- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Human monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, Myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein
-
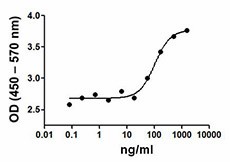
IL-8 induction on THP-1 cells stimulated with LPS+ CD14.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593002 | 10 µg | $89.00 | |||
| 593004 | 25 µg | $153.00 | |||
| 593006 | 100 µg | $347.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
CD14 is a pattern recognition receptor important in innate immunity. CD14 exists in two forms, as a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein on the surface of mononuclear cells and as a soluble protein in the blood. CD14 is shed from the surface of CD14-expressing cells, resulting in the soluble CD14 protein (sCD14). CD14 is down regulated from the cell membrane on stimulated monocytes by different factors such as LPS, IFNγ, PMA, calcium ionophore A 23187, and antibodies against CD14. CD14 can be released from the cells with GPI-phospholipase C and D (PLC/D). Membrane associated CD14 is a pro-inflammatory coreceptor for LPS, a characteristic constituent of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS interacts with LPS-binding protein (LBP) and CD14, and this complex interacts with TLR4, which subsequently induces inflammatory gene expression through NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein-kinase signaling in host cells. sCD14 enables responses to LPS by cells that do not express CD14 such as endothelial cells. In this sense, HUVEC cells respond to LPS by production of IL-6 and this responsiveness is serum dependent. Elevated levels of sCD14 has been detected in serum of patients with different diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, HIV infected patients, common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Also, high levels of sCD14 has been associated with infectious diseases, including sepsis. In addition, it has been reported that sCD14 could be a potential biomarker for predicting the prognosis of breast invasive ductal carcinoma.
Product Details
- Source
- Human CD14, amino acids (Thr20-Cys352) (Accession# NM_000591 ) was expressed in CHO cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 333 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 35.8 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced glycosylated protein migrate at approximately 50-60 kD and 40-55 kD respectively by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Thr.
- Purity
- >95% glycosylated, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is 1X PBS, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 100-400 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 1.0-2.5 x 104 units/mg, as determined by production of IL-8 from THP-1 cells trated with LPS (2 ng/ml) and CD14.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Distribution
- Activated monocytes are a source of sCD14. It is present in plasma, colostrum, and milk.
- Function
- CD14 enhances innate immune responses to infections, and it sensitizes cells to bacterial LPS. sCD14 induces B cell growth and differentiation. It enables responsivesness to LPS by non CD14-expressing cells. LPS, IFNγ, PMA, calcium ionophore A 23187, and antibodies against CD14 induce sCD14.
- Interaction
- B cells, endothelial cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- LBP, TLR2, TLR4
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- Soluble Receptors, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Simmons DL, et al. 1989. Blood 73:284.
2. Wright SD, et al. 1990. Sciences 249:1431.
3. Bazil V and Strominger JL. 1991. J. Immunol. 147:1567.
4. Frey EA, et al. 1992. J. Exp. Med. 176:1665.
5. Matsuguchi T, et al. 2000. J. Immunol. 165:5767.
6. Bochkov VN, et al. 2002. Nature 419:77.
7. Zanin-Zhorov A, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:41.
8. Baumann CL, et al. 2010. J. Exp. Med. 207:2689.
9. Litzman J, et al. 2012. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 170:321. - Gene ID
- 929 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD14 on UniProt.org
