- Clone
- 1D11 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- NKG2D
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
-
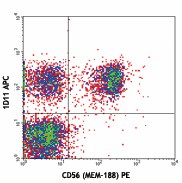
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD314 (clone 1D11) APC and CD56 PE.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320807 | 25 tests | $139.00 | |||
| 320808 | 100 tests | $273.00 | |||
CD314 is a homodimeric C-type lectin-like protein also known as NKG2D. It is expressed on NK cells, CD8+ T cells, γ/δ T cells, and in vitro induced LAK cells. Several molecules have been identified as the ligands for NKG2D, including MHC class-I chain-related protein A (MICA), MICB, and UL16-binding proteins (ULBPs). NKG2D has no intrinsic signaling capacity, but attains this by non-covalent association with DAP10 or DAP12 adaptors. In addition to being a primary activation receptor on NK cells, NKG2D is also a costimulatory receptor for TCR-mediated T cell proliferation and cytokine production. The interaction of NKG2D with its ligands plays a role in the immune surveillance against pathogen and tumor cells, and in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Reported Reactivity
- African Green, Baboon, Cynomolgus, Rhesus
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The 1D11 antibody blocks MICA binding to T cells, induces redirected lysis, and costimulates T cells activation and proliferation. Additional reported (for the relevant formats) applications include: immunoprecipitation1,2, blocking of ligand binding, induction of redirected cell lysis, and costimulation of T cells proliferation2-7. For highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 320814) with endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Wu J, et al. 1999. Science 285:730.
- Wu J, et al. 2000. J. Exp. Med. 192:1059.
- Groh V, et al. 2001. Nature Immunol. 2:255.
- Wu J, et al. 2002. J. Immunol. 169:1236.
- Roberts A, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 167:5527.
- Groh V, et al. 2003. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:9452.
- Kraetzel K et al. 2008. Eur. Respir. J. 32:563. PubMed
- Correia DV, et al. 2011. Blood 118:992. (FC) PubMed
- Watanbe M, et al. 2014. Int Immunol. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_492962 (BioLegend Cat. No. 320807)
AB_492962 (BioLegend Cat. No. 320808)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- C-type lectin
- Distribution
-
NK cells, γ/δ T cells, CD8+ T cells
- Function
- Cytolytic killing of target cells expressing NKG2D ligands, costimulation of NK cells and T cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- MICA, MICB, UL16-binding proteins (ULBPs)
- Cell Type
- NK cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Vance RE, et al. 1999. J. Exp. Med. 190:1801.
2. Raulet DH. 2003. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:781.
3. Lohwasser S, et al. 1999. Eur. J. Immunol. 29:755.
4. Jamieson AM, et al. 2002. Immunity 17:19.
5. Gilfillan S, et al. 2002. Nat. Immunol. 3:1150.
6. Ho EL, et al. 2002. J. Immunol. 169:3667.
7. Maasho K, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 174:4480.
8. Groh V, et al. 2003. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:9452. - Gene ID
- 22914 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD314 on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All CD314 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCompare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
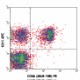
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with purifie... -
Biotin anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with biotiny... -
PE anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD314 (... -
APC anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD314 (... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD56 AP... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
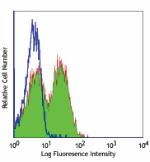
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with Ultra-L... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
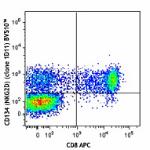
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 APC... 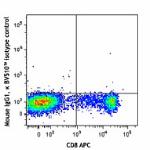
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
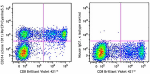
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 Bri... -
FITC anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 Bri... 
-
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 Ale... 
-
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
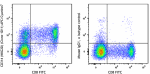
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 FIT... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
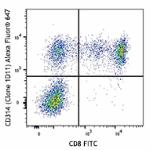
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 FIT... 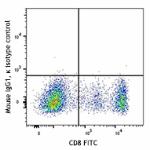
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 Ale... 
-
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
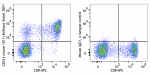
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 FIT... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
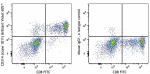
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 FIT... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
TotalSeq™-A0165 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
-
TotalSeq™-C0165 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
-
TotalSeq™-B0165 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
-
Alexa Fluor® 660 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D) Antibody
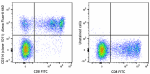
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD8 FIT... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
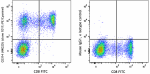
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
TotalSeq™-D0165 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
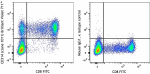
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD314 (NKG2D)
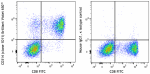
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-human CD314 (NKG2D) (Flexi-Fluor™)
