- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Delta-like protein 1, H-Delta-1, drosophila Delta homolog 1
-
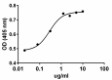
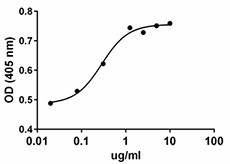
Immobilized human DLL1 enhances BMP-2 induction of alkaline phosphatase in mouse chondrogenic ATDC5 cells.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 757402 | 5 µg | $89.00 | |||
| 757404 | 25 µg | $223.00 | |||
This product is not available for shipping outside of the United States.
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
DLL1 is a member of the Delta/Serrate/Lag2 (DSL) family of ligands that bind the Notch receptor. Five DSL ligands have been identified in mammals including three Delta-like proteins (Dll1, 3, and 4) and two Serrate-like (Jagged1 and Jagged2). The canonical DSL (Delta, Serrate, Lag2) ligands are type I cell surface proteins, and like Notch have tandem EGF repeats in their extracellular domain. The DSL domain, the amino terminal, and the first two EGF domains are necessary for the binding to the Notch receptor. Jagged1 and Jagged2 have an additional cysteine rich region, not present in the Delta-like proteins. Through a cell-cell interaction the Notch signaling is activated (trans-interaction); the interaction of the ligands with Notch within the same cell (cis-interaction) induces inhibitory cell signaling. The Notch signaling pathway plays important roles in specifying cell fate during embryonic development and contributes to adult homeostasis; thus, Notch plays a key role in the development of embryonic hematopoietic stem cells, modulates T cell-mediated immune responses and development of marginal zone (MZ) B cells. DLL1 enhances the in vitro conversion of human memory CD4 T cells into FOXP3-expressing regulatory T cells. DSL ligands are cleaved by ADAMs (ADAM9, 10, 12, and 17) resulting in the shedding of the extracellular domain. Soluble intracellular derivatives are generated by presenilin-dependent intramembranous gamma-secretase processing. DLL1 intracellular domain (DICD) generated by the gamma-cleavage is transported into the nucleus where it plays a role in transcriptional events.
Product Details
- Source
- Human DLL1, amino acids (Ser22- Phe543 ) (Accession# NM_005618) was expressed in E.coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 522 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 56.2kD. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Ser.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered protein solution from PBS, pH 7.5 with no additives.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 1 EU per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored at -20°C or -70°C. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. Do not vortex. It is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein such as 0.1% BSA and store working aliquots at -20°C to -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Immobilized human DLL1 enhances BMP-2 induction of alkaline phosphatase in mouse chondrogenic ATDC5 cells in a dose dependent manner. The ED50 = 0.15 - 0.75 µg/ml.
- Application
-
Bioassay
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
Thymic stromal cells, fibroblasts in secondary lymphoid organs niches.
- Function
- DLL1-mediated cell—cell interactions, play an important role in somitogenesis, myogenesis, retinal development , homeostasis of intestinal stem cells, and differentiation of the intestinal epithelium.
- Interaction
- Multiple stem cells precursors, bone marrow precursors, memory CD4 T cells, peripheral T cells, paraxial (somitic) mesoderma.
- Ligand/Receptor
- Notch receptors.
- Bioactivity
- Immobilized human DLL1 enhances BMP-2 induction of alkaline phosphatase in mouse chondrogenic ATDC5 cells.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cell Biology, Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Ikeuchi T, et al. 2003. J. Biol. Chem. 278:7751.
2. Parks AL, et al. 2006. Genetics 174:1947.
3. Schuster-Gossler K, et al. 2007. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:537.
4. Sun D, et al. 2008. J. Cell. Sci. 121:3815.
5. Rocha SF, et al. 2009. Dev. Biol. 328:54.
6. D'Souza, et al. 2010. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 92:73.
7. Radtke F, et al. 2010. Immunity 32:14.
8. Pellegrinet L, et al. 2011. Gastroenterology 140:1230.
9. Zhang L, et al. 2011. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1813:2036.
10. Mota C, et al. 2014. J. Immunol. 193:5854.
11. Fasnacht N, et al. 2014. J. Exp. Med. 211:2265.
12. Shimojo H, et al. 2016. Genes Dev. 30:102. - Gene ID
- 28514 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about DLL1 on UniProt.org
