- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Vascular endothelial growth factor D, c-Fos-induced growth factor, FIGF
-
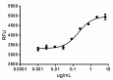
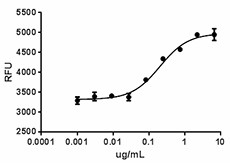
Human VEGF-D induces the proliferation of HMVEC human microvascular endothelial cells in a dose dependent manner.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 760501 | 2 µg | $89.00 | |||
| 760502 | 10 µg | $223.00 | |||
This product is not available for shipping outside of the United States.
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D), also known as c-fos-induced growth factor (FIGF), is a member of the VEGF family. VEGF-D is structurally similar to VEGF-C and both are specific ligands for the tyrosine kinase receptor VEGFR-3 (flt-4). They are both secreted as non-covalent homodimers. The secreted VEGF-D undergoes a complex proteolytic process enabling it to also act as a ligand for VEGFR-2 (KDR/flk-1). VEGF-D is expressed in adult lungs, heart, muscles, and small intestines. It is most abundantly expressed in the fetal lungs and skin. VEGF-D exhibits mitogenic effects on vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. VEGF-D functions in the formation of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis and in the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. Both VEGF-C and VEGF-D are over-expressed in certain cancers and promote tumor lymphangiogenesis. TGF-β1 has been shown to downregulate VEGF-D expression in human lung fibroblasts.
Product Details
- Source
- Human VEGF-D, amino acids (Phe89-Arg205) (Accession# O43915), was expressed in HEK293.
- Molecular Mass
- The 117 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 13.1 kD. The protein migrates at approximately 20-22 kD under non-reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Phe.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE gel and HPLC analysis.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered protein solution in 10 mM Sodium Citrate, pH 4.0.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 1.0 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored at -20°C or -70°C. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in water to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/ml. Do not vortex. It is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein such as 0.1% BSA and store working aliquots at -20°C to -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.15 — 0.6 µg/mL as measured by the ability of the protein to induce proliferation of HMVEC.
- Application
-
Bioassay
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Non-covalent homodimer.
- Distribution
- VEGF-D is expressed in the adult lungs, heart, muscles, and small intestines; it is most abundantly expressed in the fetal heart and lungs and skin.
- Function
- VEGF-D plays a key role in lymphangiogenesis, stimulates the migration, proliferation, and the survival of human endothelial cells.
- Interaction
- Lymphatic endothelial cells and vascular endothelial cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- VEGF-R3, VEGF-R2, and Neuropilin-1.
- Bioactivity
- Measured by the ability of humanVEGF-D to induce the proliferation of HMVEC human microvascular endothelial cells.
- Cell Type
- Neural Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology, Angiogenesis, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Yamada Y, et al. 1997. Genomics 42:483-488.
2. Achen MG, et al. 1998. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2:548-553.
3. Stacker SA, et al. 2001. Nat. Med. 2:186-91.
4. Duff SE, et al. 2003. Br. J. Cancer 89:426-430.
5. Tammela T, et al. 2005. Cardiovasc. Res. 65:550-563.
6. Roy H, et al. 2006. FEBS Letters 580:2879-87.
7. Cui Y, et al. 2014. Mol. Med. 20:120-134. - Gene ID
- 2277 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about VEGF-D on UniProt.org
