- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- FGF-2, HBGF-2, BFGF, FGFB, Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor, Heparin binding growth factor 2, HBGF2
-
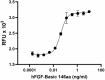
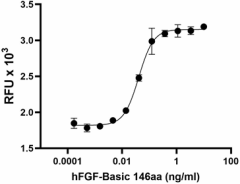
Recombinant human FGF-basic (146 aa) induces the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.015 - 0.075 ng/mL. -
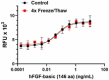
Stability Testing for Recombinant Human FGF-basic (146 aa). Recombinant human FGF-basic was aliquoted in pH 7.5, 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw) and compared to the control that was kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested for their ability to induce the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.025 – 0.125 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 792502 | 10 µg | $71.00 | |||
| 792504 | 25 µg | $147.00 | |||
| 792506 | 100 µg | $253.00 | |||
| 792508 | 500 µg | $703.00 | |||
FGF-basic, also known as FGF-2, is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, which includes 22 members. FGF-acidic and FGF-basic do not have classical secretory signal peptides. The secretion of FGF-2 occurs by direct translocation across the plasma membrane. Multiple forms of FGF-2 derived by alternative translation from AUG and CUG codons from the same mRNA transcript have been described. FGF-2 is expressed in almost all tissues and plays an important role in a variety of normal and pathological processes, including development, wound healing, and neoplastic transformation. FGF-2 is mitogenic for many cell types, both epithelial and mesenchymal. It shows potent angiogenic activity and has been implicated in tumor angiogenesis. FGF-2 significantly promotes the proliferation of adipose-derived mesenchymal cells (AMC) and enhances chondrogenesis in three-dimensional micromass culture. FGF-2 binds to a family of four distinct, high affinity tyrosine kinase receptors, designated FGFR-1 to FGFR-4. In addition, FGF-2 binds to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and heparan sulfate (HS), and is an essential and dynamic regulator of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling. Two fundamentally different crystallographic models have been proposed to explain, at the molecular level, how heparan sulphate enables FGF and FGF receptor (FGFR) to assemble into a functional dimer on the cell surface, although there is controversy regarding the exact manner by which this occurs. FGF-2, αvβ3 integrin, and FGFR-1, form a trimolecular complex required for ERK1/2 activation. MT1-MMP (MMP-14) downregulates the amount of FGF-2 bound to the cell surface, and therefore, it reduces FGF-2 signaling.
Product Details
- Source
- Human FGF-basic (146 aa), amino acid Pro143-Ser288 (Accession # P09038) was expressed in E.coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 146 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 16.5 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 17 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Pro.
- Purity
- > 95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in pH 7.5, 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Recombinant human FGF-basic (146 aa) induces the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.015 - 0.075 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Monomer
- Distribution
-
Brain, retina, pituitary, kidney, placenta, testis, corpus luteum, adrenal glands, monocytes, prostate, bone, liver, cartilage, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells
- Function
- Possesses broad mitogenic and potent angiogenic activity, plays a key role in physiological and pathological conditions, including embryonic development, wound repair, inflammation, and tumor growth. MT1-MMP downregulates fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) signaling.
- Interaction
- FGF-basic binds to αvβ3 integrin. Fibroblasts, myoblasts, osteoblasts, neuronal cells, endothelial cells, keratinocytes, chondrocytes, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and smooth muscle cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Low affinity coreceptor heparan sulfate (HS) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) required for full activity.
- Bioactivity
- Recombinant human FGF-basic (146 aa) induces the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner.
- Cell Type
- Astrocytes, Embryonic Stem Cells, Endothelial cells, Epithelial cells, Fibroblasts, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Mesenchymal cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells, Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cancer Biomarkers, Cardiovascular Biology, Cell Proliferation and Viability, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Schlessinger J, et al. 2000. Mol Cell. 6:743-50.
- Ibrahimi OA, et al. 2001. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:7182-7.
- Yu PJ, et al. 2007. J Cell Biochem. 100:1100-8.
- Beenken A & Mohammadi M. 2009. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:235-53.
- Prudovsky I, et al. 2013. Int J Mol Sci. 14:3734-72.
- Tassone E, et al. 2015. J Cell Physiol. 230:366-77.
- Ornitz DN & Itho N. 2015. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 4:215-66.
- Chien SY, et al. 2016. Clin Sci (Lond). 130:667-81.
- Gene ID
- 2247 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FGF-basic on UniProt.org
