- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Adipose tissue-specific secretory factor (ADSF), C/EBP-epsilon-regulated myeloid-specific secreted cysteine-rich protein, Cysteine-rich secreted protein A12-alpha-like 2, RSTN, XCP1, FIZZ3, RETN1, RSTN
-
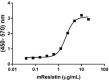
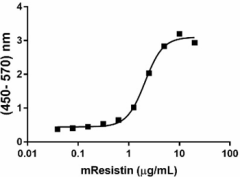
Mouse Resistin induces the expression of IL-6 in mouse 3T3-L1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.8 - 4 µg/mL. -
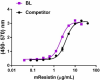
Comparison for Recombinant Mouse Resistin. Recombinant mouse Resistin induces the expression of IL-6 in mouse 3T3-L1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. BioLegend's protein was compared side-by-side to a competitor’s equivalent product. The ED50 for this effect is 0.8 - 4 µg/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 785801 | 5 µg | $89.00 | |||
| 785804 | 25 µg | $223.00 | |||
This product is not available for shipping outside of the United States.
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Resistin, originally found in the inflammatory zone in humans, is a cysteine-rich secreted peptide hormone. It belongs to a member of the resistin-like molecule family. In rodents, resistin exists in two distinct states in circulating serum, noncovalent coiled-coil trimers and disulfide bond-linked tail-to-tail hexamers. Rodent resistin is mainly secreted by mature adipocytes, and it has been linked to the pathogenesis of obesity-mediated insulin resistance and of type 2 diabetes. Resistin-deficient mice exhibit low glucose levels and reduced hepatic glucose production after fasting, suggesting a role of resistin in the maintenance of blood glucose during fasting. Administration of recombinant resistin to normal mice leads to impairment of glucose tolerance and insulin action. Rodent resistin inhibits adipocyte differentiation, as a feedback regulator of adipogenesis. In addition, resistin stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 via NF-κB activation in rat pancreatic acinar cells. In humans, resistin is primarily expressed and secreted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, bone marrow cells and macrophages. Resistin serum levels are associated with insulin resistance, disease severity, clinical complications, and prognosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Human resistin directly aggravates atherosclerosis by stimulating monocytes to induce vascular inflammation. Human resistin stimulates the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α/IL-12 in macrophages and TNF-α/IL-6 in adipocytes via an NF-κB-dependent pathway. TNF-α induces upregulation of resistin in human macrophages. Resistin promotes neutrophil pro-inflammatory activation, neutrophil extracellular trap formation, and increases the severity of acute lung injury in humanized resistin mice (hRTN+/−/−) (mice that express human resistin but lack murine resistin). Resistin is increased in the circulation of patients with acute respiratory distress syndromes and sepsis.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse Resistin, amino acids (Ser21 - Ser114) (Accession: NP_075360.1), was expressed in .E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 94 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 10 kD. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Ser.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered protein solution is in PBS pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for one month, at -20°C for six months, or at -70°C for one year. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C to -70°C. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in sterile buffer (PBS, HPBS, DPBS, or EBSS) containing carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA and stored in working aliquots at -20°C to -70°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Mouse Resistin induces the expression of IL-6 in mouse 3T3-L1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 0.8 - 4 µg/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in lyophilized format are shipped on blue ice. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Monomer and disulfide bond-linked homodimer
- Distribution
-
Predominantly expressed in rodent adipocytes, detectable level in stomach, intestines, adrenal gland, and skeletal muscle.
- Function
- Rodent resistin antagonizes insulin action, and it has been linked to the pathogenesis of obesity-mediated insulin resistance and of type 2 diabetes. Resistin inhibits adipoctye differentiation.
- Interaction
- Rodent adipocytes, skeletal muscle, cardiomyocytes.
- Ligand/Receptor
- ND
- Bioactivity
- Rat Resistin induces the expression of IL-6 in mouse 3T3-L1 cells.
- Cell Sources
- E. coli
- Molecular Family
- Enzymes and Regulators
- Antigen References
-
- Banerjee RR, et al. 2004. Science. 303:1195-8.
- Steppan CM, et al. 2001. Nature. 409:307-12.
- Hsu WY, et al. 2011. J. Cell. Physiol. 10.1002/jcp.22555.
- Mu H, et al. 2006. Cardiovasc. Res. 70:146-57.
- Holcomb IN, et al. 2000. EMBO J. 15:4046-455.
- Patel L, et al. 2003. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 300:472-6.
- Bokarewa M, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 174:5789-95.
- Silswal N, et al. 2005. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 334:1092-101.
- Yagmur E, et al. 2006. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 101:1244-52.
- Cho Y, et al. 2011. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.07.035.
- Fang JD, Lee SL. 2014. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 7:1285-94.
- Jiang S, et al. 2014. J. Immunol. 192:4795-803.
- Stojsavljević S, et al. 2014. World J. Gastroenterol 48:18070-91.
- Pravenec M, et al. 2003. J. Biol. Chem. 278:45209-15.
- Nogueiras R, et al. 2003. FEBS Lett. 548:21-27.
- Jiang CY, et al. 2013. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 36:986-92.
- Kusminski CM, et al. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92:270-6.
- Kim KH, et al. 2001. J. Biol. Chem. 76:11252-6.
- Patel SD, et al. 2004. Science. 304:1154-58.
- Park HK, Ahima RS. 2013. Diabetes Metab. J. 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.404.
- Gene ID
- 57264 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Resistin on UniProt.org
