- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Placenta Growth Factor 2, PLGF2,
-
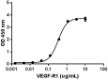
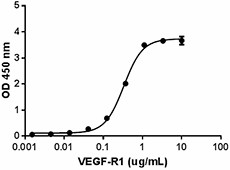
When human PLGF-2 is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL, human VEGF-R1 binds in a dose dependent manner with EC50 of 0.1 - 0.4 µg/mL. -
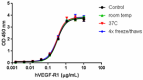
Human PLGF-2 was aliquoted in PBS at 0.2 mg/ml and was treated as followed: one aliquot was kept at 4°C (control), another was freeze-thawed four times (4x freeze-thaws), one incubated for seven days at room temperature (RT), and another incubated at 37°C for one week. After this procedure, the samples were tested for their ability to bind human VEGF-R1 in a functional ELISA.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 765202 | 10 µg | $106.00 | |||
| 765204 | 25 µg | $223.00 | |||
Placenta growth factor (PLGF) was initially cloned from a term placenta cDNA library. It is a member of the PDGF/VEGF family of growth factors that share a conserved pattern of eight cysteines. As a result of alternative splicing, four isoforms for PLGF has been described, PLGF-1 (PLGF-131), PLGF-2 (PLGF-152), PLGF-3 (PLGF-203), and PLGF-4 (PLGF-224). While PLGF isoforms are present in most placental tissues, PLGF-2 is specific to early placenta and only PLGF-1 is found in the colon and mammary carcinomas. The PLGFs are secreted, but PLGF-2 appears to remain cell attached unless released by heparin. PLGF-2 binds to heparin with high affinity, whereas PLGF-1, PLGF-3, and PLGF-4 do not bind heparin. PLGF-2 is the only isoform found in mouse. PLGF binds to VEGF-R1 and neuropilins, but not to VEGF-R2. PLGF induces monocyte activation, migration, and production of inflammatory cytokines. PLGF plays a key role in the maternal vascular function during pregnancy. Circulating PLGF increases during pregnancy, reaching a peak in mid‑gestation. Low levels of PLGF have been associated with patients experiencing preeclampsia. High expression of PLGF has been associated to colorectal cancer (CRC), and its expression in CRC tissues correlates with high levels of MMP-9 and VEGF-R1. PLGF has been shown to increase tumor cell migration in lung cancer, leukemia, and melanoma cells. In colorectal cancer, PLGF induces tumor cell migration and invasion through upregulation of MMP9. PLGF is expressed in the majority of medulloblastomas, and high expression of PLGF receptor neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) correlates with poor survival in patients. In a mouse model, PLGF/Nrp1 blockade provided direct antitumor effects in vivo, including medulloblastoma regression, decreased metastasis, and increased survival.
Product Details
- Source
- Human PLGF-2, amino acids Leu19-Arg170 (Accession # NP_002623) was expressed in CHO cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 152 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 17.3 kDa. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 25 kDa, and non-reduced proteins migrate at approximately 50 kDa by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Leu.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 1.0 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 - 100 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- When human PLGF-2 is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL, human VEGF-R1 binds in a dose dependent manner with EC50 of 0.1 - 0.4 µg/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homodimer
- Distribution
-
Expressed in vascular endothelial cells, chondrocytes, placental syncytiotrophoblasts, stromal cells of mesenchymal origin, smooth muscle cells, hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells, activated monocytes, and leukemic cells of lymphoid and myeloid lineage.
- Function
- PLGF is an angiogenic factor and induces proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. It stimulates endothelial cells and synergistically amplifies the action of VEGF. Soluble VEGFR1 (sFLT1) can regulate the accessibility of PLGF.
- Interaction
- Endothelial cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- VEGF-R1, Neuropilin-1
- Bioactivity
- Measured by the ability of immobilized protein to support the adhesion of C6 glioma cells.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Signal Transduction, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Maglione D, et al. 1991. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:9267.
2. Carmeliet P, et al. 2001. Nat. Med. 7:575.
3. Casalou C, et al. 2007. Leukemia 21:1590.
4. Marcellini M, et al. 2006. Am. J. Pathol. 169:643.
5. Yao J, et al. 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108:11590.
6. Cai J, et al. 2011. PLoS One 6:e18076.
7. Sibiude J, et al. 2012. PLoS One 7:e50208.
8. Snuderl M, et al. 2013 Cell 152:1065. - Gene ID
- 5228 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about PLGF-2 on UniProt.org
