- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interferon beta-1, Beta-interferon, IFB, interferon fibroblast, IFF
-
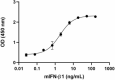
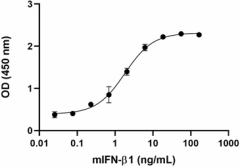
Mouse IFN-β1 induces the production of mouse CCL2 in RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.9 – 4.5 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 581302 | 10 µg | $265.00 | |||
| 581304 | 25 µg | $586.00 | |||
| 581306 | 100 µg | $1641.00 | |||
IFN-β1 is part of the type I IFN multigene family which includes at least eight subclases: IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-ε, IFN-κ, IFN-ω, IFN-τ, IFN-δ, and IFN-ζ (limitin). Type I interferons (IFNs) (alpha/beta interferon [IFN-α/β]) are expressed as a first line of defense against viruses and play a critical role in the antiviral response. The antiviral activity of type I IFNs is exerted by different mechanisms, e.g. blockage of viral entry into the cell, control of viral transcription, cleavage of RNA, and preventing translation; therefore, type I IFNs block virus replication. In addition, type I INFs modulate the innate and adaptive immune responses. IFN-α/β induces natural killer cell cytotoxicity and expression of major histocompatibility complex class I on most cells and costimulatory molecules on antigen-presenting cells. Also, type I interferons act directly on CD8 T cells to allow clonal expansion and memory formation in response to viral infection.
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) produce high amounts of type I interferons (IFNs) and a variety of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in response to viral infections. Mice deficient for IFN-β type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) have demonstrated an increased susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Animal studies have shown that neutralization of IL-23 or the lack of IL-23 p19 gene expression completely ameliorated EAE. These data correlate with the fact that IFN-β has been used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in humans, and it has been suggested that IFN-β inhibits human Th17 cell differentiation. It is known that Th17 cells play a central role in the immunopathogenesis of MS, and IL-23 plays a role in the expansion of differentiated TL17 cells in mice and differentiation of Th17 cells in humans.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse INF-β1, amino acids Ile22-Apn182 (Accession# NM_010510.1) was expressed in 293E cells. The carboxi-terminal has a TG8HisGGQ-tag.
- Molecular Mass
- The 175 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 21.2 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 36 kD by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Ile.
- Purity
- >98%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Mouse IFN-β1 induces the production of mouse CCL2 in RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.9 – 4.5 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine
- Distribution
-
Macrophages, spleenocytes, fibroblasts, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and osteoclast precursor cells.
- Function
- IFN-β induces an antiviral state. It is produced by virus-infected cells within hours and plays an important role in preventing virus spreading (antiviral effects). IFN-β activates natural killer cells and CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity, and induces the upregulation of genes required for antigen presentation and activation of adaptive immunity.
- Interaction
- T cells, dendritic cells, receptor genes for type I IFNs are ubiquitously expressed on all cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- IFNAR1/IFNAR2
- Biology Area
- Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cell Biology, Signal Transduction
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Kolumam GA, et al. 2005. J. Exp. Med. 202:637.
2. Chen Y, et al. 2006. J. Clin. Invest. 116:1317.
3. Li M, et al. 2009. J. Leukocyte Biol. 86:23.
4. Ramgolam VS, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 183:5418.
5. Zhang X, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 182:3928.
6. Sun M, et al. 2011. PLoS One 6:e19870.
7. Rodriguez C, et al. 2011. PLoS One 6:e28709. - Gene ID
- 15977 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IFN-beta1 on UniProt.org
