- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- SAv-Brilliant Violet 605™
-
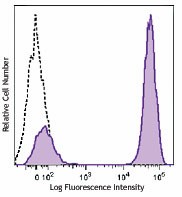
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with biotinylated CD3 (filled histogram) or mouse IgG1 isotype control (open histogram), followed with Sav-Brilliant Violet 605™.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 405229 | 100 µL | $231.00 | |||
Streptavidin binds to biotin with high affinity. Streptavidin-Brilliant Violet 605™ is useful for detecting biotinylated antibodies. The excitation of Brilliant Violet 605™ by 405 nm laser light induces a fluorescence maximum emission of 603 nm.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, All Species
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
- Preparation
- Streptavidin was conjugated with Brilliant Violet 605™ under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.1 mg/ml (concentration relates to the Streptavidin only component of the conjugate)
- Storage & Handling
- The streptavidin solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
ICFC - Verified
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this Streptavidin-Brilliant Violet 605™ is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. The concentration provided is based upon molecular mass of streptavidin independent of any additional molecular mass that might be added by the Brilliant Violet 605™ conjugation. For immunofluorescent staining, we recommend using ≤0.25 µg in 100 µl staining volume per million cells. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 605™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 603 nm. The bandpass filter 610/20 nm is recommended for detection, although filter optimization may be required depending on other fluorophores used. Be sure to verify that your cytometer configuration and software setup are appropriate for detecting this channel. Refer to your instrument manual or manufacturer for support. Brilliant Violet 605™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet™.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents. - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The average molecular weight of Streptavidin-Brilliant Violet 605™ is 340 kD and Streptavidin alone is 52 kD.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Altin JA, et al. 2014. PNAS. 111:2067. PubMed
- Perez-Quintero LA, et al. 2014. J Exp Med. 211:727. PubMed
- Cartwright EK, et al. 2014. J. Immunol. 192:4666. PubMed
- Guo H, et al. 2014. J Leukoc Biol. 96:419. PubMed
- Arlehamnn CL, et al. 2014. J Immunol. 193:2931. PubMed
- Sakaguchi S, et al. 2015. J Leukoc Biol. 97:635. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Gene ID
- NA
- UniProt
- View information about Biotin on UniProt.org
