- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Insulin-like growth factor I, somatomedin C, Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity I (NSILA-I)
-
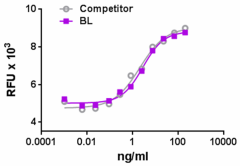
Recombinant human IGF-I induces the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cell line in a dose dependent manner. BioLegend’s protein was compared side-by-side to the leading competitor’s equivalent product.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 590904 | 25 µg | $101.00 | |||
| 590906 | 100 µg | $171.00 | |||
| 590908 | 1 mg | $347.00 | |||
IGF-I (insulin-like growth factor 1), initially described in 1957, is a hormone that is important in childhood growth and also has anabolic effects in adults. It is a member of the IGF family that is comprised of three members: IGF-I, IGF-II, and insulin. IGF-I and IGF-II share approximately 50% similarity with insulin at the amino acid level. Human IGF-I is synthesized as a 191 amino acid prepro-IGF-I; pro-IGF-I is processed to the mature, active protein, and this procedure requires glucose regulating protein 94 (GRP94) that possesses chaperone activity towards IGF-I. Deletion of muscle GRP94 impairs muscle and body growth by inhibiting local production of IGF proteins. Seven binding proteins have been described (IGFBP-1 to -7). IGFBPs extend the half life and regulate the availability of IGF-I and IGF-II. It has been described that IGFBP3 is the main circulating binding protein for IGFs; in serum approximately 75% of circulating IGF-I and IGF-II bind to IGFBP3 and the co-carrier acid labile subunit (ALS). IGF-I binds to three receptors, and the binding to IGFIR promotes cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration. IGF-I deficiency is associated to growth hormone insensitivity syndrome (GHIS) also called Laron syndrome, liver cirrhosis, age-related cardiovascular and neurological diseases, and intrauterine growth restriction.
Product Details
- Source
- Human IGF-I, amino acids Gly49-Ala118 (Accession# p056019) was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 70 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 7.6 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrate at approximately 11 kD by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Gly.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 300 mM ammonium acetate pH 5.5.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 1.5 - 7.5 ng/ml, as determined by the dose dependent stimulation of MCF-7 cell proliferation.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
Astrocytes, hepatocytes, microglia, intestinal smooth muscle, myoblast, NK cells.
- Function
- IGF-I induces mitogenesis, proliferation, growth, differentiation, and angiogenesis. IGF-I is a mediator of growth hormone action. IGF-I is involved in neuronal myoblast proliferation and differentiation, and organ development. IGF-I promotes NK cell development and cytotoxic activity in NK cells.
- Interaction
- Neuronal cells, myoblast, T cells, B cells, NK cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- IGF-I receptor, Insulin receptor isoform A, and IGF-II receptor (M-6-P-R).
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Signal Transduction, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Bell GI, et al. 1984. Nature 310:775.
2. Karey KP and Sirbasku DA, 1988. Cancer Res. 48:4083.
3. Mohan S and Baylink DJ, 2002. J. Endocrinol. 175:19.
4. Ostrovsky O, et al. 2010. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1803:333.
5. Barton ER, et al. 2012. FASEB. J. 26:3691.
6. Puche JE and Castilla-Cortázar I. 2012. J. Transl. Med. 10:224.
7. Ni F, et al. 2013. Nat. Commun. 4:1479. - Gene ID
- 3479 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IGF-I on UniProt.org
