- Clone
- RMdO-20 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- 160 kD neurofilament protein, neurofilament triplet M protein, neurofilament-3 (150 kD medium), neurofilament, medium polypeptide 150kD
- Previously
-
Covance Catalog# MMS-544R
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
-
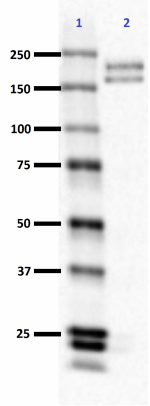
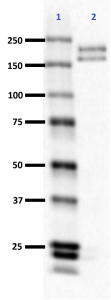
Western blot of anti-Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) antibody (clone RMdO-20). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 20 µg of rat brain lysate. The blot was incubated with a 1:1000 dilution of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system. -
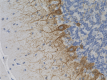
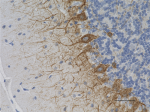
IHC staining of anti-Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) antibody (clone RMdO-20) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with a 1:1000 dilution of the primary antibody for 60 minutes at room temperature. BioLegend's Ultra-Streptavidin (USA) HRP kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
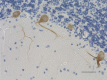
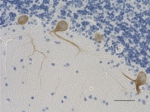
IHC staining of anti-Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) antibody (clone RMdO-20) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with a 1:1000 dilution of the primary antibody for 60 minutes at room temperature. BioLegend's Ultra-Streptavidin (USA) HRP kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
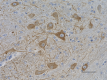
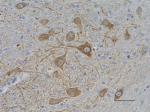
IHC staining of anti-Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) antibody (clone RMdO-20) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with a 1:1000 dilution of the primary antibody for 60 minutes at room temperature. BioLegend's Ultra-Streptavidin (USA) HRP kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 801901 | 200 µL | $375.00 | |||
Neurofilaments (NF) are ~10 nanometer intermediate filaments found in neurons. They are a major component of the neuronal cytoskeleton, and function primarily to provide structural support for the axon and regulate axon diameter. Neurofilaments belong to the same protein family as the intermediate filaments of other tissues such as keratins, which make the filaments expressed in epithelia. The family of proteins that includes the intermediate filaments is divided into 5 major classes, the keratins forming the classes I and II. Class III contains the proteins vimentin, desmin, peripherin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). The major neurofilament subunits occupy the class IV family of intermediate filaments, along with two other filament proteins of neurons, alpha-internexin and nestin. The class IV intermediate filament genes share two unique introns not found in other intermediate filament gene sequences. Finally, class V corresponds to intermediate filaments of the nuclear cytoskeleton, the nuclear lamins. Neurofibrils are bundles of neurofilaments.
There are three major neurofilament subunits, and the names given to these subunits are based upon the apparent molecular mass of the mammalian subunits on SDS-PAGE: The light or lowest (NF-L) runs at 68-70 kD. The medium or middle (NF-M) runs at about 145-160 kD. The heavy or highest (NF-H) runs at 200-220 kD.
These three proteins are referred to as the "neurofilament triplet”. Antibodies against neurofilaments are useful for identification of neurons and their processes in histological sections and in tissue culture. The true molecular masses of these proteins are considerably lower than estimated based on SDS-PAGE mobility, particularly in the case of NF-H and NF-M. This is due to the highly charged C-terminal regions of the molecules. All three triplet proteins contain long stretches of polypeptide sequence rich in glutamic acid residues, and NF-M and especially NF-H also contain multiple tandemly repeated serine phosphorylation sites. These sites contain the peptide sequence lysine-serine-proline, and phosphorylation is predominantly found on axonal and not dendritic neurofilaments. Human NF-M has 13 of these KSP sites, while human NF-H is expressed from two alleles one of which produces 44 and the other 45 KSP repeats.
The fourth class IV subunit, alpha-internexin (NF66) was discovered much later than NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, and is found co-polymerized with these proteins in most mature neurons. The fifth protein belonging to class IV, Nestin, is found in developing neurons and glia, and the presence of this protein is widely used to define neurogenesis. This protein is lost as development proceeds.
The class III intermediate filament protein subunit peripherin is found in neurofilaments along with the class IV subunits in a few neurons, mostly in the peripheral nervous system. Finally another class III intermediate filament subunit, vimentin, is found in developing neurons and a few very unusual neurons in the adult in association with class IV proteins, such as the horizontal neurons of the retina.
In the adult mammal neurofilament subunit proteins coassemble , forming a heteropolymer that contain NF-L or alpha-internexin plus NF-M or NF-H. Peripherin and vimentin may incorporate into neurofilaments along with these proteins. The NF-H and NF-M proteins have lengthy C-terminal tail domains that appear to control the spacing between neighboring filaments, generating aligned arrays with a fairly uniform interfilament spacing as seen in axons.
During axonal growth, new neurofilament subunits are incorporated all along the axon in a dynamic process that involves the addition of subunits along the filament length, as well as the addition of subunits at filament ends. The level of neurofilament gene expression correlates with axonal diameter, which controls how fast electrical signals travel down the axon. Mutant mice with neurofilament abnormalities have phenotypes resembling amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurofilament, NF, immunostaining is common in diagnostic neuropathology. It is useful for differentiating neurons (positive for NF) from glia (negative for NF).
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Preparation
- Ascites
- Concentration
- The concentration is not quantified as this product is sold as undiluted crude mouse ascites fluid. The concentration might vary from lot-to-lot and an estimated concentration would be 1-3 mg/ml.
- Storage & Handling
- Store at -20°C. Upon initial thawing, apportion into working aliquots and store at -20°C Avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles to prevent denaturing the antibody.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
IHC-P - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested dilution is 1:500 - 1:1000. For immunohistochemistry, the suggested dilution is 1:500 - 1:1000. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- VM Lee, MJ Carden, WW Schlaepfer, JQ Trojanowski. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish several differentially phosphorylated states of the two largest rat neurofilament subunits (NF-H and NF-M) and demonstrate their existence in the normal nervous system of adult rats. J. Neurosci. 7(11):3474-88, 1987.
- VM Lee, L Otvos Jr, ML Schmidt, JQ Trojanowski. Alzheimer disease tangles share immunological similarities with multiphosphorylation repeats in the two large neurofilament proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85(19):7384-7388, 1988.
- RRID
-
AB_2564644 (BioLegend Cat. No. 801901)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Expected MW: 160 and 200 kD
- Cell Type
- Mature Neurons
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Intermediate Filaments
- Gene ID
- 4741 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Neurofilament M/H on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Neurofilament M/H (NF-M, NF-H) | RMdO-20 | WB,IHC-P |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.