- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic, bFGF, FGF-2, Heparin-binding growth factor
-
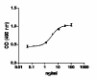
3NIH/3T3 cell proliferation induced by human FGFb.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 571502 | 10 µg | $77.00 | |||
| 571504 | 25 µg | $124.00 | |||
| 571506 | 100 µg | $270.00 | |||
| 571508 | 500 µg | $815.00 | |||
FGFb is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family which includes 23 members. FGFb is expressed in almost all tissues and play important roles in a variety of normal and pathological processes, including development, wound healing, and neoplastic transformation. FGFb is mitogenic for many cell types, both epithelial and mesenchymal. FGFb shows potent angiogenic activity and has been implicated in tumor angiogenesis (2). In prostate, bladder, and renal cancers, FGFb regulates the induction of metalloproteinases (MMP) that degrade extracellular matrix proteins, thus facilitating tumor metastasis (3). FGFb binds to a family of four distinct, high affinity tyrosine kinase receptors, designated FGFR-1 to -4 (4). In addition, FGFb binds to the ECM, and heparan sulfate (HS) that is an essential and dynamic regulator of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling. Two fundamentally different crystallographic models have been proposed to explain, at the molecular level, how HS/heparin enables FGF and FGF receptor (FGFR) to assemble into a functional dimer on the cell surface (5), although there is controversy regarding the exact manner by which this occurs.
Product Details
- Source
- Human FGF-basic, amino acids Ala144-Ser288 (Accession # NM_002006) was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 145 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of 16,310 Da. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrate at approximately 18kDa by SDS-PAGE. This protein may or may not contain an N-terminal methionine.
- Purity
- Purity is >98%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 10mM NaH2PO4, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.2, 1mM DTT.
- Endotoxin Level
- Endotoxin level is <0.1 EU/µg (<0.01ng/µg) protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
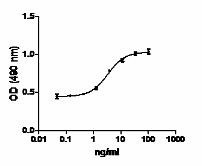
- ED50 = 1 - 4 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 1 - 0.25 x 106 units/mg, as determined by the dose dependent stimulation of NIH/ 3T3 cell proliferation. The bioactivity is equivalent to competitor reported values.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Wang J, et al. 2013. Biosens Bioelectron. 41:143. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- FGF
- Distribution
-
Brain, retina, pituitary, kidney, placenta, testis, corpus luteum, adrenal glands, monocytes, prostate, bone, liver, cartilage, endothelial cells, epithelial cells
- Function
- FGFb is a potent angiogenic factor, and plays a key role in various physiological and pathological conditions, including embryonic development, wound repair, inflammation, and tumor growth (1).
- Interaction
- Fibroblasts, myoblasts, osteoblasts, neuronal cells, endothelial cells, keratinocytes, chondrocytes, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, smooth muscle
- Ligand/Receptor
- FGFR-1 (flg), FGFR-2 (bek, K-sam), FGFR3, and FGFR-4 (flg-2); low affinity coreceptor heparin sulfate and heparin sulfate proteoglycans required for full activity.
- Bioactivity
- FGFb is a heparin-binding growth factor that is an angiogenic agent in vivo and also a potent mitogen for a variety of cell types in vitro.
- Cell Type
- Neural Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Rusnati M and Presta M Current Pharm Des 13:2025-2044 2007.
2. Chaffer CL, et al. Differentiation 75(9):831-42 2007.
3. Cronauer NV, et al. Eur Urol 43:309-319 2003.
4. Shimizu A, et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276:11031-11040 2001.
5. Mahammadi M, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:506-516 2005. - Gene ID
- 2247 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FGF-basic on UniProt.org
