- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-AB
-
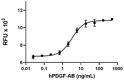
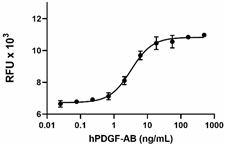
Recombinant human PDGF-AB induces the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 1 - 5 ng/mL. -
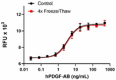
Stability Testing for Recombinant Human PDGF-AB. Recombinant Human PDGF-AB was aliquoted in 4 mM HCl at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw) and compared to the control that was kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested for their ability to induce the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 1 - 5 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 788602 | 10 µg | $206.00 | |||
| 788604 | 25 µg | $375.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) are homo- or heterodimers of four polypeptides, known as A, B, C and D chains. PDGFs are primarily synthesized, stored in α-granules, and released by platelets upon activation. Five PDGF isoforms (AA, BB, AB, CC and DD) have been identified. PDGF-A and PDGF-B undergo intracellular activation during transport in the exocytic pathway and PDGF-C and PDGF-D are activated by extracellular proteases. PDGF-AA, AB, and BB dimers readily activate PDGF receptors (PDGFRs). PDGF-AA binds to PDGFRαα, PDGF-AB binds to PDGFRαα and PDGFRαβ, while PDGF-BB binds to the three dimeric receptors PDGFRαα, PDGFRαβ, and PDGFRββ. PDGFs are potent mitogens for connective tissue cells, including dermal fibroblasts, glial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells and some epithelial and endothelial cells. PDGFs act primarily in a paracrine manner and may be engaged in autocrine loops in tumors. In addition to its activity as a mitogen, PDGF is a chemotactic for fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, neutrophils and mononuclear cells. PDGF-AA and -AB promote cell proliferation, cell survival, cytoskeletal rearrangement, cell migration and extracellular matrix production. They are important for the development of oligodendrocytes, testicular Leydig cells, alveolar smooth muscle cells, hair follicles, and intestinal villi. Abnormalities of PDGFR/PDGF are thought to contribute to a number of human diseases, and especially malignancy. The combinantion of PDGF-AB and a nucleoside analog, 5-Azacytidine, induces primary somatic cells into tissue-regenerative multipotent stem cells.
Product Details
- Source
- Human PDGF-AB, amino acids Ser87-Thr211 (A chain, Accession# P04085.1) and Ser82-Thr190 (B chain, Accession# P01127.1), with a N-terminal Met, was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 126 (α chain) and 110 (β chain) amino acid recombinant proteins have predicted molecular masses of approximately 14.4 kD and 12.4 kD respectively. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met for both the α and β chains.
- Purity
- > 95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 4 mM HCl.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for one month, at -20°C for six months, or at -70°C for one year. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Stock solutions should be prepared at no less than 50 - 100 µg/mL in sterile buffer (PBS, HPBS, DPBS, and EBSS) containing carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA and stored in working aliquots at -20°C to -70°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 1 - 5 ng/mL as measured by the ability of protein to induce proliferation of NIH/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Deep Blue Cell Viability Kit™ (Cat. No. 424702) was used to quantitate cell proliferation.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulfide-linked heterodimer
- Distribution
-
Platelets, monocytes, macrophages, and mast cells.
- Function
- Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin.
- Interaction
- Platelets, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, muscle cells, neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neutrophils.
- Ligand/Receptor
- PDGFRα homodimer and heterodimer formed by PDGFRα and PDGFRβ.
- Bioactivity
- Human PDGF-AB induces the proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Endothelial cells, Epithelial cells, Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Mesenchymal cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Platelets
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cancer Biomarkers, Cardiovascular Biology, Cell Proliferation and Viability, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Carlin SM, et al. 2003. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 284:L1020-6.
- Ustach CV, et al. 2005. Mol Cell Biol. 25:6279-88.
- Jones AV & Cross NCP. 2004. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:2912-23.
- Andrae J, et al. 2008. Genes Dev. 22:1276-312.
- Heldin CH & Westermark B. 1999. Physiol Rev. 79:1283-316.
- Fredriksson L, et al. 2004. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:197-204.
- Hu JG, et al. 2012. J Mol Neurosci. 46:644-53.
- Schneider L, et al. 2010. Cell Physiol Biochem. 25:279-92.
- Karlsson C & Paulsson Y. 1994. J Cell Physiol. 158:256-62.
- Shure D, et al. 1992. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 186:151-4.
- Fretto LJ, et al. 1993. J Biol Chem. 268:3625-31.
- Abboud HE, et al. 1992. Kidney Int. 41:581-3.
- Chandrakanthan V, et al. 2016. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 133:E2306.
- Gene ID
- 5154 View all products for this Gene ID 5159 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about PDGF-AB on UniProt.org
