- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF-1, FGF1), Acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF), Endothelial cell growth factor (ECGF), Heparin-binding growth factor 1 (HBGF-1), HBGF1, FGF
-
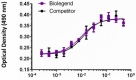
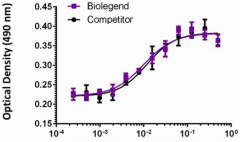
Mouse FGF acidic induces NIH3T3 cell proliferation in the presence of 10 μg/mL of heparin, in a dose-dependent manner. Proliferation was measured by the colormetric MTS assay. BioLegend’s mouse FGF acidic product was compared side-by-side to a competitor’s equivalent product.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750906 | 100 µg | $347.00 | |||
FGF acidic, one of the most studied members of the fibroblast growth factor family, is a powerful mitogen that exhibits strong actions on many different cell types. FGF acidic activities can be mediated not only by autocrine/paracrine pathways, but also in intracrine pathways. FGF acidic lacks a secretion signal peptide and is exported through a non-classical pathway. Endogenous FGF acidic is found in the nucleus of most of the cell-types tested. The nuclear localization is required for FGF acidic mitogenic activity. FGF acidic promotes tumor development by promoting cancer cell proliferation and survival. Increased FGF acidic expression in early stages of many different cancers have been reported. MCF-7 breast cells overexpressing FGF acidic can form vascularized and metastatic tumors in ovariectomized or tamoxifen-treated nude mice. FGF acidic also induces angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. FGF acidic is an attractive candidate for cancer immunotargeting. FGF acidic also plays a role in neuronal cells' differentiation and survival. FGF acidic is highly expressed in motor neurons. In response to damage, motor neurons can release FGF acidic and subsequently astrocyte activation. Astrocytes release FGF acidic under oxidative stress, which stimulates apoE/HDL generation in an autocrine manner for brain protection. The participation of FGF acidic has been reported in inflammation, cardioprotection, wound healing, adipocyte remodeling, and restenosis.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse FGF acidic, amino acids (Phe16-Asp155) (Accession# BC037601), with an N-terminal Met was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 141 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 15.9 kD. The protein migrates approximately at 20 kD in both DTT-reducing and non-reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filterd protein solution is in 20 mM MOPS, 100 mM NaCl, and 0.2 mM EDTA, pH 7.2
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.01 - 0.1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity activity of 1.0 X 107 - 10 X 107 units/mg, as determined by a dose-dependent stimulation of NIH3T3 cell proliferation in the presence of 10 µg/ml of heparin. Proliferation was measured by the colormetric MTS assay.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Growth factor.
- Distribution
-
FGF acidic is widely expressed in developing and adult tissues.
- Function
- FGF acidic plays an important role in many biological processes, which include cell proliferation, inflammation, and angiogenesis. FGF acidic has low stability and a very short half life in vivo. Binding to heparin increases FGF1 stability, and this binding is important for the formation of active FGF acidic/FGFR complex.
- Interaction
- Intracellular FGF acidic interacts directly with CK2, FIBP, mortalin, and LRRC59 (ribosome-bind protein p34/leucine-rich repeat containing 59).
- Ligand/Receptor
- Cell-surface FGFR isoforms (FGFR1b, 1c, 2b, 2c, 3b, 3c, and 4), heparin, and heparin sulfate proteoglycans on the cell surface.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Gene ID
- 14164 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FGF-1-acidic on UniProt.org
