- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CSF3, CSFG, MGI-IG, Granulocyte colony stimulating factor
-
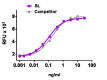
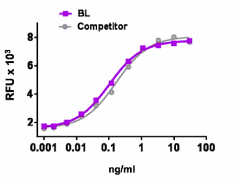
Recombinant mouse G-CSF induces the proliferation of mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast M-NFS-60 cell line in a dose dependent manner. BioLegend’s protein was compared side-by-side to a competitor’s equivalent product.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 752102 | 10 µg | $218.00 | |||
| 752104 | 25 µg | $347.00 | |||
| 752106 | 100 µg | $897.00 | |||
| 752108 | 500 µg | $2338.00 | |||
G-CSF is the key hematopoietic cytokine involved in the control of neutrophil production and therefore is a critical regulator of the innate immunity against bacterial infections. G-CSF mobilizes stem cells indirectly by down-regulating the expression of CXCL12 on marrow osteoblasts and by releasing neutrophils and monocyte proteolytic enzymes, which include neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G, and MMP9. In turn, they degrade important HSC-trafficking and adhesion molecules including c-kit, CXCR4, VCAM-1(CD106), fibronectin, and OPN, which leads to reduced cellular adhesion of HSC through their receptor VLA-4 to bone marrow stroma. In addition, G-CSF possesses immunosuppressive effects on monocytes/ macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes. The receptor for G-CSF is expressed not only in hematopoietic cells, but is also expressed on cardiomyocytes, skeletal muscle, and neurons. G-CSF influences mouse skeletal muscle development and regeneration by stimulating myoblast proliferation. In vitro, G-CSF displays strong antiapoptotic activity in neuronal cells. The beneficial effects of G-CSF have been demonstrated in rodent stroke models. G-CSF is used in patients with leukocytopenia and in donors of peripheral blood-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells prior to collection for transplantation.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse G-CSF, amino acids (Val31-Ala208) (Accession# NM_009971), was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 178 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 18.9 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately at 23-26 kD by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Val.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.05 - 0.25 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 4 - 20 x 106 units/mg, as determined by M-NFS-60 cell proliferation induced by mouse G-CSF in a dose dependent manner.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homotrimer.
- Distribution
-
Monocytes, mesothelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and neurons.
- Function
- G-CSF acts on myeloid progenitor cells to stimulate survival, proliferation, and neutrophilic maturation. On mature neutrophils, it enhances survival, superoxide anion and alkaline phosphatase production, arachidonic acid release, and antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
- Interaction
- Hematopoietic progenitor cells, neutrophilic granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, osteo macrophages, platelets, endothelial cells, trophoblastic cells, myoblasts, cardiomyocytes, neurons, and some small cell lung carcinoma cell lines.
- Ligand/Receptor
- G-CSFR (CD114)
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Levesque J, et al. 2001. Blood 98:1289.
2. Kim HK, et al. 2006. Blood 108:812.
3. Donahue RE, et al. 2009. Blood 114:2530.
4. Shimoji K, et al. 2010. Cell Stem Cell 6:227.
5. Martins A, et al. 2010. IUBMB Life 8:611.
6. Hara M, et al. 2011. J. Exp. Med. 208:715.
7. Bonig H and Papayannopoulou T. 2012. Methods Mol. Biol. 904:1.
8. Kadota R, et al. 2012. PLoS One 7(11):e50391. - Gene ID
- 12985 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about G-CSF on UniProt.org
