- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Ciliary neurotrophic factor
-
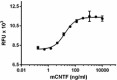
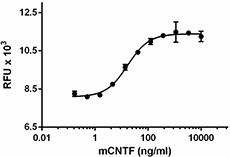
Mouse CNTF induces the proliferation of TF-1 cells.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 761702 | 10 µg | $141.00 | |||
| 761704 | 25 µg | $247.00 | |||
| 761708 | 500 µg | $1933.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
CNTF, ciliary neurotrophic factor, was initially identified as a survival factor for cultured embryonic chick parasympathetic neurons. The human protein has 84% similarity to the rat and rabbit proteins. It lacks the N-terminal signal sequence and consensus sequences for glycosylation or hydrophobic regions. The CNTF profile shows similar sequence and structure motifs to hematopoietic cytokines (IL-6, IL-11, LIF, oncostatin M, cardiotrophin-1) and thus was considered a member of the IL-6 family. CNTF exerts effects on glial cells and neurons. CNTF activates astrocytes and promotes their capacity to support neurons and oligodendroglia. CNTF stimulates astrocytes to secrete FGF-2 and rat microglia to secrete glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). CNTF is produced by astrocytes after brain injury. The CNTF receptor complex includes the CNTF binding protein (CNTFRα), the LIF binding protein (LIFRb), and the signal transducer of IL-6 (gp130). CNTFRα does not have transmembrane or intracellular domains, which means it does not induce signal transduction per se. CNTFRα is linked to the cell membrane via glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage, and it can be released by phospholipase C to produce a soluble receptor. The complex formed by CNTFRα and CNTF serve as agonists for cells that do not express CNTFRα. Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC) also binds to CNTFRα, which proposed to the activation of gp130, which are LIFRb subunits. CNTF reduces the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and its absence exacerbates the severity of multiple sclerosis disability. CNTF has been studied in retinal degenerative disorders and was shown as a potential clinical application.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse CNTF, amino acids Met1-Met198 (Accession# BC027539), was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 198 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 22.59 kD. The protein migrates approximately at 23 kD in DTT-reducing and non-reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met.
- Purity
- >98%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 2 mM CHAPS, 2 mM TCEP, pH 7.5.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 10-40 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 0.25 - 1 x 105 units/mg, as determined by TF-1 cell proliferation induced by CNTF in a dose dependent manner.
- Recommended Usage
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Dimer.
- Distribution
-
Astrocytes, microglia, hepatocytes, skeletal muscle, embryonic stem cells, and bone marrow stromal cells.
- Function
- Stimulates gene expression, along with cell survival or differentiation in neuronal cell types. It has a potent trophic factor for motor neurons. IL-1b, TNFα (TNF-α), and EGF induces the release of CNTF from astrocytes.
- Interaction
- Sensory, sympathetic, ciliary, motor neurons, microglia, retinal ganglion cells, adipocytes, and skeletal muscle cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- Trimeric complex form by CNTF receptor-α (CNTFRα), LIF receptor (LIFR), and gp130.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Negro A, et al. 1991. Eur. J. Biochem. 201:289.
2. Bazan JF. 1991. Neuron. 7:197.
3. Davis S, et al. 1993. Science. 260:1805.
4. Plun-Favreau H, et al. 2001. EMBO J. 20:1692.
5. Lin HW, et al. 2009. J. Neuroinflammation 6:7.
6. Wen R, et al. 2012. Prog. Retin. Eye. Res. 31:136. - Gene ID
- 12803 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CNTF on UniProt.org
