- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Fibroblast growth factor 6 (FGF-6), Heparin secretory-transforming protein 2 (HST-2), HSTF-2, Heparin-binding growth factor 6 (HBGF-6)
-
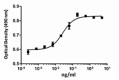
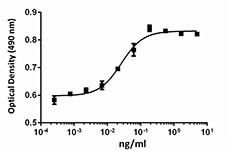
NIH3T3 proliferation induced by human FGF-6 In the presence of 1.5 µg/ml heparin.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 554202 | 10 µg | $124.00 | |||
| 554204 | 25 µg | $223.00 | |||
FGF-6 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, and it is closely related in structure to FGF-4. FGF-6 exhibits a very restricted expression profile predominantly in the developing muscle in embryos. FGF-6 mRNA can also be detected in testis, heart, and skeletal muscle in adults. FGF-6 is involved in both proliferation and differentiation of the myogenic lineages. In vitro studies have shown that the effects of FGF-6 are concentration dependent. At lower concentration, FGF-6 can increase the expression of many muscle cell differentiation markers. At higher concentrations, FGF-6 can downregulate the expression of myogenic markers and some myogenic transcription factors, and can delay C2 myogenic cell differentiation. Injection of FGF-6 recombinant protein into damaged mouse muscle can induce cyclin D1 mRNA and differentiation markers, including Cdkl1, MHC I and Tn1, which results in the acceleration of muscle regeneration. It has been shown that the expression of FGF-6 can transiently be upregulated by muscle injuries in both fast and slow myofibers. FGF-6 can stimulate migration of myogenic stem cells and also control the maintenance of muscle progenitor cells. During muscle regeneration, it has been shown that FGF-6 can be released from necrotic myofibers and be sequestered by basal laminae. FGF-6 regulates muscle differentiation through a calcineurin-dependent pathway and regulates myofiber size through IGF-II/TGF2R pathway. FGF-6 is also involved in bone metabolism.
Product Details
- Source
- Human FGF-6, amino acids Gly41-Ile208 (Accession# P10767.4) with an N-terminal Met, was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 169 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 18.9 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 20 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2, 10% glycerol and 1% CHAPS.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- The ED50 is 0.02 - 0.1 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity 1.0 - 5.0 x 107 units/mg, as determined by a dose-dependent proliferation of NIH3T3 cells in the presence of 1.5 µg/mL heparin.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Growth factor.
- Distribution
-
Myogenic lineage cells, heart, and testis.
- Function
- FGF-6 plays important roles in myogenesis (proliferation, differentiation, and muscle regeneration) depending on concentration and alternative receptor usage. FGF-6 is upregulated by muscle injuries.
- Interaction
- Myogenic lineage cells, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts.
- Ligand/Receptor
- FGFR1 and FGFR4.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. DeLapeyriere O et al. 1993. Development. 118: 601.
2. Coulier, et al. 1994. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 5:1.
3. Pizette S, et al. 1996. Exp. Cell Res. 224:143.
4. Armand AS, et al. 2003. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1642:97.
5. Armand AS, et al. 2006. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1763:773.
6. Bosetti M, et al. 2010. J. Cell Physiol. 225:466. - Gene ID
- 2251 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FGF-6 on UniProt.org
