- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- AAA, ABETA, ABPP, AD1, APPI, CTFgamma, CVAP, PN-II, PN2, Amyloid beta A4 protein, preA4, protease nexin-II, peptidase nexin-II, beta-amyloid peptide, alzheimer disease amyloid protein, cerebral vascular amyloid peptide, APP, Amyloid Precursor Protein
-
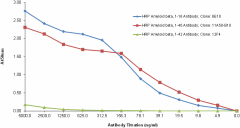
Direct ELISA of HRP anti-β-Amyloid, 1-16 Antibody (clone 6E10; Cat. No. 803011), HRP anti-β-Amyloid, 1-40 Antibody (clone 11A50-B10; Cat. No.805407), and HRP anti-β-Amyloid, 1-42 Antibody (clone 12F4; Cat. No. 805507) binding to plate-immobilized Human β-Amyloid Peptide (1-40). ELISA was performed by coating wells with 10 ng of Human β-Amyloid Peptide (1-40). The wells were then incubated with the primary antibodies at 37°C for 45 minutes. TMB (3, 3', 5, 5' tetramethylbenzidine, Cat. No. 421501) was used as the detection system.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 932601 | 500 µg | $218.00 | |||
| 932602 | 1 mg | $440.00 | |||
Amyloid Beta (Aβ) peptides are derived from amyloid precursor proteins (APP) through sequential proteolytic cleavage of APP by β- and γ-secretases generating diverse Aβ species. Aβ can aggregate to form soluble oligomeric species and insoluble fibrillar or amorphous assemblies. Some forms of the aggregated peptides are toxic to neurons. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation of aggregated Aβ peptides in senile plaques and vascular deposits.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Source
- Chemically Synthesized
- Molecular Mass
- 4329.9
- Purity
- ≥95%, % Peak Area by HPLC
- Formulation
- Lyophilized white powder
- Storage & Handling
-
Peptide is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store lyophilized powder at ≤ -20°C. Reconstituted peptide should be aliquoted and stored at ≤ -20°C. Do not freeze/thaw.
Peptide reconstitution: It is recommended to use 1% NH4OH as the solvent followed by immediate dilution in buffer (i.e. PBS). Add 1% NH4OH directly to the lyophilized powder (add 35-40 µL to 0.5mg or 70-80 µL to 1.0 mg), then immediately dilute the solution in your buffer to a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL or less. The peptide cannot be stored in 1% NH4OH long-term. - Application
-
Direct ELISA Assay
- Recommended Usage
-
Validated in Direct ELISA as coating peptide.
The peptide may also be useful in additional applications such as Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation. Optimal conditions to be determined by end user.
- Application Notes
-
Direct ELISA: Peptide Coat Concentration 0.2 µg/mL
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Aβ denotes peptides of 36-43 amino acids generated from cleavage of APP by secretases. Aβ has an apparent molecular mass of about 4 kD.
- Distribution
-
Tissue sources: Primarily nervous system, but also adipose tissue, intestine, and muscle.
Distribution: Cytosol, endosomes, nucleus, plasma membrane, extracellular, and golgi apparatus. - Function
- The normal function of Aβ is not well understood. Several potential physiological roles have been proposed, including: activation of kinase enzymes; protection against oxidative stress; regulation of cholesterol transport; transcription factor, and as an anti-microbial agent.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Protein Misfolding and Aggregation
- Molecular Family
- APP/β-Amyloid
- Antigen References
-
- Kumar A, et al. 2015. Pharmacol. Rep. 67(2):195.
- Sadigh-Eteghad S, et al. 2015. Med. Princ. Pract. 24(1):1
- Hampel H, et al. 2015. Expert Rev. Neurother. 15(1):83.
- Puig KL, et al. 2012. Exp. Gerontol. 48(7): 608.
- Selkoe DJ, et al. 2016. EMBO Mol. Med. 8(6):595.
- Walsh DM, et al. 2007. J. Neurochem. 101(5):1172.
- Gene ID
- 351 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about beta-Amyloid 1-40 on UniProt.org
