- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- E-cadherin, Cadherin-1, CAD1, CDH1, CADH1, ARC-1, CD324, CAM 120/80, Epithelial cadherin, Uvomorulin, CDHE, UVO
-
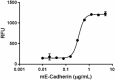
Immobilized Recombinant Mouse E-Cadherin supports the adhesion of MCF-7 cells in a dose dependent manner. ED50 for this effect is 0.25 – 1.0 µg/mL. Calcein-AM (Cat. No. 425201) was used to measure the number of adherent cells. -
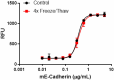
Stability testing for Mouse E-Cadherin. Mouse E-Cadherin was aliquoted in PBS, pH 7.2 at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw), and compared to a control kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested for their ability to support the adhesion of MCF-7 cells.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 780002 | 10 µg | $94.00 | |||
| 780004 | 25 µg | $171.00 | |||
| 780006 | 100 µg | $563.00 | |||
| 780008 | 500 µg | $1289.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
E-cadherin, also known as cadherin-1, CDH1 and CD324, is a member of the cadherin superfamily. E-cadherin is widely expressed in epithelial cells. It is a calcium-dependent, transmembrane cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein composed of four extracellular cadherin repeats and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail region. E-cadherin functions as a cell adhesion molecule involved in development, bacterial pathogenesis, and tumor invasion. E-cadherin forms homophilic clusters via cis and trans interaction to stabilize the catenin and actin cytoskeleton in epithelial adherens junctions. E-cadherin and α-catenin can form the distinct complexes with β-catenin and plakoglobin, respectively. Mice lacking E-cadherin in the epidermis leads to perinatal death and loss of barrier function. Regulating E-cadherin turnover is essential to modulate epithelial plasticity during tissue remodeling and stretching. In bacterial pathogenesis, the ectodomain of E-cadherin mediates bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells, while the cytoplasmic domain is required for internalization. E-cadherin binds to the αEβ7 integrin to mediate cell adhesion. It also interacts with a number of intracellular proteins including including erbin, ezrin, caspase-3, caspase-8, β-catenin, presenilin 1, and casein kinase II as well as other extracellular proteins including the EGF receptor. E-cadherin is phosphorylated on multiple residues (S857, S866, S870, S872), and can be proteolytically cleaved at residue D769 by caspase-3. There are several diseases associated with dysregulation of E-cadherin, including Hailey-Hailey disease and Blepharocheilodontic syndrome 1 (BCDS1).
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse E-Cadherin, amino acid Asp157-Val709 (Accession: #P09803.1) with a C-terminal 6x His tag, was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 559 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 61.7 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 75 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Asp.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH7.2
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
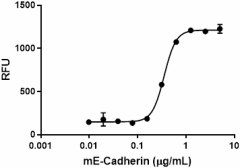
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.25 – 1.0 µg/mL as measured by the ability of immobilized protein to support the adhesion of MCF-7 cells. Calcein-AM (Cat. No. 425201) was used to measure the number of adherent cells.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Member of the cadherin superfamily
- Distribution
-
Widely expressed in epithelial cells in the colon, uterus, liver, keratinocytes, brain, heart, muscle, kidney, and pancreas, as well as erythroid cells; plasma membrane
- Function
- E-Cadherin is involved in development, bacterial pathogenesis, and tumor invasion
- Interaction
- Interacts with a variety of proteins including erbin, ezrin, caspase-3, caspase-8, EGF receptor, β-catenin, presenilin 1, casein kinase II, and others
- Ligand/Receptor
- αEβ7 integrin
- Bioactivity
- Measured by its ability to support the adhesion of MCF-7 cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules
- Antigen References
-
- Guillot C, et al. 2013. Science. 340: 1185.
- Yamada S, et al. 2005. Cell. 123: 889.
- Tunggal JA, et al. 2005. EMBI J. 24: 1146.
- Huber AH, et al. 2001. Cell. 105: 391.
- Nagafuchi A, et al. 1987. Nature. 329: 341.
- Cepek KL, et al. 1994. Nature. 372: 190.
- Butz S, et al. 1994. FEBS Letters. 355: 195.
- Fukunaga Y, et al. 2005. Cell Struct Funct. 30: 25.
- Gumbiner BM. 2005. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6: 622.
- Overduin M, et al. 1995. Science 267:386.
- Boggon TJ, et al. 2002. Science 296:1303.
- Berx G, et al. 1995. EMBO J. 14:6107.
- Perl AK, et al. 1998. Nature 392:190.
- Ghoumid J, et al. 2017. Genet Med. 19: 1013.
- Hakuno M, et al. 2000. Br J Dermatol. 142: 702.
- Gene ID
- 12550 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about E-Cadherin on UniProt.org
