- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Human SIRPa, SIRPα, SIRPA, SIRPalpha, CD172a, Brain Ig-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs, BIT, Macrophage Fusion Receptor, MFR, P84, MYD-1, SHP substrate 1, SHPS1, Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1, PTPNS1
-
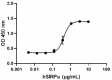
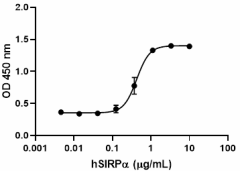
When Human SIRPα-Fc Chimera is coated at 1:3 serial dilutions with a starting concentration of 10.0 µg/mL (100 µL/well), human red blood cells adhere with an ED50 of 0.15 - 0.6 µg/mL after a 30 minute incubation at 37°C. -
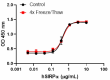
Stability testing for human SIRPα-Fc Chimera Recombinant human SIRPα-Fc Chimera was aliquoted in PBS, pH 7.2 at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw), and compared to a control kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested in a human red blood cell adhesion assay.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 786502 | 10 µg | $112.00 | |||
| 786504 | 25 µg | $229.00 | |||
| 786506 | 100 µg | $675.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Signal Regulatory Proteins (SIRPs) are a family of transmembrane glycoproteins with extracellular IgG domains. SIRPα is an inhibitory receptor expressed on neurons and myeloid cells, including macrophages, granulocytes, myeloid dendritic cells, mast cells, and their precursors (including hematopoietic stem cells). The extracellular regions of the SIRPs are comprised of three Ig-like loops; the proximal loops contain IgC domains, whereas the distal membrane loop contains an IgV domain. While these extracellular domains are fairly similar between SIRPs, their transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains differentiate them from one another. The C-terminal intracellular domains of the SIRPα subfamily contain a relatively long amino acid sequence that includes four tyrosine residues to form two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIM). SIRPα is best known for its inhibitory role following its interaction with the widely distributed protein CD47 (on host target cells). CD47 is a “marker of self”, which upon binding to SIRPα signals against phagocytosis by macrophages expressing SIRPα. When CD47 binds the N-terminal IgG domain of SIRPα, this causes clustering and phosphorylation of SIRPα. SIRPα phosphorylation results in the recruitment and activation of the tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which regulate cellular functions in a negative fashion, including the regulation of leukocyte adhesion and transmigration, T cell activation, macrophage fusion and phagocytosis. In addition to its role in "self-signaling", SIRPα also functions as a scaffold for membrane-bound signaling molecules, plays a role in macrophage and osteoclast fusion, regulates T cell/DC activation and controls myeloid cell migration.
Product Details
- Source
- Human SIRPα, amino acid Gly27-Arg370 (Accession #P78324.2), with a C-terminal human IgG1 Fc tag, was expressed in CHO cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 579 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 63.9 kD. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 75 - 100 kD and and the non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 150 - 200 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Gly.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.15 - 0.6 µg/mL as measured by the ability of immobilized protein to support the adhesion of human red blood cells. When human SIRPα-Fc Chimera is coated at 2.0 µg/mL (100µL/well), human CD47 binds with an EC50 of 5 - 20 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulfide-linked homodimer
- Distribution
-
Broadly distributed in normal adult tissues including brain, endocrine tissues, bone marrow/immune system, lung, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, testis, and ovary
- Function
- An inhibitory receptor present on myeloid cells that interacts with a widely distributed membrane protein CD47 to prevent phagocytosis of healthy cells.
- Interaction
- Interacts with CD47-expressing cells throughout the body.
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD47
- Bioactivity
- Measured by the ability of immobilized protein to induce the adhesion of human red blood cells. Also measured by its ability to bind CD47 in a functional ELISA.
- Cell Type
- Macrophages, Neurons
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, Soluble Receptors
- Antigen References
-
- van Beek EM, et al. 2005. J Immunol. 12:7781-7.
- Lee WY, et al. 2007. J Immunol. 11:7741–50.
- Subramanian S, et al. 2006. Blood 107: 2548-56.
- Barclay AN. 2009. Current Opinion in Immunology 21:47-52.
- Liu Y, et al. 2005. J Biol Chem. 43:36132-40.
- Gene ID
- 140885 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about SIRPalpha on UniProt.org
