- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Leukemia inhibitory factor, HILDA (human interleukin in DA cells), MLPLI (melanoma-derived LPL inhibitor), DIA (differentiation-inducing factor)
-
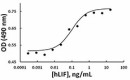
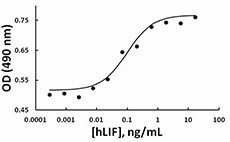
Human leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) induces proliferation of TF-1 cells in a dose dependent manner.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593902 | 10 µg | $141.00 | |||
| 593904 | 25 µg | $223.00 | |||
| 593906 | 100 µg | $768.00 | |||
| 593908 | 500 µg | $1870.00 | |||
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) is a 20 kD protein that belongs to the IL-6 receptor family. It binds to a heterodimeric membrane receptor made up of a LIF-specific subunit, gp190 or LIFR, and the subunit gp130, which is shared with the other members of the IL-6 family. The LIF complex receptor signals though STAT3 and JAK kinases. LIF expression has been observed in various tissues including thymus, lung, and neuronal tissue. LIF displays diverse biological effects but is best known for its ability to inhibit the differentiation of embryonic stem cells in mice and contribute to stem cell self-renewal. Human and mouse LIF share 79% sequence homology and exhibit cross-species activity. However, LIF inhibition of stem cell differentiation appears to be mouse specific. It is involved in the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, induction of neuronal cell differentiation, regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial conversion during kidney development, and may also have a role in immune tolerance at the maternal-fetal interface. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. LIF can be upregulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and IL-17, and elevated levels of LIF have been found in cases of rheumatoid arthritis, neural injury, systemic inflammation, and tuberculosis.
Product Details
- Source
- Human LIF, amino acids (Ser23-Phe202) (Accession# NP_002300.1), was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 180 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 20 kD. The protein migrates at about 20 kD in DTT-reducing conditions and about 18 kD in non-reducing condition by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Ser.
- Purity
- >97%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.4.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg of protein as determine by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Human LIF induces proliferation of TF-1 cells. ED50 = 0.03-0.12 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 8.3-33.3 x 106 units/mg.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Distribution
- Expressed in the trophectoderm of the developing embryo, activated CD4+ T cells.
- Function
- Inhibits embryonic stem cell differentiation, induces the terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. LIF is upregulated by TNFα and IL-17. LIF is downregulated by IL-4 and IL-13 in fibroblasts.
- Interaction
- Embryonic stem cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- LIFR complex (gp190 and gp130).
- Bioactivity
- Human LIF induces proliferation of TF-1 cells.
- Cell Type
- Tregs, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Moreau JF, et al. 1988. Nature 336:690.
2. Tomida M, et al. 1993. FEBS Lett. 334:193.
3. Metcalfe SM. 2011. Genes Immun. 12:157.
4. Voyle RB, et al. 1999. Exp. Cell Res. 249:199.
5. Slaets H et al. 2010. Trends Mol. Med. 16:493.
6. Souza PP, et al. 2012. Mol. Immunol. 49:601. - Gene ID
- 3976 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about LIF on UniProt.org
