- Clone
- SMI 24 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- Previously
-
Covance Catalog# SMI-24R
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
-
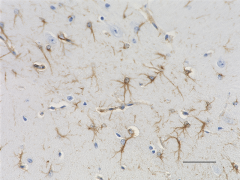
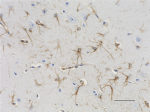
IHC staining of anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3: Acidic, 100X (Cat. No. 927601), the tissue was incubated with a 1:2000 dilution of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend´s Ultra-Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
IHC staining of anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3: Acidic, 100X (Cat. No. 927601), the tissue was incubated with a 1:2000 dilution of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend´s Ultra-Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
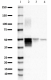
Western blot of anti-GFAP antibody antibody (clone SMI 24). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 20 µg of human brain lysate; Lane 3: 20 µg of rat brain lysate; Lane 4: 20 µg of mouse brain lysate. The blot was incubated with the primary antibody at a 1:2000 dilution overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP goat anti-mouse IgG antibody (Cat. No. 405306). Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 837401 | 100 µL | $310.00 | |||
Glial fibrillary acidic protein is an intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS) including astrocytes and ependymal cells. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular fibroblasts, Leydig cells of the testis, keratinocytes, osteocytes and chondrocytes and stellate cells of the pancreas and liver. GFAP is a type III IF protein that is closely related to its non-epithelial family members, vimentin, desmin, and peripherin, which are all involved in the structure and function of the cell’s cytoskeleton. GFAP is thought to help to maintain astrocyte mechanical strength, as well as the shape of cells.
Type III intermediate filaments are highly conserved and contain three domains, named the head, rod and tail domains. This rod domain coils around that of another filament to form a dimer, with the N-terminal and C-terminal of each filament aligned. Type III filaments such as GFAP are capable of forming both homodimers and heterodimers; GFAP can polymerize with other type III proteins or with neurofilament protein (NF-L). Interestingly, GFAP and other type III IF proteins cannot assemble with keratins, the type I and II intermediate filaments: in cells that express both proteins, two separate intermediate filament networks form.
To form networks, the initial GFAP dimers combine to make staggered tetramers, which are the basic subunits of an intermediate filament. The non-helical head and tail domains are necessary for filament formation. The head and tail regions have greater variability of sequence and structure. In spite of this increased variability, the head of GFAP contains two conserved arginines and an aromatic residue that are required for proper assembly.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Ascites Fluid (contains 0.01M sodium azide).
- Preparation
- Ascites
- Concentration
- The concentration is not quantified as this product is sold as undiluted crude mouse ascites fluid. The concentration might vary from lot-to-lot and an estimated concentration would be 1-3 mg/ml.
- Storage & Handling
- Store at -20°C. Upon initial thawing, apportion into working aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to prevent denaturing the antibody.
- Application
-
IHC-P - Quality tested
WB - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining. For immunohistochemistry, a dilution range of 1:1000 - 1:2000 is suggested. For western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1:1000 - 1:2000 dilution. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Monoclonal antibody against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) derived from the Bigner-Eng clone MAb2E1.
SMI 24 provides for general visualization of GFAP in astrocytes and Bergman glia, it detects a more selected group of astrocytomas than mixtures of SMI 23, 24 and 25. The significance of this selectivity has not yet been explored. Possibilities are different characteristics of individual tumors or cooperativity of antibodies.
Multiple protein fragments ranging from 38 to 48 kD have been reported in human CNS lysates resulting from caspase- and calpain-mediated cleavage of GFAP. - Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2565375 (BioLegend Cat. No. 837401)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- GFAP is a 432 amino acid protein with a molecular mass of approximately 50 kD.
- Distribution
-
GFAP is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS) including astrocytes, ependymal cells, and Bergmann glia cells (unipolar protoplasmic astrocyte). GFAP is expressed in cells lacking fibronectin.
- Function
- GFAP is a class-III intermediate filament and a structural constituent of the cytoskeleton. It is a cell-specific marker that is used to distinguish astrocytes from other glial cells during the development of the CNS.
- Cell Sources
- Cytoskeleton and cytosol
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Intermediate Filaments
- Antigen References
- Gene ID
- 2670 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about GFAP on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All GFAP Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-GFAP | SMI 24 | IHC-P,WB |
| Purified anti-GFAP | SMI 24 | IHC-P,WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Anti-GFAP
IHC staining of anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) on formali... 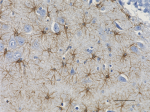
IHC staining of anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) on formali... 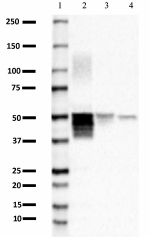
Western blot of anti-GFAP antibody antibody (clone SMI 24). ... -
Purified anti-GFAP
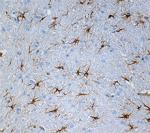
IHC staining of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) o... 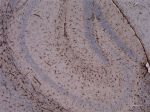
IHC staining of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) o... 
IHC staining of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) o... 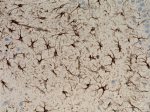
IHC staining of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) o... 
IHC staining of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24) o... 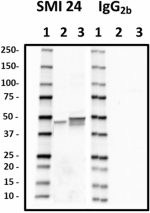
Western blot of purified anti-GFAP antibody (clone SMI 24). ...
