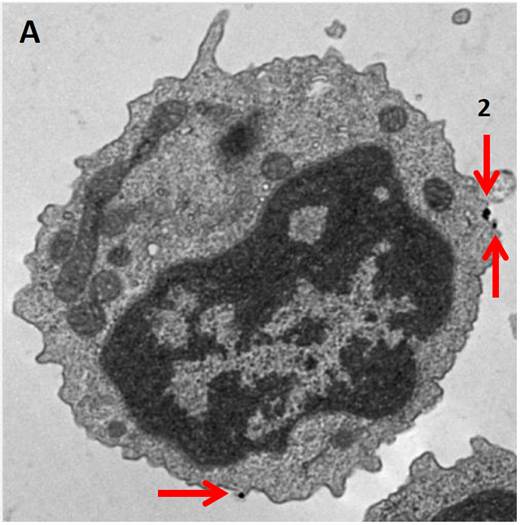 B cells isolated with MojoSort™ CD19 nanobeads using separation columns. |
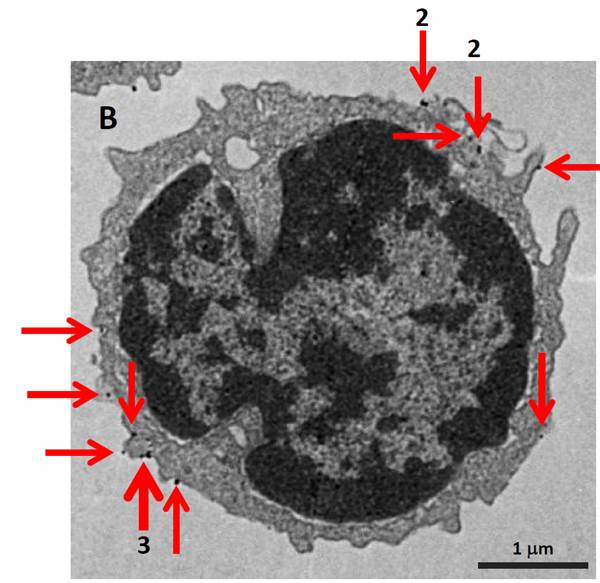 B cells isolated with competitor's CD19 magnetic beads using separation columns. |

 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us