- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- p75TNFR, CD120b, TNF RII, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B (TNFRSF1B), TNFBR, TNFR80, TNF receptor beta chain, p75 TNFR, p80 TNF-alpha receptor, tumor necrosis factor receptor 2
-
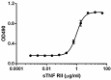
Inhibition of mouse TNF-α-induced cytotoxicity in L929 cells by mouse TNFRII (CD120b).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 758904 | 25 µg | $347.00 | |||
| 758906 | 100 µg | $698.00 | |||
The biological effects of TNF are mediated by two cell surface TNF receptors: TNFRI (TNF-RI) and TNFRII (also known as TNFRII (CD120B) and TNF-RII). TNFRI and TNFRII are structurally related, but functionally distinct. Also, TNFRI is widely expressed on most cells, whereas TNFRII is more restricted and is primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells and cells of the immune system. The function of TNFRII is less understood and has fewer biological effects than TNFRI. Unlike TNFRI, TNFRII does not have a death domain and will induce NF-κB activation through a different pathway. It is generally accepted that TNFRI induces both apoptosis and survival pathways, while TNFRII induces only survival pathway. Only membrane-bound TNF can active TNFRII effectively. Soluble TNF can bind TNFRII, but can not induce TNFRII signaling. Upon binding of TNF, TNFRII will form a trimer and will recruit TRAF2, therefore leading to the activation of NF-κB. In T cells, TNFRII costimulation provides survival signals during the differentiation program triggered by TCR-mediated stimulation and also during clonal expansion in response to intracellular bacterial pathogens. Both TNFRI and TNFRII can be released from cell surface by ectodomain shedding. The resulting soluble TNFRI and TNF-RII can bind TNF with high affinity and modulate TNF effects. An in vitro study showed that both TNFRI and TNFRII are constitutively released from monocytes. LPS stimulation can further increase soluble TNFRII release. It has been reported that TNFRII polymorphism is associated with some lymphomas, solid tumors, and autoimmune diseases. The plasma level of soluble TNFRII is increased in obese people and is related to insulin resistance. In addition, recombinant Fc-tagged soluble TNFRII has been used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Product Details
- Source
- Mouse TNFRII (CD120b), amino acids (Val23-Gly258) (Accession#: Q545P4), was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 236 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 25.46 kD. The protein migrates at approximately 26 kD in DTT-reducing conditions and at approximately 25 kD in non-reducing conditions respectively by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Val.
- Purity
- >98%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 20 mM glycine, 150 mM NaCl, pH 3.0.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
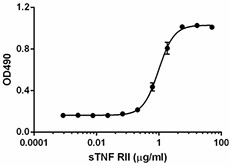
- ED50 = 0.6 - 1.5 µg/mL as determined by a dose-dependent inhibition of 0.1 ng/mL mouse TNF-α induced cytotoxicity in L929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of 4 µg/mL actinomycin D.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine receptor.
- Distribution
-
TNFRII is expressed in T cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, monocytes, endothelial cells, human mesenchymal stem cells, macrophages, and Langerhans cells. Soluble TNFRII can be detected in the urine and the blood.
- Function
- TNFRII transduces TNF signals through TRAF2. Soluble TNFRII can neutralize the biological activity of TNF, which dampens the inflammatory responses. The level of circulating soluble TNFRII is increased in patients with sepsis, cancer, HIV, and autoimmune diseases.
- Ligand/Receptor
- TNF.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience, Transcription Factors
- Molecular Family
- Soluble Receptors, Cytokine/Chemokine Receptors, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Hehlgans T, Mannel DN. 2002. Biol. Chem. 383:1581.
2. Glossop JR, et al. 2005. Arthritis Res. Ther. 7:R1227.
3. Kollias G, Kontoyiannis D. 2002. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13(4-5):315-21.
4. Gordon AC, et al. 2004. Genes Immun. 5:631.
5. Lantz M, et al. 1990. Cytokine 2:402.
6. Nophar Y, et al. 1990. EMBO. J. 9:3269.
7. Eisel UL, et al. 2011. FEBS. J. 278:888. - Gene ID
- 21938 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD120b on UniProt.org
