- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Hepatocyte Growth Factor, Scatter Factor, SF, Lung-Fibroblast-derived Mitogen, Hepatopoietin A, HPTA
-
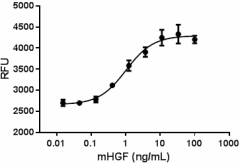
Mouse HGF induces proliferation of mouse IMCD-3 cells in a dose dependent manner with ED50 of 1 – 4 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 771601 | 5 µg | $83.00 | |||
| 771604 | 20 µg | $218.00 | |||
This product is not available for shipping outside of the United States.
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF ) was initially purified from plasma of a patient with fulminant hepatic failure. HGF is a dimeric molecule composed of the α-subunit and β-subunit, linked by a disulfide bond. The two chains are derived from a precursor encoded by the same open reading frame. The C-terminus of the α-subunit is followed directly by the N-terminus of the β-subunit. The pro-HGF possesses 728 amino acids and the subunits are formed by proteolytic cleavage. Proteolytic activation of the precursor form in the extracellular milieu is performed by HGF activator (HGFA). HGFA is a factor XII-like serine proteinase that is not inhibited by serum proteinase inhibitors. Two inhibitors have been described for HGFA, HGFA inhibitor type 1 and type 2 (HAI-1 and -2). Both inhibitors have two well-defined Kunitz inhibitor domains and a presumed transmembrane domain. HGF protects the epithelium, neurons and cardiomyocytes during organ diseases; this protective effect is mediated through anti-apoptotic signals via inhibition of caspase-3 activity or induction of anti-apoptotic molecules, such as Bcl-xL. In addition, HGF prohibits Fas-mediated apoptosis signals via sequestration of Fas and Met receptor on cell surfaces. Also, HGF elicits the regression of fibrosis in numerous organs, such as scleroderma, cardiomyopathy, vocal scarring, and peritoneal fibrosis. Human and murine HGFs are cross-reactive.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse HGF, amino acids Gln33-Arg495 (alpha chain) and Val496-Leu728 (beta chain) (Accession # Q53WS5), was expressed in insect cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The alpha and beta chains contains 463 and 233 amino acids and have predicted molecular masses of approximately 53.4 and 26 kD respectively. The predicted N-terminal amino acids are Gln and Val.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE gel and HPLC analysis.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered protein solution in 10 mM Tris, 100 mM L-Arginine, 200 mM NaCl, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored at -20°C or -70°C for one year. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in water to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/ml. Reconstituted samples can be kept at 4°C for one week and six months at -20°C to -80°C. Do not vortex. It is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein such as 0.1% BSA and store working aliquots at -20°C to -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 1 – 4 ng/mL as measured by the ability of protein to induce proliferation of mouse IMCD-3 cells. Deep Blue Cell Vialibity Kit (Cat. No. 424702) was used to quantitate cell proliferation.
- Application
-
Bioassay
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Heterodimer (alpha and beta chains)
- Distribution
-
Mesenchymal cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial, macrophages
- Function
- Potent mitogen for mature parenchymal hepatocyte cells, hepatotrophic factor, and a growth factor for a broad spectrum of tissues and cell types. Activating ligand for the receptor tyrosine kinase MET by binding to it and promoting its dimerization.
- Interaction
- Hepathocytes, epithelial cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- MET receptor
- Bioactivity
- Measured by its ability to induce proliferation of mouse IMCD-3 cells.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cancer Biomarkers, Cell Biology, Cell Proliferation and Viability, Immunology, Signal Transduction, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors, Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Kataoka H, et al. 2000. J. Biol. Chem. 275:40453.
2. Wang X, et al. 2002. Mol. Cell. 9:411.
3. Wu MH, et al. 2004. Gene Ther. 11:170.
4. Mizuno S, et al. 2008. Front. Biosci. 13:7072.
5. D'Angelo F, et al. 2013. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 174:60. - Gene ID
- 15234 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about HGF on UniProt.org
