- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Colony stimulating factor 2, CSF2, CSF-2, CSF, Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, GMCSF, CSF-alpha, Pluripoietin-alpha, Eosinophil colony stimulating factor (Eo-CSF), Burst promoting activity (BPA)
-
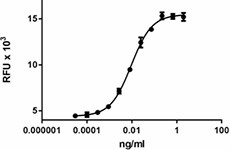
Human GM-CSF induces the proliferation of TF 1 human erythroleukemic cells.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 766102 | 10 µg | $101.00 | |||
| 766104 | 25 µg | $235.00 | |||
| 766106 | 100 µg | $750.00 | |||
GM-CSF plays a key role in signaling emergency hemopoiesis (predominantly myelopoiesis) in response to infection, including the production of granulocytes and macrophages in the bone marrow and their maintenance, survival, and functional activation at sites of injury or insult. GM-CSF in conjuction with IL–3 and IL-5 regulates the production and functional activation of hemopoietic cells; GM-CSF acting on monocyte/macrophages and all granulocytes. GM-CSF also controls dendritic cell and T-cell function, thus linking innate and acquired immunity. The receptor for GM-CSF is a heterodimer that comprises a major binding subunit (GMRa) and a major signaling subunit (bc) that is shared with IL-3 and IL-5 receptors. The receptor subunits are always coexpressed on the surface of leukocytes, and the bc subunit is expressed at lower levels than GMRa. Certain non-hemopoietic cell types have also been reported to express the GM-CSF receptor and to respond to GM-CSF stimulation. In the lung, GM-CSF plays a role in allergic airway disease. It is crucial for antimicrobial pulmonary host defense function and essential for surfactant homeostasis. GM-CSF has been used to protect against influenza, secondary bacterial pneumonia, and acute lung injury. In addition to the FDA approved application for GM-CSF for treating bone marrow suppression.
Product Details
- Source
- Human GM-CSF (a.a. Ala18-Glu144) (Accession #NM_000758) was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 127 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 14.4 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrate at approximately 20 - 28 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Ala.
- Purity
- > 95% by SDS-PAGE gel as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg (0.01 ng/µg) cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Human GM-CSF induces the proliferation of TF 1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 = 0.010 – 0.050 ng/ml.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine
- Distribution
-
T cells, macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, mast cells, alveolar endothelial cells, fibroblasts.
- Function
- Promotes proliferation, differentiation, and survival in myeloid precursors. Promotes activation of monocytes, granulocytes, macrophages, and DCs. Stored in ECM with heparan sulfate proteoglycans.
- Interaction
- Granulocyte/macrophage/erythroid/megakaryocytic progenitors, myeloblasts, monoblasts, dendritic cells, T cell, endothelial cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- Heterodimer GM-CSFR α subunit (CDw116); β-subunit (CDw131).
- Bioactivity
- GM-CSF stimulates the TF-1 cell proliferation.
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Kitamura T, et al. 1989. J. Cell Physiol. 140:323.
2. Walker F, Burgess AW. 1985. EMBO J. 4:933.
3. Hayashida K, et al. 1990. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 87:9655.
4. Hercus TR, et al. 2009. Blood 114:1289.
5. Greter M, et al. 2012. Immunity 36:1031
6. Willart MA, 2012. J. Exp. Med. 209:1505.
7. Subramaniam R, et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10:e0124593.
8. Chen GH, et al. 2016. J. Immunol. 196:1810.
9. Rösler B, Herold S. 2016. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 3:29. - Gene ID
- 1437 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about GM-CSF on UniProt.org
